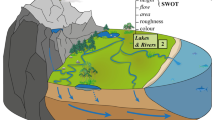
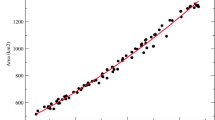
Abstract
The systematic decline of in situ networks for hydrologic measurements has been recognized as a crucial limitation to advancing hydrologic monitoring in medium to large basins, especially those that are already sparsely instrumented. As a collective response, sections of the hydrologic community have recently forged partnerships for the development of space-borne missions for cost-effective, yet global, hydrologic measurements by building upon the technological advancements since the last two decades. In this article, we review the state-of-the-art on flood monitoring in medium and large ungauged basins where satellite remote sensing can facilitate development of a cost-effective mechanism. We present our review in the context of the current hydro-political situation of flood monitoring in flood-prone developing nations situated in international river basins (IRBs). Given the large number of such basins and the difficulty in acquisition of multi-faceted geophysical data, we argue that the conventional data-intensive implementation of physically based hydrologic models that are complex and distributed is time-consuming for global assessment of the utility of proposed global satellite hydrologic missions. A more parsimonious approach is justified at the tolerable expense of accuracy before such missions begin operation. Such a parsimonious approach can subsequently motivate the identified international basins to invest greater effort in conventional and detailed hydrologic studies to design a prototype flood forecasting system in an effort to overcome the hydro-political hurdles to flood monitoring. Through a modeling exercise involving an open-book watershed concept, we demonstrate the value of a parsimonious approach in understanding the utility of NASA-derived satellite rainfall products. It is critical now that real-world operational flood forecasting agencies in the under-developed world come forward to collaborate with the research community in order to leverage satellite rainfall data for greater societal benefit for inhabitants in IRBs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADPC (2002) Application of climate forecasts in the agriculture sector. Climate Forecasting Applications in Bangladesh Project, Report 3, Asian Disaster Preparedness Center (ADPC), Bangkok.
Alsdorf D, Rodriguez E, Lettenmaier DP, Famiglietti J (2005) WatER: Water Elevation Recovery satellite mission. Response to National Research Council Decadal Survey Request for Information (available online: http://www.geology.ohio-state.edu/water/publications/WatER_NRC_RFI.pdf, last accessed May 3, 2006)
Alsdorf D, Lettenmaier DP, Vorosomarty C (2003) The need for global satellite-based observations of terrestrial surface waters. EOS Trans 84(29):269–271
Entekhabi D, Njoku EG, Houser P, Spencer M, Doiron T, Kim Y, Smith J, Girard R, Belair S, Crow W, Jackson TJ, Kerr YH, Kimball JS, Koster R, McDonald KC, O’Neill PE, Running SW, Shi J, Wood E, van Zyl J (2004) The Hydrosphere State (HYDROS) satellite mission: an earth system path finder for global mapping of soil moisture and land/freeze thaw. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(10):2184–2195
Giordano MA, Wolf AT (2003) Sharing waters: post-Rio international water management. Nat Resour Forum 27:163–171
Griffith CG, Woodley WL, Grube PG (1978) Rain estimation from geosynchronous satellite imagery-visible and infrared studies. Monthly Weather Rev 106:1153–1171
Gutowski WJ, Vorosomarty CJ, Person M, Otles Z, Fekete B, York J (2002) A coupled land–atmosphere simulation program (CLASP): calibration and validation. Water Resour Res 107(D16)
Hossain F (2006) Towards formulation of a fully space-borne system for early warning of floods: can cost-effectiveness outweigh flood prediction uncertainty? Nat Hazards 37(3):263–276 (doi: 10.1007/s11069-005-4645-0)
Hossain F, Katiyar N (2006) Improving flood forecasting in international river basins. EOS Trans (AGU) 87(5):49–50
Hossain F, Lettenmaier DP (2006) Flood prediction in the future: recognizing hydrologic issues in anticipation of the global precipitation measurement mission – opinion paper. Water Resour Res 42:W11301. DOI 10.1029/2006WR005202
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Stocker EF, Bolvin DT, Nelkin EJ (2003) Analysis of TRMM 3-hourly multi-satellite precipitation estimates computed in both real and post-real time. 12th Conf. on Sat. Meteor., 2 and Oceanog., Long Beach, California, Feb. 9–13, 2003
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Morrissey MM et al (2001) Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J Hydrometeorol 2:36–50
Katiyar N, Hossain F (2007) An open-book watershed model for prototyping space-borne flood monitoring systems in international river basins. Environ Model Software (In review: available online http://iweb.tntech.edu/fhossain/papers/EnvSoft_GPM.pdf)
Lettenmaier DP, Wood EF (1993) Hydrological forecasting, chapter 26. In: Maidment D (ed) Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York, USA
Niedzialek J, Ogden FL (2004) Numerical investigation of saturated source area behavior at the small catchment scale. Adv Water Resour 27:925–936
Ninno C, del Dorosh PA, Smith LC, Roy DK (2001) The 1998 floods in Bangladesh: disaster impacts, household coping strategies, and response. In: International Food Policy and Research Institute, Research Report 122. Washington, DC, ISBN 0-89629-127-8
Paudyal GN (2002) Forecasting and warning of water-related disaster in a complex hydraulic setting – the case of Bangladesh. Hydrol Sci J 47(Suppl):S5–S18
Shiklomanov AI, Lammers RB, Vörösmarty CJ (2002) Widespread decline in hydrological monitoring threatens pan-arctic research. EOS Trans 83(2):16–17
Smith E et al (2006) The international global precipitation measurement (GPM) program and mission: an overview. In: Levizzani V, Turk FJ (eds) Measuring precipitation from space: EURAINSAT and the future. Kluwer Academic Publishers (Available online: http://gpm.gsfc.nasa.gov)
Stokstad E (1999) Scarcity of rain, stream gages threatens forecasts. Science 285:1199
USAID/OFDA (2004) Fact Sheet report #2 by U.S. Agency for International Development and Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance, July 6, 2004 (Available online: http://www.cidi.org/humanitarian/hsr/ixl8.html), Accessed October, 2006
Webster PJ, Hoyos C (2004) Prediction of monsoon rainfall and river discharges on 15–30 day time scales. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 85(11):1745–1765
Wolf A, Nathrius J, Danielson J, Ward B, Pender J (1999) International river basins of the world. Int J Water Resour Dev 15(4):387–427
Woolhiser DA, Smith RE, Goodrich DC (1990) KINEROS, a kinematic runoff and erosion model: documentation and user manual. In: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service ARS-77, pp 130
Yen BC, Chow VT (1969) A laboratory study of surface runoff due to moving rainstorms. Water Resour Res 5(5):989–1006
Zielinski S (2005) Earth observation programs may be at risk. EOS Trans AGU 86(43):414
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, F., Katiyar, N., Hong, Y. et al. The emerging role of satellite rainfall data in improving the hydro-political situation of flood monitoring in the under-developed regions of the world. Nat Hazards 43, 199–210 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-006-9094-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-006-9094-x