Abstract
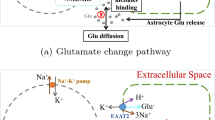
Epilepsy is the second largest neurological disease which seriously threatens human life and health. The one important reason of inducing epileptic seizures is ischemic stroke which causes insufficient oxygen supply from blood vessels to neurons. However, few studies focus on the underlying mechanism of the generation and propagation of epileptic seizures after ischemic stroke by utilizing modeling methods. To explore the mechanism, this paper establishes a coupled network model consisting of neurons and astrocytes, and introduces a blood vessel to simulate the condition of ischemic stroke. First, we study the effect of the degree of vascular blockage on the generation of epileptic seizures. The results demonstrate that the important reason of epileptic seizures after ischemic stroke is the disruption of ion concentration gradient. Then, we study three factors that influence the epileptic seizures propagation after ischemic stroke: massive glutamate release, excessive receptor activation and high extracellular potassium concentration. The results demonstrate that massive glutamate acting on postsynaptic neurons and the excessive activation of glutamate receptors on postsynaptic neurons promote the epileptic seizures propagation in neuronal population, and massive glutamate acting on astrocytes and excessive activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors on presynaptic neurons inhibit the epileptic seizures propagation, and the potassium uptake by astrocytes suppresses the epileptic seizures propagation. The results are consistent with the experimental phenomena. The simulation results also shed light on the fact that astrocytes have neuroprotective effect. Our results on the generation and propagation of epileptic seizures after ischemic stroke could offer theoretical guidelines for the treatment of epileptic seizures after ischemic stroke.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Li, J., Song, J., Tan, N., Cao, C., Du, M., Xu, S., Wu, Y.: Channel block of the astrocyte network connections accounting for the dynamical transition of epileptic seizures. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 3571–3583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06737-0
Scheffer, I.E., Berkovic, S., Capovilla, G., Connolly, M.B., French, J., Guilhoto, L., Hirsch, E., Jain, S., Mathern, G.W., Moshé, S.L., Nordli, D.R., Perucca, E., Tomson, T., Wiebe, S., Zhang, Y.-H., Zuberi, S.M.: ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE commission for classification and terminology. Epilepsia 58, 512–521 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13709
Assis, T.M.R., Bacellar, A., Costa, G., Nascimento, O.J.M.: Mortality predictors of epilepsy and epileptic seizures among hospitalized elderly. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 73, 510–515 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282X20150043
Stefan, H., May, T.W., Pfäfflin, M., Brandt, C., Füratsch, N., Schmitz, B., Wandschneider, B., Kretz, R., Runge, U., Geithner, J., Karakizlis, C., Rosenow, F., Kerling, F.: Epilepsy in the elderly: comparing clinical characteristics with younger patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 129, 283–293 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12218
Menon, B., Shorvon, S.D.: Ischaemic stroke in adults and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 87, 1–11 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.08.007
Graham, N.S.N., Crichton, S., Koutroumanidis, M., Wolfe, C.D.A., Rudd, A.G.: Incidence and associations of poststroke epilepsy. Stroke 44, 605–611 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000220
GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke Collaborators: Global, regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 2429–2437 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1804492
Adelöw, C., Andersson, T., Ahlbom, A., Tomson, T.: Prior hospitalization for stroke, diabetes, myocardial infarction, and subsequent risk of unprovoked seizures. Epilepsia 52, 301–307 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02757.x
Stefanidou, M., Das, R.R., Beiser, A.S., Sundar, B., Kelly-Hayes, M., Kase, C.S., Devinsky, O., Seshadri, S., Friedman, D.: Incidence of seizures following initial ischemic stroke in a community-based cohort: the framingham heart study. Seizure 47, 105–110 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2017.03.009
Campbell, B.C.V., De Silva, D.A., Macleod, M.R., Coutts, S.B., Schwamm, L.H., Davis, S.M., Donnan, G.A.: Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 5, 70 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0118-8
Bélanger, M., Allaman, I., Magistretti, P.J.: brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 14, 724–738 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Attwell, D., Buchan, A.M., Charpak, S., Lauritzen, M., MacVicar, B.A., Newman, E.A.: Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 468, 232–243 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09613
