Abstract
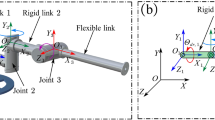
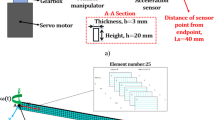
The flexible redundant manipulator, i.e., the flexible manipulator with redundant rigid degrees of freedom, possesses the same kinematic redundancy property as the rigid redundant manipulator. Some undesired effects on the flexible redundant manipulator are expected to alleviate via kinematic redundancy. Due to the presence of structural flexibility, a manipulator will inevitably vibrate when performing tasks. Therefore, how to reduce its vibration responses is a significant problem. Moreover, the manipulator’s mobility, i.e., its ability to move, is another important issue, because good mobility is a desirable goal for almost all robotic manipulator systems. In this paper, how to reduce vibration and improve mobility is studied for the flexible redundant manipulator. Firstly, a method for vibration control via redundancy resolution is put forward. Secondly, the self-motions satisfying vibration reduction are analyzed, and its additional optimization ability is revealed. Based on this ability, a strategy is proposed to both reduce vibration and improve mobility for the flexible redundant manipulator. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of this strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsi, S., Bouzakis, K.D.: Simulation of redundant manipulators for collision avoidance in manufacturing and assembly environments. Mech. Mach. Theory 28(1), 13–21 (1993)
Kireanski, M.V., Petrovic, T.M.: Combined analytical-pseudo inverse kinematic solution for simple redundant manipulators and singularity avoidance. Int. J. Robot. Res. 12(2), 188–196 (1993)
Walker, I.D.: Impact configurations and measures for kinematically redundant and multiple armed robot systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 10(5), 670–683 (1994)
Kim, J.O., Khosal, P., Chung, W.K.: Dynamical resolution of redundancy for robot manipulators. J. Mech. Des. 115, 592–598 (1993)
Saglia, J.A., Dai, J.S., et al.: Geometry and kinematic analysis of a redundantly actuated parallel mechanism that eliminates singularities and improves dexterity. J. Mech. Des. 130, 124501 (2008)
Masayuli, S., Hiromu, K., Woo-Keum, et al.: Analytical inverse kinematic computation for 7-DOF redundant manipulators with joint limits and its application to redundancy resolution. IEEE Trans. Robot. 24(5), 1131–1142 (2008)
Patel, R.V., Shadpey, R., Ranjbaran, F., et al.: A collision-avoidance scheme for redundant manipulators: Theory and experiments. J. Robot. Syst. 22(12), 737–757 (2005)
Benosman, M., Le Vey, G.: Control of flexible manipulators: a survey. Robotica 22, 533–545 (2004)
Dwivedy, S.K., Eberhard, P.: Dynamic analysis of flexible manipulators, a literature review. Mech. Mach. Theory 41(7), 749–777 (2006)
Nguyen, L.A., Walker, I.D., Defigueiredo, R.J.P.: Dynamic control of flexible kinematically redundant robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8(6), 759–767 (1992)
Bian, Y.: Research on dynamics and control of flexible redundant manipulators. Dissertation for Ph.D., Beihang University (1998)
Yue, S.: Weak-vibration configurations for flexible robot manipulators with kinematic redundancy. Mech. Mach. Theory 35(2), 165–17 (2000)
Zhang, X.P., Yu, Y.Q.: Motion control of flexible robot manipulators via optimizing redundant configurations. Mech. Mach. Theory 36(7), 883–89 (2001)
Xu, W.L., Yue, S.G.: Pre-posed configuration of flexible redundant robot manipulators for impact vibration alleviating. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 51(1), 195–200 (2004)
Salisbury, J.K., Craig, J.: Articulated hands: kinematic and force control issues. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1(1), 4–17 (1982)
Klein, C.A.: Use of redundancy in the design of robotic systems. In: Hanafusa, H., Inoue, H. (eds.) Robotics Research: The Second International Symposium, pp. 207–214. MIT Press, Cambridge (2010)
Angeles, J., Rojas, A.A.: Manipulator inverse kinematics via condition number minimization and condition. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2(2), 61–69 (1987)
Yoshikawa, T.: Dynamic manipulability of robotics mechanism. Int. J. Robot. Res. 4(2), 3–9 (1985)
Klein, C.A., Blaho, B.E.: Dexterity measures for the design and control of kinematically redundant manipulators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 6(2), 72–83 (1987)
Pons, J.L., Ceres, R., et al.: Multifingered dextrous robotics hand design and control: a review. Robotica 17(6), 661–674 (1999)
Gosselin, C., Angeles, J.: Global performance index for the kinematic optimization of robotic manipulators. J. Mech. Transm. Autom. Des. 113(3), 220–226 (1991)
Liu, X.-J., Wang, J.A.: new methodology for optimal kinematic design of parallel mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 42(9), 1210–1224 (2007)
Bian, Y., Lu, Z.: Method for dynamic modeling of flexible manipulators. Beijing Hangkong Hangtian Daxue Xuebao 25, 486–490 (1999)
Dubey, R.V., Luh, J.Y.S.: Performance measures and their improvement for redundant robots. In: Paul, F.W., Toumi, K.Y. (eds.) Robotics: Theory and Application, California (1986)
Dubey, R.V., Luh, J.Y.S.: Redundant robot control for higher flexibility. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1066–1072 (1987)
Chen, W., Zhang, Q., Wu, Z., et al.: Singularity avoidance based on avoiding joint velocities limits for redundant manipulators. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern. 4, 3578–3583 (1998)
Kane, T.R., Levinson, D.A.: Dynamics: Theory and Application. McGraw Hill, New York (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Y., Gao, Z. & Yun, C. Study on vibration reduction and mobility improvement for the flexible manipulator via redundancy resolution. Nonlinear Dyn 65, 359–368 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-010-9897-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-010-9897-x