Abstract
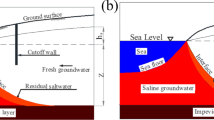
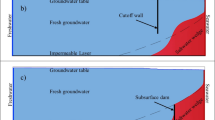
Subsurface barriers have been used as one of the engineering measures to prevent saltwater intrusion in the coastal aquifers in China. However, the effectiveness of those barriers has not been studied thoroughly. In this research, comparative studies using sandbox test as a physical model and the FEFLOW-based groundwater numerical model were conducted for better understanding of the dynamic processes of saltwater intrusion with and without subsurface barriers. Both laboratory tests and numerical simulation without subsurface barriers showed that the saltwater front intruded to 18, 55 and 63 in the aquifer in 10, 20 and 40 min, respectively. The impact of the different permeability of the subsurface barriers to the migration distance and diffusion of saltwater front was also tested in the laboratory and simulated by using the two-dimensional numerical model. Results showed the saltwater front could still pass through the subsurface barrier and continued moving forward when the permeability K of the subsurface barriers was 9.9 × 10−7 m/s. When the K of the subsurface barriers was 1.3 × 10−7 m/s, the salt–front passed through the subsurface barrier in 40 min, and the migration rate of the salt–fresh water interface did not change in 70 min. When the K was 3.7 × 10−8 m/s, the saltwater front could not go through the subsurface barriers. These research results indicated that the subsurface barriers with low permeability (K = 3.7 × 10−8 m/s) could prevent the saltwater intrusion effectively. The results of this case study provide important practical significance for the prevention of saltwater intrusion in coastal areas.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarca E, Carrera J, Sánchez-Vila X et al (2007) Quasi-horizontal circulation cells in 3D seawater intrusion. J Hydrol 339(s3–4):118–129
Abd-Elhamid HF, Javadi AA (2011) A cost-effective method to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manage 25(11):2755–2780
Allow KA (2012) The use of injection wells and a subsurface barrier in the prevention of seawater intrusion: a modelling approach. Arab J Geosci 5(5):1–11
Chekirbane A, Tsujimura M, Kawachi A et al (2015) 3D simulation of a multi-stressed coastal aquifer, northeast of Tunisia: salt transport processes and remediation scenarios. Environ Earth Sci 73:1427–1442
Chen HH, Wang XM, Zhang YX et al (2000) Three-dimensional numerical simulation and analysis of sea-salt water intrusion dynamic system in the lower reaches of Weihe River. Earth Sci Front 7:297–304
Cheng JM (1999) Coastal seawater intrusion in the multilayer aquifer system three dimensional water quality model and application. China university of Geosciences
Cobaner M, Yurtal R, Dogan A et al (2012) Three dimensional simulation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: a case study in the Goksu Deltaic Plain. J Hydrol 464–465(2):262–280
Galeati G, Gambolati G, Neuman SP (1992) Coupled and partially coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian model of freshwater-seawater mixing. Water Resour Res 28(1):149–165
Guo W, Bennett GD (1998) SEAWAT version 1.1: a computer program for simulation of groundwater flow of variable density. Missimer International Inc, Fort Myers
Guo W, Langevin CD (2002) User’s guide to SEAWAT: a computer program for simulation of three-dimensional variable density groundwater flow: techniques of water-resources investigations book 6, Chapter A7, p 77 (Supersedes OFR 01-434)
Huyakorn PS, Jones BG, Parker JC, Wadsworth TD, White HO (1987) Finite element simulation of moisture movement and solute transport in a large caisson. In: Springer EP, Fuentes HR (eds) Modeling study of solute transport in the unsaturated zone, Los Alamos National Laboratory U.S. NRC, NUREG/CR-4615, pp 117–170
Li GM, Chen CX (1995) WeiZhou island seawater intrusion simulation. Hydrogeol Eng Geol (5):1–5
Lin HJ, Rechards, Talbot CA et al (1997) A three-dimensional finite-element computer model for simulating density-dependent flow and transport in variable saturated media: version 3.1. US Army Engineering Research and Development Center, Vicksburg
Lu W, Yang QC, Martín JD et al (2013) Numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in Shenzhen (China) using a 3D density-dependent model including tidal effects. J Earth Syst Sci 122(2):451–465
Rumer RR, Harleman DRF (1963) Intruded salt-water wedge in porous media. J Hydraul Div 86:192–220
Tang J, Lv XB, Yu CZ (1998) Experimental investigation the mechanisms of freshwater-saltwater transition zone in groundwater. J Tsinghua Univ 38:63–66
Todd DK (1980) Saline water intrusion in aquifers in groundwater hydrology [M]. Wiley, pp 494–517
Wu JC, Xue YQ, Xie CH et al (1996) Water-rock interaction cation exchange in the process of sea water intrusion. Hydrogeol Eng Geol (3):18–19
Yuan Y, Liang D (2001) Afterwards prediction of seawater intrusion and controlling engineering. Appl Math Mech 22(11):163–171
Zhang Q (2005) An experimental study of seawater intrusion. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 32(4):43–47
Zhang W, Ying H, Yu X et al (2015) Multi-component transport and transformation in deep confined aquifer during groundwater artificial recharge. J Environ Manage 152:109–119
Zhao J, Jin L, Wu JF et al (2016) Numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in Zhoushuizi district of Dalian City in northern China. Environ Earth Sci 75(9):1–18
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their insightful comments, which greatly improved this manuscript. The authors would also like to thank the Special Project of Public Welfare Research of Water Resources Ministry of China (No. 200901076) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40776050) for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Fl., Chen, Xq., Liu, Ch. et al. Laboratory tests and numerical simulations on the impact of subsurface barriers to saltwater intrusion. Nat Hazards 91, 1223–1235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3176-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3176-4