Abstract
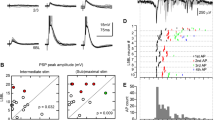
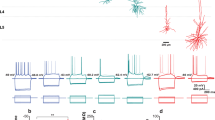
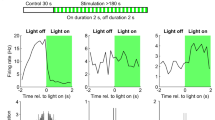
Recently, intense interest has focussed on electrical coupling between interneurones in cortical regions and their contributions towards oscillatory network activity. Despite mounting circumstantial evidence that pyramidal cells are also coupled, the paucity of direct evidence has made this controversial. Dual intracellular recordings from pairs of cortical and hippocampal pyramids demonstrated strong, but sparse coupling. Approximately 70% of CA1 pyramids close to the stratum radiatum border were coupled to another pyramid, but only to one or two of their very closest neighbours. On average 25% of the steady state and 10% of the peak action potential voltage change in one cell transferred to the other, supporting synchrony and promoting burst firing. The very high incidence of convergent inputs from coupled pyramids onto single targets provided additional evidence that ‘spikelets’ reflected full action potentials in a coupled cell, since the EPSPs activated by APs and by ‘spikelets’ had significantly different amplitude distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, A. B., Deuchars, J., Pawelzik, H., and Thomson, A. M. (1998). CA1 pyramidal to basket and bistratified cell EPSPs: dual intracellular recordings in rat hippocampal slices. J. Physiol. 507, 201–217.
Baimbridge, K. G., Peet, M. J., McLennan, H., and Church, J. (1991). Bursting response to current- evoked depolarization in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons is correlated with lucifer yellow dye coupling but not with the presence of calbindin-D28k. Synapse 7, 269–277.
Beierlein, M., Gibson, J. R., and Connors, B. W. (2000). A network of electrically coupled interneurons drives synchronized inhibition in neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 904–910.
Beierlein, M., Gibson, J. R., and Connors, B. W. (2003). Two dynamically distinct inhibitory networks in layer 4 of the neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 90, 2987–3000
Bruzzone, R., Barbe, M. T., Jakob, N. J., and Monyer, H. (2005). Pharmacological properties of homomeric and heteromeric pannexin hemichannels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurochem. 92, 1033–1043.
Church, J. and Baimbridge, K. G. (1991). Exposure to high-pH medium increases the incidence and extent of dye coupling between rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in vitro. J. Neurosci. 11, 3289–3295
Deuchars, J. and Thomson, A. M. (1996). CA1 pyramid-pyramid connections in rat hippocampus in vitro: dual intracellular recordings with biocytin filling. Neuroscience 74, 1009–1018
Deans, M. R., Gibson, J. R., Sellitto, C., Connors, B. W., and Paul, D. L. (2001). Synchronous activity of inhibitory networks in neocortex requires electrical synapses containing connexin36. Neuron 31, 477–485.
Draguhn, A. Traub, R. D., Schmitz, D. and Jefferys, J. G. R. (1998). Electrical coupling underlies high-frequency oscillations in the hippocampus in vitro. Nature 394, 189–192
Galarreta, M. and Hestrin, S. (2002). Electrical and chemical synapses among parvalbumin fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons in adult mouse neocortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 12438–12443
Galarreta, M., Erdelyi, F., Szabo, G., and Hestrin, S. (2004). Electrical coupling among irregular- spiking GABAergic interneurons expressing cannabinoid receptors. J. Neurosci. 24, 9770–9778.
Gibson, J. R., Beierlein, M., Connors, B. W. (1999). Two networks of electrically coupled inhibitory neurons in neocortex. Nature 402, 75–79.
Gibson, J. R., Beierlein, M., and Connors, B. W. (2005). Functional properties of electrical synapses between inhibitory interneurons of neocortical layer 4. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 467–480.