Myint, P.K., Staufenberg, E.F.A., Sabanathan, K.: Post-stroke seizure and post-stroke epilepsy. Postgrad. Med. J. 82, 568–572 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.2005.041426
Lees, G.J.: Inhibition of sodium-potassium-ATPase: a potentially ubiquitous mechanism contributing to central nervous system neuropathology. Brain Res. Rev. 16, 283–300 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(91)90011-V
Kamp, M.A., Dibué, M., Schneider, T., Steiger, H.-J., Hänggi, D.: Calcium and potassium channels in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage and transient global ischemia. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, e382146 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/382146
Szydlowska, K., Tymianski, M.: Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 47, 122–129 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2010.01.003
Zlokovic, B.V.: The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57, 178–201 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003
Lu, X.-C.M., Williams, A.J., Yao, C., Berti, R., Hartings, J.A., Whipple, R., Vahey, M.T., Polavarapu, R.G., Woller, K.L., Tortella, F.C., Dave, J.R.: Microarray analysis of acute and delayed gene expression profile in rats after focal ischemic brain injury and reperfusion. J. Neurosci. Res. 77, 843–857 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20218
Trevelyan, A.J., Sussillo, D., Yuste, R.: Feedforward inhibition contributes to the control of epileptiform propagation speed. J. Neurosci. 27, 3383–3387 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0145-07.2007
Khoo, H.M., von Ellenrieder, N., Zazubovits, N., He, D., Dubeau, F., Gotman, J.: The spike onset zone: the region where epileptic spikes start and from where they propagate. Neurology 91, e666–e674 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000005998
Reato, D., Cammarota, M., Parra, L.C., Carmignoto, G.: Computational model of neuron-astrocyte interactions during focal seizure generation. Front. Comput. Neurosci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2012.00081
Martinet, L.-E., Fiddyment, G., Madsen, J.R., Eskandar, E.N., Truccolo, W., Eden, U.T., Cash, S.S., Kramer, M.A.: Human seizures couple across spatial scales through travelling wave dynamics. Nat. Commun. 8, 14896 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14896
Proix, T.: Predicting the spatiotemporal diversity of seizure propagation and termination in human focal epilepsy. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–15 (2018)
Bezzi, P., Carmignoto, G., Pasti, L., Vesce, S., Rossi, D., Rizzini, B.L., Pozzan, T., Volterra, A.: Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature 391, 281–285 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/34651
Nedergaard, M., Ransom, B., Goldman, S.A.: New roles for astrocytes: redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neurosci. 26, 523–530 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2003.08.008
Du, M.-M., Li, J.-J., Yuan, Z.-X., Fan, Y.-C., Wu, Y.: Astrocyte and ions metabolism during epileptogenesis: a review for modeling studies. Chinese Phys. B. 29, 038701 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab6961
Du, M., Li, J., Chen, L., Yu, Y., Wu, Y.: Astrocytic Kir4.1 channels and gap junctions account for spontaneous epileptic seizure. PLOS Comput. Biol. 14, e1005877 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005877
Coulter, D.A., Eid, T.: Astrocytic regulation of glutamate homeostasis in epilepsy. Glia 60, 1215–1226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22341
Kirischuk, S., Kettenmann, H., Verkhratsky, A.: Membrane currents and cytoplasmic sodium transients generated by glutamate transport in Bergmann glial cells. Pflugers Arch. – Eur. J. Physiol. 454, 245–252 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0207-5
Mergenthaler, K., Oschmann, F., Obermeyer, K.: Glutamate uptake by astrocytic transporters. In: De Pittà, M., Berry, H. (eds.) Computational Glioscience, pp. 329–361. Springer, Cham (2019)
Sun, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, E., Ma, Q., Anatol, M., Han, H., Yan, J.: The roles of astrocyte in the brain pathologies following ischemic stroke. Brain Inj. 33, 712–716 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2018.1531311
Hirayama, Y., Ikeda-Matsuo, Y., Notomi, S., Enaida, H., Kinouchi, H., Koizumi, S.: Astrocyte-mediated ischemic tolerance. J. Neurosci. 35, 3794–3805 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4218-14.2015
Rossi, D.J., Brady, J.D., Mohr, C.: Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1377–1386 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2004
Schmidt-Kastner, R., Freund, T.F.: Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience 40, 599–636 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(91)90001-5
Kelly, K.M.: Poststroke seizures and epilepsy: clinical studies and animal models. Epilepsy Curr. 2, 173–177 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1535-7597.2002.00064.x
