Abstract
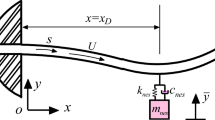
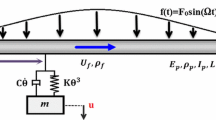
In this paper, a nonlinear energy sink and a negative stiffness element are integrated for achieving enhanced, passive, and adaptive vibration suppression for a pipe conveying fluid. The enhanced NES simultaneously processes a negative linear and a cubic nonlinearity, which is implemented by two linear springs with a special configuration with preloaded deformation. The governing equation of the NES–pipe system is derived and simulated for examining the isolation effectiveness. The performance of the enhanced and classical NESs is compared. It is found that the enhanced NES can absorb vibration energy with a faster decay rate, achieving simultaneous small threshold, high energy dissipation efficiency, and higher robustness. By performing optimal design, a maximum efficiency \(\sim \,98.19\%\) is realized, which is much higher than previous research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paidoussis, M.P., Issid, N.T.: Dynamic stability of pipes conveying fluid. J. Sound Vib. 33, 267–294 (1974)
Yang, T.Z., Ji, S.D., Yang, X.D., Fang, B.: Microfluid-induced nonlinear free vibration of microtubes. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 76, 47–55 (2014)
Tang, Y., Yang, T.Z.: Post-buckling behavior and nonlinear vibration analysis of a fluid-conveying pipe composed of functionally graded material. Compos. Struct. 185, 393–400 (2018)
Guo, C., Zhang, C., Paidoussis, M.: Modification of equation of motion of fluid-conveying pipe for laminar and turbulent flow profiles. J. Fluids Struct. 26, 793–803 (2010)
Dai, H.L., Wu, P., Wang, L.: Nonlinear dynamic responses of electrostatically actuated microcantilevers containing internal fluid flow. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 21, 162 (2017)
Dai, H.L., Wang, L., Ni, Q.: Dynamics and pull-in instability of electrostatically actuated microbeams conveying fluid. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 18, 49–55 (2015)
Dai, H.L., Wang, Y.K., Wang, L.: Nonlinear dynamics of cantilevered microbeams based on modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 94, 103–122 (2015)
Wang, L., Hong, Y.Z., Dai, H.L., Ni, Q.: Natural frequency and stability tuning of cantilevered CNTs conveying fluid in magnetic field. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 29, 567–576 (2016)
Lu, P., Lee, H.: A treatment for the study of dynamic instabilities of fluid-conveying pipes. Mech. Res. Commun. 36, 742–746 (2009)
Liang, F., Yang, X.D., Zhang, W., Qian, Y.J.: Dynamical modeling and free vibration analysis of spinning pipes conveying fluid with axial deployment. J. Sound Vib. 417, 65–79 (2018)
Georgiades, F., Vakakis, A.: Dynamics of a linear beam with an attached local nonlinear energy sink. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 12, 643–651 (2007)
Georgiades, F., Vakakis, A.F.: Passive targeted energy transfers and strong modal interactions in the dynamics of a thin plate with strongly nonlinear attachments. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46, 2330–2353 (2009)
Panagopoulos, P., Georgiades, F., Tsakirtzis, S., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A.: Multi-scaled analysis of the damped dynamics of an elastic rod with an essentially nonlinear end attachment. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 6256–6278 (2007)
Zulli, D., Luongo, A.: Nonlinear energy sink to control vibrations of an internally nonresonant elastic string. Nolinear Dyn. 50, 781–794 (2015)
Chen, J., Zhang, W., Yao, M.H.: Vibration reduction in truss core sandwich plate with internal nonlinear energy sink. Compos. Struct. 193, 180–188 (2018)
Luongo, A., Zulli, D.: Dynamic analysis of externally excited NES-controlled systems via a mixed Multiple scale/harmonic balance algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 2049–2061 (2012)
Yan, Z., Ragab, S.A., Hajj, M.R.: Passive control of transonic flutter with a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 577–590 (2018)
Blanchard, A., Bergman, L., Vakakis, A.F.: Targeted energy transfer in laminar vortex-induced vibration of a sprung cylinder with a nonlinear dissipative rotator. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 350, 26–44 (2017)
Zhang, Y.W., Zhang, Z., Chen, L.Q., Yang, T.Z., Fang, B., Zang, J.: Impulse-induced vibration suppression of an axially moving beam with parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(1–2), 61–71 (2015)
