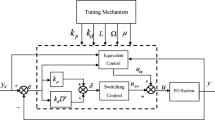
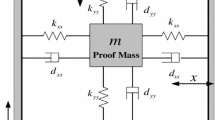
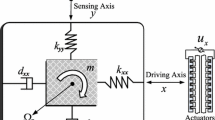
Abstract
This study presents a new nonlinear model-based predictive control scheme using fractional-order calculus and interval type-3 (IT3) fuzzy logic systems (FLSs) for Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System gyroscopes (MEMS-Gs). The dynamics of MEMS-G are unknown and perturbed by actuator faults and disturbances. Two IT3-FLSs are used for online modeling of uncertainties and predicting of tracking error. The IT3-FLSs are online optimized by Lyapunov adaptation rules such that the stability and robustness to be guaranteed. Also, the designed compensators adaptively tackle the effects of perturbations and estimation errors. In various conditions such as dynamic perturbations, actuator nonlinearities, tracking of a chaotic system, and tracking of a pulse signal with sharp rising and falling, we examine the capability of the suggested controller and compare with new controllers and other type of FLSs. We show that a well tracking accuracy with the desired transient performance and least overshoot is obtained.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study. The suggested controller is online applied on the dynamic mathematical model of the case-study MEMS-G.
References
Luo, S., Li, S., Tajaddodianfar, F., Hu, J.: Observer-based adaptive stabilization of the fractional-order chaotic MEMS resonator. Nonlinear Dynam. 92(3), 1079–1089 (2018)
Luo, S., Li, S., Tajaddodianfar, F.: Adaptive chaos control of the fractional-order arch MEMS resonator. Nonlinear Dynam. 91(1), 539–547 (2018)
Hamed, Y., El-Sayed, A., El-Zahar, E.: On controlling the vibrations and energy transfer in MEMS gyroscope system with simultaneous resonance. Nonlinear Dynam. 83(3), 1687–1704 (2016)
Rahmani, M., Rahman, M.H.: A novel compound fast fractional integral sliding mode control and adaptive PI control of a MEMS gyroscope. Microsyst. Technol. 25(10), 3683–3689 (2019)
Guo, Y., Xu, B., Zhang, R.: Terminal sliding mode control of mems gyroscopes with finite-time learning, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3018107
Rahmani, M., Rahman, M.H., Nosonovsky, M.: A new hybrid robust control of MEMS gyroscope. Microsyst. Technol. 26(3), 853–860 (2020)
Wu, X., Xie, Z., Bai, X., Kwan, T.: Design of a 1-bit MEMS gyroscope using the model predictive control approach. Sensors 19(3), 730 (2019)
Gu, H., Su, W., Zhao, B., Zhou, H., Liu, X.: A design methodology of digital control system for MEMS gyroscope based on multi-objective parameter optimization. Micromachines 11(1), 75 (2020)
Hosseini-Pishrobat, M., Keighobadi, J.: Extended state observer-based robust non-linear integral dynamic surface control for triaxial MEMS gyroscope. Robotica 37(3), 481–501 (2019)
Shi, Y., Shao, X., Yang, W., Zhang, W.: Event-triggered output feedback control for MEMS gyroscope with prescribed performance. IEEE Access 8, 26293–26303 (2020)
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Wei, Q., Yang, T., Zhao, W., Zhang, P.: Serial-parallel estimation model-based sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscopes, IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst(2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.2981807
Hosseini-Pishrobat, M., Keighobadi, J.: Robust vibration control and angular velocity estimation of a single-axis MEMS gyroscope using perturbation compensation. J. Intell. Robotic Syst. 94(1), 61–79 (2019)
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Zhao, W.: Finite-time prescribed performance control of MEMS gyroscopes. Nonlinear Dyn. 101, 2223–2234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05959-y
Fazeli Asl, S.B., Moosapour, S.S.: Fractional order fuzzy dynamic backstepping sliding mode controller design for triaxial MEMS gyroscope based on high-gain and disturbance observers. IETE J. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2019.1568917
Shao, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, W., Cao, H.: Neurodynamic approximation-based quantized control with improved transient performances for MEMS gyroscopes: Theory and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Indus. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3026297
Shao, X., Cao, Z., Si, H.: Neurodynamic formation maneuvering control with modified prescribed performances for networked uncertain quadrotors. IEEE Syst. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.3022901
Shao, X., Yue, X., Li, J.: Event-triggered robust control for quadrotors with preassigned time performance constraints. Appl. Mathem. Computat. 392, 125667 (2021)
Shao, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, W.: Fault-tolerant quantized control for flexible air-breathing hypersonic vehicles with appointed-time tracking performances. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2020.3040519 (2020)
Shao, X., Si, H., Zhang, W.: Event-triggered neural intelligent control for uncertain nonlinear systems with specified-time guaranteed behaviors. Neural Comput. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05357-w
Shao, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, W.: Input-and-measurement event-triggered control for flexible air-breathing hypersonic vehicles with asymmetric partial-state constraints. Nonlinear Dynam. 102(1), 163–183 (2020)
