Abstract
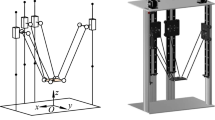
In this paper, adaptive robust control of fully constrained cable-driven parallel robots with elastic cables is studied in detail. A composite controller is proposed for the system under the assumption of linear axial spring model as the dominant dynamics of the cables and in presence of model uncertainties. The proposed controller which is designed based on the singular perturbation theory, consists of two main parts. An adaptive robust controller is designed to counteract the unstructured and parametric uncertainties of the robot and a fast control term which is added to control the longitudinal vibrations of the cables. Moreover, to ensure that all cables remain in tension, the proposed control algorithm benefits from internal force concept. Using the results of the singular perturbation theory, the stability of the overall closed-loop system is analyzed through Lyapunov second method, and finally, the effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm is verified through some simulations on a planar cable-driven parallel robot.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({{\varvec{x}}}\) :
-
The generalized coordinates vector
- \({{\varvec{x}}}_{d}\) :
-
The reference trajectories vector
- \({{\varvec{S}}}\) :
-
The sliding surface vector
- \({{\varvec{L}}}_2\) :
-
The cables length vector
- \({{\varvec{L}}}_1\) :
-
The tensioned cables length vector
- \({{\varvec{L}}}_0\) :
-
The cables length vector at \({{\varvec{x}}}=0\)
- \({{\varvec{q}}}\) :
-
The vector of motors shaft position
- \({\varvec{\rho }}\) :
-
The upper bound of the robot uncertainties
- \({{\varvec{I}}}_{m}\) :
-
The moments of inertia matrix of the motors
- \({{\varvec{K}}}\) :
-
The stiffness matrix of the cables
- \({{\varvec{F}}}_{d}\) :
-
The coefficient matrix of viscous friction
- r :
-
The radius of the actuator drum
- n :
-
The degrees of freedom of the robot
- \({{\varvec{M}}}\) :
-
The mass matrix of the robot
- \({{\varvec{C}}}\) :
-
The Coriolis and centrifugal terms
- \({{\varvec{G}}}\) :
-
The vector of gravity terms
- \({{\varvec{F}}}_{s}\) :
-
The vector of Coulomb friction terms
- \({{\varvec{T}}}_{d}\) :
-
The vector of disturbance terms
- \({{\varvec{J}}}\) :
-
The Jacobian matrix of the robot
- \({{\varvec{Q}}}\) :
-
The vector of internal forces
- \({{\varvec{F}}}\) :
-
The Cartesian force control law
- \({{\varvec{u}}}\) :
-
The vector of motors input torque
- \({\varvec{\epsilon }}\) :
-
The threshold width of the sliding surface
- \({{\varvec{K}}}_v\) :
-
The gain matrix of the fast control term
- \({{\varvec{K}}}_{D}\) :
-
The gain matrix of the Cartesian control law
- \({\varvec{\Lambda }}\) :
-
The constant matrix of the sliding surface
- \({\varvec{\Gamma }}\) :
-
The constant matrix of the adaptation law
References
Gouttefarde, M., Gosselin, C.M.: Analysis of the wrench-closure workspace of planar parallel cable-driven mechanisms. Robot. IEEE Trans. 22(3), 434–445 (2006)
Kawamura, S., Kino, H., Won, C.: High-speed manipulation by using parallel wire-driven robots. Robotica 18(01), 13–21 (2000)
Gagliardini, L., Caro, S., Gouttefarde, M., Wenger, P., Girin, A.: A reconfigurable cable-driven parallel robot for sandblasting and painting of large structures. In: Pott, A., Bruckmann, T. (eds.) Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol. 32, pp. 275–291. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Shao, Z.F., Tang, X., Wang, L.-P., Chen, X.: Dynamic modeling and wind vibration control of the feed support system in FAST. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 965–985 (2012)
Surdilovic, D., Radojicic, J., Bremer, N.: Efficient calibration of cable-driven parallel robots with variable structure. In: Pott, A., Bruckmann, T. (eds.) Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol. 32, pp. 113–128. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Robust PID control of fully-constrained cable driven parallel robots. Mechatronics 24(2), 87–97 (2014)
Oh, S.-R., Agrawal, S.K.: A reference governor-based controller for a cable robot under input constraints. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 13(4), 639–645 (2005)
Oh, S.R., Agrawal, S.K.: Cable suspended planar robots with redundant cables: controllers with positive tensions. Robot. IEEE Trans. 21(3), 457–465 (2005)
Korayem, M.H., Tourajizadeh, H., Zehfroosh, A., Korayem, A.H.: Optimal path planning of a cable-suspended robot with moving boundary using optimal feedback linearization approach. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(2), 1515–1543 (2014)
