Abstract
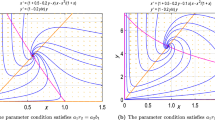
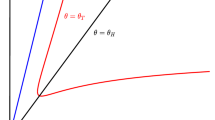
Cannibalism, which is the act of killing and consumption of conspecifics, has been considered primarily in the predator, despite strong ecological evidence that it exists among prey. In the current manuscript, we investigate both the ODE and spatially explicit forms of a Holling–Tanner model, with ratio-dependent functional response, and show that cannibalism in the predator provides a stabilizing influence as expected. However, when cannibalism in the prey is considered, we show that it cannot stabilize the unstable interior equilibrium in the ODE case, in certain parameter regime, but can destabilize the stable interior equilibrium, leading to a stable limit cycle or “life boat” mechanism, for prey. We also show that prey cannibalism can lead to pattern forming Turing dynamics, which is an impossibility without it. The effects of a stochastic prey cannibalism rate are also considered.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams, P.A., Ginzburg, L.R.: The nature of predation: prey dependent, ratio dependent or neither? Trends Ecol. Evol. 15(8), 337–341 (2000)
Asllani, M., Challenger, J.D., Pavone, F.S., Sacconi, L., Fanelli, D.: The theory of pattern formation on directed networks. Nat. Commun. 5, 1–9 (2014)
Banerjee, M., Banerjee, S.: Turing instabilities and spatio-temporal chaos in ratio-dependent Holling-Tanner model. Math. Biosci. 236(1), 64–76 (2012)
Biswas, S., Chatterjee, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Cannibalism may control disease in predator population: result drawn from a model based study. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 38(11), 2272–2290 (2015)
Buonomo, B., Lacitignola, D.: On the stabilizing effect of cannibalism in stage-structured population models. Math. Biosci. Eng. 3(4), 717–731 (2006)
Buonomo, B., Lacitignola, D., Rionero, S.: Effect of prey growth and predator cannibalism rate on the stability of a structured population model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(2), 1170–1181 (2010)
Chan, A.A.Y.-H., Giraldo-Perez, P., Smith, S., Blumstein, D.T.: Anthropogenic noise affects risk assessment and attention: the distracted prey hypothesis. Biol. Lett. 6(4), 458–461 (2010)
Chow, Y., Jang, S.R.-J.: Cannibalism in discrete-time predator-prey systems. J. Biol. Dyn. 6(1), 38–62 (2012)
Claessen, D., De Roos, A.M., Persson, L.: Population dynamic theory of size-dependent cannibalism. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 271(1537), 333–340 (2004)
Don, W.S., Solomonoff, A.: Accuracy and speed in computing the chebyshev collocation derivative. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 16(6), 1253–1268 (1995)
Fasani, S., Rinaldi, S.: Remarks on cannibalism and pattern formation in spatially extended prey-predator systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(4), 2543–2548 (2012)
Francis, C.D., Ortega, C.P., Cruz, A.: Noise pollution changes avian communities and species interactions. Curr. Biol. 19(16), 1415–1419 (2009)
Getto, P., Diekmann, O., De Roos, A.: On the (dis) advantages of cannibalism. J. Math. Biol. 51(6), 695–712 (2005)
Gottlieb, D., Lustman, L.: The spectrum of the chebyshev collocation operator for the heat equation. SIAM J Numer. Anal. 20(5), 909–921 (1983)
Hsu, S.-B., Huang, T.-W.: Global stability for a class of predator-prey systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55(3), 763–783 (1995)
Kelkel, J., Surulescu, C.: On a stochastic reaction-diffusion system modeling pattern formation on seashells. J. Math. Biol. 60(6), 765–796 (2010)
Kelly, D.: The culture that still practices cannibalism (Oct. 2013)
Kohlmeier, C., Ebenhöh, W.: The stabilizing role of cannibalism in a predator-prey system. Bull. Math. Biol. 57(3), 401–411 (1995)
Leslie, P., Gower, J.: The properties of a stochastic model for the predator-prey type of interaction between two species. Biometrika. 47, 219–234 (1960)
Li, L., Wang, Z.-J.: Dynamics in a predator-prey model with space and noise. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(12), 6542–6547 (2013)
Maini, P.K., Woolley, T.E., Baker, R.E., Gaffney, E.A., Lee, S.S.: Turing’s model for biological pattern formation and the robustness problem. Interface Focus, rsfs20110113 (2012)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical biology I: an introduction, volume 17 of interdisciplinary applied mathematics (2002)
Okubo, A., Levin, S.A.: Diffusion and ecological problems: modern perspectives, vol. 14. Springer, New York (2013)
Pennell, C.: Cannibalism in early modern North Africa. Br. J. Middle Eastern Stud. 18(2), 169–185 (1991)
Polis, G.A.: The evolution and dynamics of intraspecific predation. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 12, 225–251 (1981)
Press, A.: Indian doc focuses on hindu cannibal sect (Oct. 2005)
Rudolf, V.H.: Consequences of stage-structured predators: cannibalism, behavioral effects, and trophic cascades. Ecology 88(12), 2991–3003 (2007)
Rudolf, V.H.: The interaction of cannibalism and omnivory: consequences for community dynamics. Ecology 88(11), 2697–2705 (2007)
Rudolf, V.H.: The impact of cannibalism in the prey on predator-prey systems. Ecology 89(11), 3116–3127 (2008)
Sen, M., Banerjee, M., Morozov, A.: Bifurcation analysis of a ratio-dependent prey-predator model with the allee effect. Ecol. Complex. 11, 12–27 (2012)
Siemers, B.M., Schaub, A.: Hunting at the highway: traffic noise reduces foraging efficiency in acoustic predators. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 278(1712), 1646–1652 (2011)
Solis, F.J., Ku-Carrillo, R.A.: Birth rate effects on an age-structured predator-prey model with cannibalism in the prey. In: Abstract and applied analysis, vol. 501, p. 241312. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Cairo (2014)
Strogatz, S.H.: Nonlinear dynamics and chaos: with applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering. Westview press, Boulder (2014)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.-X., Li, B.-L.: Rich dynamics in a predator-prey model with both noise and periodic force. BioSystems 100(1), 14–22 (2010)
Sun, G.-Q., Zhang, G., Jin, Z., Li, L.: Predator cannibalism can give rise to regular spatial pattern in a predator-prey system. Nonlinear Dyn. 58(1–2), 75–84 (2009)
Turing, A.M.: The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 237(641), 37–72 (1952)
White, K., Gilligan, C.: Spatial heterogeneity in three species, plant-parasite-hyperparasite, systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 353(1368), 543–557 (1998)
Wyller, J., Blomquist, P., Einevoll, G.T.: Turing instability and pattern formation in a two-population neuronal network model. Phys. D 225(1), 75–93 (2007)
Zhang, L., Zhang, C.: Rich dynamic of a stage-structured prey-predator model with cannibalism and periodic attacking rate. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(12), 4029–4040 (2010)
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge very helpful conversations with Professor Volker Rudolf, in the Department of Biosciences at Rice University, on various ecological concepts pertaining to prey cannibalism, and subsequent mathematical modeling of such phenomenon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basheer, A., Quansah, E., Bhowmick, S. et al. Prey cannibalism alters the dynamics of Holling–Tanner-type predator–prey models. Nonlinear Dyn 85, 2549–2567 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2844-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2844-8