Shao, X., Si, H., Zhang, W.: Fuzzy wavelet neural control with improved prescribed performance for MEMS gyroscope subject to input quantization, Fuzzy Sets Syst. 411, 136–154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2020.08.005
Shao, X., Shi, Y.: Neural adaptive control for MEMS gyroscope with full-state constraints and quantized input, IEEE Trans. Indus. Inform 16(10), 6444–6454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.2968345
Chu, Y., Fei, J., Hou, S.: Adaptive neural backstepping PID global sliding mode fuzzy control of MEMS gyroscope. IEEE Access 7, 37918–37926 (2019)
Si, H., Shao, X., Zhang, W.: MLP-based neural guaranteed performance control for MEMS gyroscope with logarithmic quantizer. IEEE Access 8, 38596–38605 (2020)
Wang, Z., Fei, J.: Novel fuzzy neural nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscope. Complexity (2019)
Xu, B., Zhang, R., Li, S., He, W., Shi, Z.: Composite neural learning-based nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscopes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(4), 1375–1386 (2019)
Fei, J., Fang, Y., Yuan, Z.: Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for a micro gyroscope with backstepping controller. Micromachines 11(11), 968 (2020)
Liang, X., Fei, J.: Adaptive fractional fuzzy sliding mode control of microgyroscope based on backstepping design. Plos one 14(6), 0218425 (2019)
Wang, H., Yang, Y., Fei, J., Fang, Y.: Adaptive control of micro-electro-mechanical system gyroscope using neural network compensator. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11(12), 1687814019898325 (2019)
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Shi, P.: Output feedback control of micromechanical gyroscopes using neural networks and disturbance observer, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3030712
Mu, Y., Zhang, H., Su, H., Ren, H.: Unknown input observer synthesis for discrete-time T–S fuzzy singular systems with application to actuator fault estimation, Nonlinera Dynam 100(4), 3399–3412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05630-6
Khankalantary, S., Rafatnia, S., Mohammadkhani, H.: An adaptive constrained type-2 fuzzy hammerstein neural network data fusion scheme for low-cost sins/gnss navigation system. Appl. Soft Comput. 86, 105917 (2020)
Castillo, O., Melin, P., Ontiveros, E., Peraza, C., Ochoa, P., Valdez, F., Soria, J.: A high-speed interval type 2 fuzzy system approach for dynamic parameter adaptation in metaheuristics. Eng. Appl. Art. Intell. 85, 666–680 (2019)
Zhao, T., Zhang, K., Dian, S.: Security control of interval type-2 fuzzy system with two-terminal deception attacks under premise mismatch. Nonlinear Dynam. 102(1), 431–453 (2020)
Peng, W., Li, C., Zhang, G., Yi, J.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic based transmission power allocation strategy for lifetime maximization of wsns. Eng. Appl. Art. Intell. 87, 103269 (2020)
Bi, J.-W., Liu, Y., Fan, Z.-P.: Representing sentiment analysis results of online reviews using interval type-2 fuzzy numbers and its application to product ranking. Inform. Sci. 504, 293–307 (2019)
Mohammadzadeh, A., Rathinasamy, S.: Energy management in photovoltaic battery hybrid systems: a novel type-2 fuzzy control. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45(41), 20970–20982 (2020)
Fazlyab, M., Pedram, M.Z., Salarieh, H., Alasty, A.: Parameter estimation and interval type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control of a z-axis MEMS gyroscope. ISA Trans. 52(6), 900–911 (2013)
Asad, Y.P., Shamsi, A., Tavoosi, J.: Backstepping-based recurrent type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control for MIMO systems (MEMS triaxial gyroscope case study). Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowledge-Based Syst. 25(02), 213–233 (2017)
Tavoosi, J.: Sliding mode control of a class of nonlinear systems based on recurrent type-2 fuzzy RBFN. Int. J. Mech. Automat. 7(2), 72–80 (2020)
Nabipour, N., Qasem, S.N., Jermsittiparsert, K.: Type-3 fuzzy voltage management in pv/hydrogen fuel cell/battery hybrid systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45(56), 32478–32492 (2020)
Mosavi, A., Qasem, S.N., Shokri, M., Mohammadzadeh, A., et al.: Fractional-order fuzzy control approach for photovoltaic/battery systems under unknown dynamics, variable irradiation and temperature. Electronics 9(9), 1455 (2020)
Balootaki, M.A., Rahmani, H., Moeinkhah, H., Mohammadzadeh, A.: Non-singleton fuzzy control for multi-synchronization of chaotic systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 106924,(2020)
Mosavi, C.M.A.M.H.T.M.M.S.S.B.A.: Optimal type-3 fuzzy system for solving singular multi-pantograph equations. IE 8: 225692–225702 (2020)
Fei, J., Batur, C.: A novel adaptive sliding mode control with application to MEMS gyroscope. ISA Trans. 48(1), 73–78 (2009)
Fei, J., Yan, W.: Adaptive control of MEMS gyroscope using global fast terminal sliding mode control and fuzzy-neural-network. Nonlinear Dynam. 78(1), 103–116 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vafaie, R.H., Mohammadzadeh, A. & Piran, M.J. A new type-3 fuzzy predictive controller for MEMS gyroscopes. Nonlinear Dyn 106, 381–403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06830-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06830-4