Oh, S.-R., Agrawal, S.K.: Cable suspended planar robots with redundant cables: controllers with positive tensions. IEEE Trans. Robot. 21(3), 457–465 (2005)
Oh, S.-R., Albus, J.S., Mankala, K., Agrawal, S.K.: A dual-stage planar cable robot: dynamic modeling and design of a robust controller with positive inputs. J. Mech. Des. 127, 612 (2005)
Oh, S.-R., Agrawal, S.K.: Generation of feasible set points and control of a cable robot. Robot. IEEE Trans. 22(3), 551–558 (2006)
Qian, S., Zi, B., Ding, H.: Dynamics and trajectory tracking control of cooperative multiple mobile cranes. Nonlinear Dyn. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11071-015-2313-9
Zi, B., Duan, B.Y., Du, J.L., Bao, H.: Dynamic modeling and active control of a cable-suspended parallel robot. Mechatronics 18(1), 1–12 (2008)
Reichert, C., Müller, K., Bruckmann, T.: Robust internal force-based impedance control for cable-driven parallel robots. In: Pott, A., Bruckmann, T. (eds.) Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol. 32, pp. 131–143. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Korayem, M.H., Zehfroosh, A., Tourajizadeh, H., Manteghi, S.: Optimal motion planning of non-linear dynamic systems in the presence of obstacles and moving boundaries using SDRE: application on cable-suspended robot. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(2), 1423–1441 (2014)
Babaghasabha, R., Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Adaptive control of KNTU planar cable-driven parallel robot with uncertainties in dynamic and kinematic parameters. In: Pott, A., Bruckmann, T. (eds.) Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol. 32, pp. 145–159. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Kino, H., Yahiro, T., Takemura, F., Morizono, T.: Robust PD control using adaptive compensation for completely restrained parallel-wire driven robots: Translational systems using the minimum number of wires under zero-gravity condition. Robot. IEEE Trans. 23(4), 803–812 (2007)
El-Ghazaly, G., Gouttefarde, M., Creuze, V.: Adaptive terminal sliding mode control of a redundantly-actuated cable-driven parallel manipulator: CoGiRo. In: Pott, A., Bruckmann, T. (eds.) Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Mechanisms and Machine Science, vol. 32, pp. 179–200. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Babaghasabha, R., Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Adaptive robust control of fully-constrained cable driven parallel robots. Mechatronics 25, 27–36 (2015)
Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Dynamic modeling and control of parallel robots with elastic cables: singular perturbation approach. Robot. IEEE Trans. 30(3), 694–704 (2014)
Ottaviano, E., Castelli, G.: A Study on the Effects of Cable Mass and Elasticity in Cable-based Parallel Manipulators. Springer, New York (2010)
Diao, X., Ma, O.: Vibration analysis of cable-driven parallel manipulators. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 21(4), 347–360 (2009)
Meunier, G., Boulet, B., Nahon, M.: Control of an overactuated cable-driven parallel mechanism for a radio telescope application. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 17(5), 1043–1054 (2009)
Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Dynamic analysis and control of cable driven robots with elastic cables. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 35(4), 543–558 (2011)
Khosravi, M.A., Taghirad, H.D.: Robust PID control of cable-driven robots with elastic cables. In: Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), First RSI/ISM International Conference on IEEE, pp. 331–336. (2013)
Utkin, V.I., Poznyak, A.S.: Adaptive sliding mode control. In: Bandyopadhyay, B., Janardhanan, S., Spurgeon, S.K. (eds.) Advances in Sliding Mode Control. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, vol. 440, pp. 21–53. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Kokotovic, P., Khali, H.K., O’reilly, J.: Singular Perturbation Methods in Control: Analysis and Design. Siam, Philadelphia (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babaghasabha, R., Khosravi, M.A. & Taghirad, H.D. Adaptive robust control of fully constrained cable robots: singular perturbation approach. Nonlinear Dyn 85, 607–620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2710-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2710-8