Zhang, Y.W., Yuan, B., Fang, B., Chen, L.Q.: Reducing thermal shock-induced vibration of an axially moving beam via a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 87, 1159–1167 (2017)
Yang, K., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H., Yang, T.Z., Li, Y., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear energy sink for whole-spacecraft vibration reduction. J. Vib. Acoust. 139(2), 021011 (2017)
Yang, T.Z., Yang, X.D., Li, Y., Fang, B.: Passive and adaptive vibration suppression of pipes conveying fluid with variable velocity. J. Vib. Control 20(9), 1293–1300 (2014)
Lee, Y.S., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M., Kerschen, G.: Suppressing aeroelastic instability using broadband passive targeted energy transfers, part 1: theory. AIAA J. 45, 693–711 (2007)
Lee, Y.S., Kerschen, G., McFarland, D.M., JOEL HILL, W., Nichkawde, C., Strganac, T.W., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Suppressing aeroelastic instability using broadband passive targeted energy transfers, part 2: experiments. AIAA J. 45, 2391–2400 (2007)
Rocha, R.T., Balthazar, J.M., Tusset, A.M., Piccirillo, V., Felix, J.L.P.: Comments on energy harvesting on a 2: 1 internal resonance portal frame support structure using a nonlinear energy sink as a passive controller. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. (IREME) 10(3), 147–156 (2016)
Rocha, R.T., Balthazar, J.M., Tusset, A.M., Piccirillo, V.: Using passive control by a pendulum in a portal frame platform with piezoelectric energy harvesting. J. Vib. Control 24, 3684 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546317709387
Iliuk, I., Balthazar, J.M., Tusset, A.M., Piqueira, J.R., de Pontes, B.R., Felix, J.L., Bueno, A.M.: Application of passive control to energy harvester efficiency using a non-ideal portal frame structural support system. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 25(4), 417–429 (2014)
Iliuk, I., Balthazar, J.M., Tusset, A.M., Piqueira, J.R.C., de Pontes, B.R., Felix, J.L.P., Bueno, Á.M.: A non-ideal portal frame energy harvester controlled using a pendulum. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 222(7), 1575–1586 (2013)
Zang, J., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H., Yang, T., Chen, L.Q.: The evaluation of a nonlinear energy sin absorber based on the transmissibility. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.061
Gendelman, O.V., Sapsis, T., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A.: Enhanced passive targeted energy transfer in strongly nonlinear mechanical oscillators. J. Sound Vib. 1–8, 330 (2011)
Kong, X., Li, H., Wu, C.: Dynamics of 1-dof and 2-dof energy sink with geometrically nonlinear damping: application to vibration suppression. Nonlinear Dyn 91, 733 (2018)
Wei, Y.M., Peng, Z.K., Dong, X.J., Zhang, W.M., Meng, G.: Mechanism of optimal targeted energy transfer. J. Appl. Mech. 84(1), 011007 (2016)
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.: Asymmetric magnet-based nonlinear energy sink. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 10(1), 014502 (2014)
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.: Highly efficient nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 76, 1905 (2014)
Yang, X.D., Wu, H., Qian, Y.J., Zhang, W., Lim, C.W.: Nonlinear vibration analysis of axially moving strings based on gyroscopic modes decoupling. J. Sound Vib. 393, 308–320 (2017)
Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Galerkin methods for natural frequencies of high-speed axially moving beams. J. Sound Vib. 329, 3484–3494 (2010)
Vakakis, A.F., Gendelman, O.V., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M., Kerschen, G.: Nonlinear Targeted Energy Transfer in Mechanical and Structural Systems. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Moore, K.J., Bunyan, J., Tawfick, S., Gendelman, O.V., Li, S., Leamy, M., Vakakis, A.F.: Nonreciprocity in the dynamics of coupled oscillators with nonlinearity, asymmetry, and scale hierarchy. Phys. Rev. E 97(1), 012219 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11672187 and 11572182), the Natural Science Research Project of Institutions of Higher Education in Anhui Province (No. KJ2017A114), and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (201602573).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Liu, T., Tang, Y. et al. Enhanced targeted energy transfer for adaptive vibration suppression of pipes conveying fluid. Nonlinear Dyn 97, 1937–1944 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4581-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4581-7