Gutnick, M. J. and Prince, D. A. (1981). Dye coupling and possible electrotonic coupling in the guinea pig neocortical slice. Science 21, 67–70
Hamzel-Sichani, F., Janssen, W. G., Hof, P. R., Wearne, S. L., Stewart, M. G., Whittington, M. A., and Traub, R. D. (2006). Gap junctions couple hippocampal mossy fiber axons to each other and to CA3 pyramidal cell dendrites. Abstract Viewer and Itinerary Planner. Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience, 2006. 132.9 Online
Hormuzdi, S. G., Pais, I., LeBeau, F. E., Towers, S. K., Rozov, A., Buhl, E. H., Whittington, M. A., and Monyer, H. (2001). Impaired electrical signaling disrupts gamma frequency oscillations in connexin 36-deficient mice. Neuron 31, 487–495
Hughes, D. I., Bannister, A. P., Pawelzik, H., and Thomson, A. M. (2000). Double immuno-fluorescence, peroxidase labelling and ultrastructural analysis of interneurones following prolonged electrophysiological recordings in vitro. J. Neurosci. Meth. 101, 107–116.
Long, M. A., Cruikshank, S. J., Jutras, M. J., and Connors, B. W. (2005). Abrupt maturation of a spike-synchronizing mechanism in neocortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 7309–7316.
MacVicar, B. A. and Dudek, F. E. (1981). Electrotonic coupling between pyramidal cells: a direct demonstration in rat hippocampal slices. Science 213, 782–785.
MacVicar, B. A. and Dudek, F. E. (1980). Dye-coupling between CA3 pyramidal cells in slices of rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 196, 494–497.
MacVicar, B. A., Ropert, N., and Krnjevic, K. (1982). Dye-coupling between pyramidal cells of rat hippocampus in vivo. Brain Res. 238, 239–244.
Nagy, J. I., Dudek, F. E., Rash, J. E. (2004). Update on connexins and gap junctions in neurons and glia in the mammalian nervous system. Brain. Res. Brain Res. Rev. 47, 191–215.
Pawelzik, H., Hughes, D. I., and Thomson, A. M. (2002). Physiological and morphological diversity of immunocytochemically defined parvalbumin- and cholecystokinin-positive interneurones in CA1 of the adult rat hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 443, 346–67.
Schmitz, D., Schuchmann, S., Fisahn, A., Draguhn, A., Buhl, E. H., Petrasch-Parwez, E., Dermietzel, R., Heinemann, U., Traub, R. D. (2001). Axo-axonal coupling: a novel mechanism for ultrafast neuronal communication. Neuron 31, 831–840.
Simon, A., Olah, S., Molnar, G., Szabadics, J., and Tamas, G. (2005). Gap-junctional coupling between neurogliaform cells and various interneuron types in the neocortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 6278–6285.
Tamas, G., Buhl, E. H., Lorincz, A., and Somogy, I. P. (2000). Proximally targeted GABAergic synapses and gap junctions synchronize cortical interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 366–371.
Thomson, A. M. and Bannister, A. P. (2004). Electrical gap junctions involving somata and axons of neocortical and hippocampal pyramidal cells 403.13 2004. Abstract Viewer and Itinerary Planner. Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience (Online).
Thomson, A. M. and Radpour, S. (1991). Excitatory connections between CA1 pyramidal cells revealed by spike triggered averaging in slices of rat hippocampus are partially NMDA receptor mediated. Europ. J. Neurosci. 3, 587–601
Thomson, A. M. and West, D. C. (2003). Presynaptic frequency filtering in the gamma frequency band; dual intracellular recordings in slices of adult rat and cat neocortex Cereb. Cortex 13, 136–143.
Vogt, A., Hormuzdi, S. G., and Monyer, H. (2005). Pannexin1 and Pannexin2 expression in the developing and mature rat brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 141, 113–120.
West, D. C., Mercer, A., Kirchhecker, S., Morris, O. T., and Thomson, A. M. (2006). Layer 6 cortico- thalamic pyramidal cells preferentially innervate interneurons and generate facilitating EPSPs. Cereb. Cortex 16, 200–211.
Zsiros, V. and Maccaferri, G. (2005). Electrical coupling between interneurons with different excitable properties in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare of the juvenile CA1 rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 25, 8686–8695.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Audrey Mercer and Peter Bannister made equal contributions to this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercer, A., Bannister, A.P. & Thomson, A.M. Electrical coupling between pyramidal cells in adult cortical regions. Brain Cell Bio 35, 13–27 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-006-9005-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-006-9005-9