Abstract
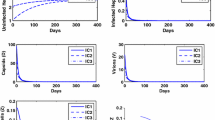
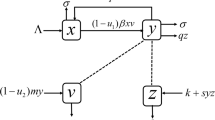
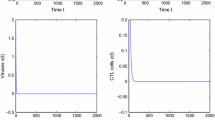
In this paper, the dynamical behavior of a hepatitis B virus model with CTL immune responses is studied. Analyzing the model, we show that the virus-free equilibrium is globally asymptotically stable if the basic reproductive ratio of virus is less than one and the endemic equilibrium is locally asymptotically stable if the basic reproductive ratio is greater than one. When the basic reproductive ratio is greater than one, the system is uniformly persistent, which means the virus is endemic. Mathematical analysis and numerical simulations show that the CTL immune responses play a significant and decisive role in eradication of disease. The study and information derived from this model may have an important impact on treatment protocols of hepatitis B virus in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization: Hepatitis B. WHO/CDS/CSR/LYO/2002.2: Hepatitis B. This document has been downloaded from the WHO/CSR Web site. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/hepatitis/whocdscsrlyo20022/en/ (2002)
Nowak, M.A., Bonhoeffer, S., Hill, A.M., Boehme, R., Thomas, H.C., McDade, H.: Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4398–4402 (1996)
Tsiang, M., Rooney, J.E., Toole, J.J., Gibbset, C.S.: Biphasic clearance kinetics of hepatitis B virus from patients during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Hepatology 29, 1863–1869 (1999)
Neumann, A.U., Lam, N.P.: Hepatitis C viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-Alpha therapy. Science 282, 103–107 (1998)
Min, L., Su, Y., Kuang, Y.: Mathematical analysis of a basic model of virus infection with application. Rocky Mt. J. Math. 38, 1573–1585 (2008)
Long, C., Qi, H., Huang, S.H.: Mathematical modeling of cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated immune responses to hepatitis B virus infection. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 38, 1573–1585 (2008)
Qesmi, R., Wu, J., Wu, J., Heffernan, J.M.: Influence of backward bifurcation in a model of hepatitis B and C viruses. Math. Biosci. 224, 118–125 (2010)
Wang, K., Wang, W.: Propagation of HBV with spatial dependence. Math. Biosci. 210, 78–95 (2007)
Wang, K., Wang, W., Song, S.: Dynamics of an HBV model with diffusion and delay. J. Theor. Biol. 253, 36–44 (2008)
Zeuzem, S., Schmidt, J.M., Lee, J.H., et al.: Effect of inferferomalt on the dynamics of hepatitis C virus turnover in vivo. J. Hepatol. 23, 366–371 (1996)
Nowak, M.A., Bangham, C.R.M.: Population dynamics of immune responses to persistent viruses. Science 272, 74–79 (1996)
Bartholdy, C., Christensen, J.P., Wodarz, D., Thomsen, A.R.: Persistent virus infection despite chronic cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activation in Gamma interferon-deficient mice infected with lymphocytic chroriomeningitis virus. J. Virol. 74, 10304–10311 (2000)
Wodarz, D., Christensen, J.P., Thomsen, A.R.: The importance of lytic and nonlytic immune responses in viral infections. Trends Immunol. 23, 194–200 (2002)
Wang, K., Wang, W., Liu, X.: Global stability in a viral infection model with lytic and nonlytic immune responses. Comput. Math. Appl. 51, 1593–1610 (2006)
Wang, Z., Liu, X.: A chronic viral infection model with immune impairment. J. Theor. Biol. 249, 532–542 (2007)
Mann, J., Roberts, M.: Modelling the epidemiology of hepatitis B in New Zealand. J. Theor. Biol. 269, 266–272 (2011)
Bocharov, G., Ludewig, B., Bertoletti, A., Klenerman, P., Junt, T., Krebs, P., Luzyanina, T., Fraser, C., Anderson, R.M.: Underwhelming the immune response: effect of slow virus growth on CD8+-T-lymphocytes responses. J. Virol. 78(5), 2247–2254 (2004)
Chisari, F.V.: Cytotoxic T cells and viral hepatitis. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 1472–1477 (1997)
Guidotti, L.G., Chisari, F.V.: To kill or to cure: options in host defense against viral infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 8, 478–483 (1996)
Liu, W.-m.: Nonlinear oscillations in models of immune responses to persistent viruses. Theor. Popul. Biol. 52, 224–230 (1997)
Butler, G., Freedman, H.I., Waltman, P.: Uniformly persistent systems. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 96, 425–430 (1986)
Freedman, H.I., Ruan, S., Tang, M.: Uniform persistence and flows near a closed positively invariant set. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 6, 583–600 (1994)
Wikipedia. Elasticity coefficient. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elasticity_Coefficient (2010)
Heinrich, R., Rapoport, T.A.: A linear steady-state treatment of enzymatic chains. General properties, control and effector strength. Eur. J. Biochem. 42, 89–95 (1974)
Woods, J.H., Sauro, H.M.: Elasticities in metabolic control analysis: algebraic derivation of simplified expressions. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 13, 123–130 (1997)
McMahon, B.J., Alward, W.L., Hall, D.B., Heyward, W.L., Bender, T.R., Francis, D.P., Maynard, J.E.: Acute hepatitis B virus infection: relation of age to clinical expression of disease and subsequent development of the carrier state. J. Infect. Dis. 151, 599–603 (1985)
Zhao, S., Xu, Z., Lu, Y.: A mathematical model of hepatitis B virus transmission and its application for vaccination strategy in China. Int. J. Epidemiol. 29, 744–752 (2000)
Medley, G.F., Lindop, N.A., Edmunds, W.J., Nokes, D.J.: Hepatitis-B virus endemicity: heterogeneity, catastrophic dynamics and control. Nat. Med. 7(5), 619–624 (2001)
Shepard, C.W., Simard, E.P., Finelli, L., Fiore, A.E., Bell, B.P.: Hepatitis B virus infection: epidemiology and vaccination. Epidemiol. Rev. 28, 112–125 (2006)
Nowak, M.A., May, R.M.: Viral Dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2000)
Pereson, A.S.: Modelling viral and immune system dynamics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 28–36 (2002)
Tian, X., Xu, R.: Asymptotic properties of a hepatitis B virus infection model with time delay. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 182340, 21 (2010). doi:1155/2010/182340
Shi, X., Zhou, X., Song, X.: Dynamical behavior of a delay virus dynamics model with CTL immune response. Nonlinear Anal. 11, 1795–1809 (2010)
Wang, K., Fan, A., Torres, A.: Global properties of an improved hepatitis B virus model. Nonlinear Anal. 11, 3131–3138 (2010)
Wang, X., Tao, Y., Song, X.: A delayed HIV-1 infection model with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Nonlinear Dyn. 62, 67–72 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, J., Cui, Ja. & Hui, J. The importance of immune responses in a model of hepatitis B virus. Nonlinear Dyn 67, 723–734 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0022-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0022-6