Meyer, F.B.: Calcium, neuronal hyperexcitability and ischemic injury. Brain Res. Rev. 14, 227–243 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(89)90002-7
Ingram, J., Zhang, C., Cressman, J.R., Hazra, A., Wei, Y., Koo, Y.-E., Žiburkus, J., Kopelman, R., Xu, J., Schiff, S.J.: Oxygen and seizure dynamics: I. Experiments. J. Neurophysiol. 112, 205–212 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00540.2013
David, Y., Cacheaux, L.P., Ivens, S., Lapilover, E., Heinemann, U., Kaufer, D., Friedman, A.: Astrocytic dysfunction in epileptogenesis: Consequence of altered potassium and glutamate homeostasis? J. Neurosci. 29, 10588–10599 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2323-09.2009
Giaume, C., Koulakoff, A., Roux, L., Holcman, D., Rouach, N.: Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 87–99 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2757
Fitzhugh, R.: Thresholds and plateaus in the Hodgkin-Huxley nerve equations. J. Gen. Physiol. 43, 867–896 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.43.5.867
Cressman, J.R., Ullah, G., Ziburkus, J., Schiff, S.J., Barreto, E.: The influence of sodium and potassium dynamics on excitability, seizures, and the stability of persistent states: I. Single neuron dynamics. J. Comput. Neurosci. 26, 159–170 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-008-0132-4
Wei, Y., Ullah, G., Ingram, J., Schiff, S.J.: Oxygen and seizure dynamics: II. Computational modeling. J. Neurophysiol. 112, 213–223 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00541.2013
Traub, R.D., Wong, R.K., Miles, R., Michelson, H.: A model of a CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neuron incorporating voltage-clamp data on intrinsic conductances. J. Neurophysiol. 66, 635–650 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1991.66.2.635
Gloveli, T., Dugladze, T., Saha, S., Monyer, H., Heinemann, U., Traub, R.D., Whittington, M.A., Buhl, E.H.: Differential involvement of oriens/pyramidale interneurones in hippocampal network oscillations in vitro: Interneurones and network oscillations. J. Physiol. 562, 131–147 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2004.073007
Chapuisat, G., Dronne, M.A., Grenier, E., Hommel, M., Gilquin, H., Boissel, J.P.: A global phenomenological model of ischemic stroke with stress on spreading depressions. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 97, 4–27 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2007.10.004
Fisher, M.: Characterizing the target of acute stroke therapy. Stroke 28, 866–872 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.28.4.866
Baron, J.-C.: Mapping the ischaemic penumbra with PET: Implications for acute stroke treatment. CED 9, 193–201 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1159/000015955
Götz-Trabert, K., Hauck, C., Wagner, K., Fauser, S., Schulze-Bonhage, A.: Spread of ictal activity in focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 49, 1594–1601 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01627.x
Yang, P.-F., Shang, M.-C., Lin, Q., Xiao, H., Mei, Z., Jia, Y.-Z., Liu, W., Zhong, Z.-H.: Three-dimensional intracranial EEG monitoring in presurgical assessment of MRI-negative frontal lobe epilepsy. Medicine (Baltimore) (2016). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005192
Ermentrout, G.B., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer, New York (2010)
Terman, D., Rubin, J.E., Yew, A.C., Wilson, C.J.: Activity patterns in a model for the subthalamopallidal network of the basal ganglia. J. Neurosci. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-07-02963.2002
Amiri, M., Hosseinmardi, N., Bahrami, F., Janahmadi, M.: Astrocyte- neuron interaction as a mechanism responsible for generation of neural synchrony: a study based on modeling and experiments. J. Comput. Neurosci. 34, 489–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-012-0432-6
Li, Y.X., Rinzel, J.: Equations for InsP3 receptor-mediated [Ca2+]i oscillations derived from a detailed kinetic model: a hodgkin-huxley like formalism. J. Theor. Biol. 166, 461–473 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1006/jtbi.1994.1041
Volman, V., Ben-Jacob, E., Levine, H.: The astrocyte as a gatekeeper of synaptic information transfer. Neural Comput. 19, 303–326 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2007.19.2.303
Perea, G., Navarrete, M., Araque, A.: Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci. 32, 421–431 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2009.05.001
Araque, A., Parpura, V., Sanzgiri, R.P., Haydon, P.G.: Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 22, 208–215 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01349-6
Araque, A., Carmignoto, G., Haydon, P.G.: Dynamic signaling between astrocytes and neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 63, 795–813 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.795
