Abstract
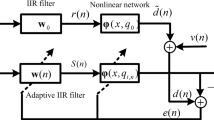
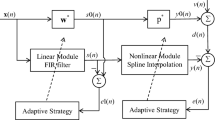
This paper presents a new spline prioritization optimization adaptive filter with arctangent-exponential hyperbolic cosine (SPOAF-ARC-EHC) to solve the high steady-state error in colored and/or impulsive noise environments. Different from the traditional spline adaptive filtering algorithm, the weight update of the spline prioritization optimization adaptive filter (SPOAF) is only based on the linear error, and the update of the spline control points is based on the error of the whole system. To improve the robustness of the proposed SPOAF algorithm, the linear part and the nonlinear part use independent cost functions. More specifically, we utilize the arctangent function (ARC) as the cost function for the linear part and the exponential hyperbolic cosine as the loss function for the nonlinear part. Through simulation, it is shown that the proposed algorithm significantly reduces the steady-state error compared with the existing algorithms in a colored and/or impulsive noise environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Comminiello, D., Príncipe, J.C.: Adaptive learning methods for nonlinear system modeling, Butterworth-Heinemann (2018)
Koh, T., Powers, E.: Second-order volterra filtering and its application to nonlinear system identification. IEEE Trans. Acoust., Speech, Signal Process. 33(6), 1445–1455 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164730
Gupta, S., Sahoo, A.K., Sahoo, U.K.: Volterra and wiener model based temporally and spatio-temporally coupled nonlinear system identification: a synthesized review. IETE Tech. Rev. 38(3), 303–327 (2021)
Peng, Z., Li, J., Hao, H., Li, C.: Nonlinear structural damage detection using output-only volterra series model. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 28(9), e2802 (2021)
Kumar, K., Pandey, R., Bhattacharjee, S.S., George, N.V.: Exponential hyperbolic cosine robust adaptive filters for audio signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1410–1414 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2021.3093862
Yin, L., Astola, J., Neuvo, Y.: A new class of nonlinear filters-neural filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41(3), 1201–1222 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.205724
Pokharel, P.P., Liu, W., Principe, J.C.: Kernel lms, in: 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - ICASSP ’07, Vol. 3, pp. III–1421–III–1424. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2007.367113
George, N.V., Panda, G.: Active control of nonlinear noise processes using cascaded adaptive nonlinear filter. Appl. Acoust. 74(1), 217–222 (2013)
Scarpiniti, M., Comminiello, D., Parisi, R., Uncini, A.: Nonlinear spline adaptive filtering. Signal Process. 93(4), 772–783 (2013)
Guan, S., Li, Z.: Normalised spline adaptive filtering algorithm for nonlinear system identification. Neural Process. Lett. 46(2), 595–607 (2017)
Liu, C., Zhang, Z., Tang, X.: Sign normalised spline adaptive filtering algorithms against impulsive noise. Signal Process. 148, 234–240 (2018)
Şeker, M.: Parameter estimation of positive lightning impulse using curve fitting-based optimization techniques and least squares algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 205, 107733 (2022)
Pradhan, Y., Dey, A.: Performance investigation of extended kalman filter during power system harmonics estimation, In: Proceedings of International Conference on Industrial Instrumentation and Control, Springer, pp. 225–235. (2022)
He, L., Wang, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, M., Hu, X., Shi, Q.: An adaptive central difference kalman filter approach for state of charge estimation by fractional order model of lithium-ion battery. Energy 244, 122627 (2022)
Kostić, S., Vasović, N., Todorović, K., Franović, I.: Effect of colored noise on the generation of seismic fault movement: Analogy with spring-block model dynamics. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 135, 109726 (2020)
Zhao, S., Chen, B., Principe, J.C.: Kernel adaptive filtering with maximum correntropy criterion. In: The 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE pp. 2012–2017. (2011)
Huang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, S.: Adaptive filtering under a variable kernel width maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 64(10), 1247–1251 (2017)
Peng, S., Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Chen, B.: Nonlinear spline adaptive filtering under maximum correntropy criterion. In: TENCON 2015-2015 IEEE Region 10 Conference, IEEE pp. 1–5. (2015)
Yang, L., Liu, J., Yan, R., Chen, X.: Spline adaptive filter with arctangent-momentum strategy for nonlinear system identification. Signal Process. 164, 99–109 (2019)
Patel, V., Bhattacharjee, S.S., George, N.V.: A family of logarithmic hyperbolic cosine spline nonlinear adaptive filters. Appl. Acoust. 178, 107973 (2021)
Yu, T., Li, W., Yu, Y., de Lamare, R.C.: Robust spline adaptive filtering based on accelerated gradient learning: Design and performance analysis. Signal Process. 183, 107965 (2021)
Guo, W., Zhi, Y.: Nonlinear spline adaptive filtering against non-gaussian noise. Circuits Systems Signal Process. 41(1), 579–596 (2022)
Shen, Z., Yu, Y., Huang, T.: Two novel arctangent normalized subband adaptive filter algorithms against impulsive interferences. Circuits Systems Signal Process. 37(2), 883–900 (2018)
Liu, Q., He, Y.: A robust fully arctangent adaptive interpolated volterra filtering algorithm against impulsive noise, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
Choi, J.-H., Kim, J., Nam, S.W.: Variable-parameter arctangent-cost-function based nlms algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. In: 2018 International Conference on Network Infrastructure and Digital Content (IC-NIDC), IEEE pp. 265–268. (2018)
Kumar, K., Pandey, R., Bhattacharjee, S.S., George, N.V.: Exponential hyperbolic cosine robust adaptive filters for audio signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 1410–1414 (2021)
Sadigh, A.N., Zayyani, H.: A proportionate robust diffusion recursive least exponential hyperbolic cosine algorithm for distributed estimation, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
Yang, L., Liu, J., Sun, R., Yan, R., Chen, X.: Spline adaptive filters based on real-time over-sampling strategy for nonlinear system identification. Nonlinear Dyn. 103(1), 657–675 (2021)
Guarnieri, S., Piazza, F., Uncini, A.: Multilayer feedforward networks with adaptive spline activation function. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 10(3), 672–683 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1109/72.761726
Catmull, E., Rom, R.: A class of local interpolating splines, Computer Aided Geometric Design 74
Liu, Q., He, Y.: A robust fully arctangent adaptive interpolated volterra filtering algorithm against impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68(7), 2742–2746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2021.3058327
Wittenmark, B.: Adaptive filter theory: Simon haykin (2003)
Peng, S., Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Chen, B.: Nonlinear spline adaptive filtering under maximum correntropy criterion, IEEE Region Conference IEEEREGION10CONFERENCE (TENCON2015)
Back, A.D., Tsoi, A.C.: A simplified gradient algorithm for iir synapse multilayer perceptrons. Neural Comput. 5(3), 456–462 (1993)
Panicker, T.M., Mathews, V.J., Sicuranza, G.L.: Adaptive parallel-cascade truncated volterra filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 46(10), 2664–2673 (1998)
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U20B2040 and 61671379).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Zhi, Y. & Feng, K. Nonlinear spline prioritization optimization adaptive filter with arctangent-exponential hyperbolic cosine. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 611–621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07636-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07636-8