Newman, E.A.: New roles for astrocytes: regulation of synaptic transmission. Trends Neurosci. 26, 536–542 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(03)00237-6
Koizumi, S., Fujishita, K., Tsuda, M., Shigemoto-Mogami, Y., Inoue, K.: Dynamic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by astrocyte-derived ATP in hippocampal cultures. PNAS 100, 11023–11028 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1834448100
Bladin, C.F., Alexandrov, A.V., Bellavance, A., Bornstein, N., Chambers, B., Coté, R., Lebrun, L., Pirisi, A., Norris, J.W.: Seizures after stroke study group: seizures after stroke: a prospective multicenter study. Arch. Neurol. 57, 1617–1622 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.57.11.1617
Lambrakis, C.C., Lancman, M.E.: The phenomenology of seizures and epilepsy after stroke. J. Epilepsy 11, 233–240 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6974(98)00029-2
Traynelis, S.F., Dingledine, R.: Potassium-induced spontaneous electrographic seizures in the rat hippocampal slice. J. Neurophysiol. 59, 259–276 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1988.59.1.259
Jensen, M.S., Yaari, Y.: Role of intrinsic burst firing, potassium accumulation, and electrical coupling in the elevated potassium model of hippocampal epilepsy. J. Neurophysiol. 77, 1224–1233 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.1997.77.3.1224
Heinemann, U., Lux, H.D., Gutnick, M.J.: Extracellular free calcium and potassium during paroxysmal activity in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Exp. Brain Res. (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235500
Ullah, G., Cressman, J.R., Jr., Barreto, E., Schiff, S.J.: The influence of sodium and potassium dynamics on excitability, seizures, and the stability of persistent states: II. Network and glial dynamics. J. Comput. Neurosci. 26, 171–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-008-0130-6
Chever, O., Djukic, B., McCarthy, K.D., Amzica, F.: Implication of Kir4.1 channel in excess potassium clearance: an in vivo study on anesthetized glial-conditional Kir4.1 knock-out mice. J. Neurosci. 30, 15769–15777 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2078-10.2010
Walz, W.: Role of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extracellular potassium. Neurochem. Int. 36, 291–300 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-0186(99)00137-0
Bullock, R., Zauner, A., Woodward, J., Young, H.F.: Massive persistent release of excitatory amino acids following human occlusive stroke. Stroke 26, 2187–2189 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.26.11.2187
Dávalos, A., Castillo, J., Serena, J., Noya, M.: Duration of glutamate release after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 28, 708–710 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.28.4.708
Losi, G., Cammarota, M., Chiavegato, A., Gomez-Gonzalo, M., Carmignoto, G.: A new experimental model of focal seizures in the entorhinal cortex: NMDA-Induced seizure-like events. Epilepsia 51, 1493–1502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02472.x
Koizumi, S., Fujishita, K., Tsuda, M., Shigemoto-Mogami, Y., Inoue, K.: Dynamic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by astrocyte-derived ATP in hippocampal cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1834448100
Sun, D.A., Sombati, S., DeLorenzo, R.J.: Glutamate injury-induced epileptogenesis in hippocampal neurons. Stroke 32, 2344–2350 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1161/hs1001.097242
Rose, C.R., Felix, L., Zeug, A., Dietrich, D., Reiner, A., Henneberger, C.: Astroglial glutamate signaling and uptake in the hippocampus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00451
Iversen, L., Mulvihill, E., Haldeman, B., Diemer, N.H., Kaiser, F., Sheardown, M., Kristensen, P.: Changes in metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA levels following global ischemia: increase of a putative presynaptic subtype (mGluR4) in highly vulnerable rat brain areas. J. Neurochem. 63, 625–633 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63020625.x
Nicholls, J.G., Martin, A.R., Wallace, B.G., Fuchs, P.A.: From Neuron to Brain, 5th edn. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA (2001)
Yu, Y., Yuan, Z., Fan, Y., Li, J., Wu, Y.: Dynamic transitions in neuronal network firing sustained by abnormal astrocyte feedback. Neural Plast. 2020, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8864246
Leis, J.A., Bekar, L.K., Walz, W.: Potassium homeostasis in the ischemic brain. Glia 50, 407–416 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20145
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yeyin Xu for helpful comments.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12132012 and 11972275).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Li, J., Yuan, Z. et al. Dynamic mechanism of epileptic seizures generation and propagation after ischemic stroke. Nonlinear Dyn 109, 3113–3132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07577-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07577-2