Abstract
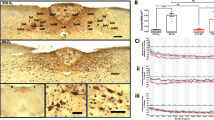
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) are members of the neurotrophin family and are expressed in the developing and adult tongue papillae. BDNF null-mutated mice exhibit specific impairments related to innervation and development of the gustatory system while NT-3 null mice have deficits in their lingual somatosensory innervation. To further evaluate the functional specificity of these neurotrophins in the peripheral gustatory system, we generated double BDNF/NT-3 knockout mice and compared the phenotype to BDNF−/− and wild-type mice. Taste papillae morphology was severely distorted in BDNF−/− xNT-3−/− mice compared to single BDNF−/− and wild-type mice. The deficits were found throughout the tongue and all gustatory papillae. There was a significant loss of fungiform papillae and the papillae were smaller in size compared to BDNF−/− and wild-type mice. Circumvallate papillae in the double knockouts were smaller and did not contain any intraepithelial nerve fibers. BDNF−/− xNT-3−/− mice exhibited additive losses in both somatosensory and gustatory innervation indicating that BDNF and NT-3 exert specific roles in the innervation of the tongue. However, the additional loss of fungiform papillae and taste buds in BDNF−/− xNT-3−/− mice compared to single BDNF knockout mice indicate a synergistic functional role for both BDNF-dependent gustatory and NT-3-dependent somatosensory innervations in taste bud and taste papillae innervation and development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AGERMAN, K., HJERLING-LEFFLER, J., BLANCHARD, M. P., SCARFONE, E., CANLON, B., NOSRAT, C. & ERNFORS, P. (2003) BDNF gene replacement reveals multiple mechanisms for establishing neurotrophin specificity during sensory nervous system development. Development 130, 1479–1491.
BARLOW, L. A. & NORTHCUTT, R. G. (1995) Embryonic origin of amphibian taste buds. Developmental Biology 169, 273–285.
CHO, T. T. & FARBMAN, A. I. (1999) Neurotrophin receptors in the geniculate ganglion. Brain Research Molecular Brain Research 68, 1–13.
CHOI, S., YATES, P. A. & O'LEARY, D. D. M. (1998) Localized BDNF application induces branch-like structures along retinal axons. Society of Neuroscience Abstract 24, 27.
ERNFORS, P., LEE, K. F. & JAENISCH, R. (1994a) Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature 368, 147–150.
ERNFORS, P., LEE, K. F., KUCERA, J. & JAENISCH, R. (1994b) Lack of neurotrophin-3 leads to deficiencies in the peripheral nervous system and loss of limb proprioceptive afferents. Cell 77, 503–512.
ERNFORS, P., MERLIO, J. & PERSSON, H. (1992) Cells expressing mRNA for neurotrophins and their receptors during embryonic rat development. European Journal of Neuroscience 4, 1140–1158.
ERNFORS, P., VANDEWATER, T., LORING, J. & JAENISCH, R. (1995) Complementary roles of BDNF and NT-3 in vestibular and auditory development. Neuron 14, 1153–1164.
FAN, L., GIRNIUS, S. & OAKLEY, B. (2004) Support of trigeminal sensory neurons by nonneuronal p75 neurotrophin receptors. Brain Research Developmental Brain Research 150, 23–39.
FARBMAN, A. I. (2003) Neurotrophins and taste buds. Journal of Comparative Neurology 459, 9–14.
FARBMAN, A. I. & MBIENE, J. P. (1991) Early development and innervation of taste bud-bearing papillae on the rat tongue. Journal of Comparative Neurology 304, 172– 186.
FARINAS, I., YOSHIDA, C. K., BACKUS, C. & REICHARDT, L. F. (1996) Lack of neurotrophin-3 results in death of spinal sensory neurons and premature differentiation of their precursors. Neuron 17, 1065–1078.
FRITZSCH, B., SARAI, P. A., BARBACID, M. & SILOSSANTIAGO, I. (1997) Mice with a targeted disruption of the neurotrophin receptor trkB lose their gustatory ganglion cells early but do develop taste buds. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 15, 563–576.
GANCHROW, D., GANCHROW, J. R., VERDIN-ALCAZAR, M. & WHITEHEAD, M. C. (2003a) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-, neurotrophin-3-, and tyrosine kinase receptor-like immunoreactivity in lingual taste bud fields of mature hamster. Journal of Comparative Neurology 455, 11–24.
GANCHROW, D., GANCHROW, J. R., VERDIN-ALCAZAR, M. & WHITEHEAD, M. C. (2003b) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-, neurotrophin-3-, and tyrosine kinase receptor-like immunoreactivity in lingual taste bud fields of mature hamster after sensory denervation. Journal of Comparative Neurology 455, 25–39.
HÖUKFELT, T., FUXE, K., GOLDSTEIN, M. & JOH, T. H. (1973) Immunohistochemical localization of three catecholamine synthesizing enzymes: aspects on methodology. Histochemie 33, 231–254.
KRIMM, R. F., MILLER, K. K., KITZMAN, P. H., DAVIS, B. M. & ALBERS, K. M. (2001) Epithelial overexpression of BDNF or NT4 disrupts targeting of taste neurons that innervate the anterior tongue. Developmental Biology 232, 508–521.
LIEBL, D. J., MBIENE, J. P. & PARADA, L. F. (1999) NT4/5 mutant mice have deficiency in gustatory papillae and taste bud formation. Developmental Biology 213, 378– 389.
LINDEMANN, B. (2001) Receptors and transduction in taste. Nature 413, 219–225.
MBIENE, J. P., MACCALLUM, D. K. & MISTRETTA, C. M. (1997) Organ cultures of embryonic rat tongue support tongue and gustatory papilla morphogenesis in vitro without intact sensory ganglia. Journal of Comparative Neurology 377, 324–340.
MISTRETTA, C. M., GOOSENS, K. A., FARINAS, I. & REICHARDT, L. F. (1999) Alterations in size, number, and morphology of gustatory papillae and taste buds in BDNF null mutant mice demonstrate neural dependence of developing taste organs. Journal of Comparative Neurology 409, 13–24.
MISTRETTA, C. M., LIU, H. X., GAFFIELD, W. & MACCALLUM, D. K. (2003) Cyclopamine and jervine in embryonic rat tongue cultures demonstrate a role for Shh signaling in taste papilla development and patterning: fungiform papillae double in number and form in novel locations in dorsal lingual epithelium. Developmental Biology 254, 1–18.
NOSRAT, C. A. (1998) Neurotrophic factors in the tongue; expression patterns, biological activity, relation to innervation and studies of neurotrophin knockout mice. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 855, 28– 50.
NOSRAT, C. A., BLOMLÖF, J., ELSHAMY, W. M., ERNFORS, P. & OLSON, L. (1997) Lingual deficits in BDNF and NT3 mutant mice leading to gustatory and somatosensory disturbances, respectively. Development 124, 1333–1342.
NOSRAT, C. A., EBENDAL, T. & OLSON, L. (1996) Differential expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin 3 mRNA in lingual papillae and taste buds indicates roles in gustatory and somatosensory innervation. Journal of Comparative Neurology 376, 587– 602.
NOSRAT, C. A., FRIED, K., EBENDAL, T. & OLSON, L. (1998) NGF, BDNF, NT-3, NT-4 and GDNF in tooth development. European Journal of Oral Sciences 106, 94– 99.
NOSRAT, C. A. & OLSON, L. (1995) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA is expressed in the developing taste bud-bearing tongue papillae of rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology 360, 698– 704.
NOSRAT, C. A. & OLSON, L. (1998) Changes in neurotrophin 3 mRNA expression patterns in the prenatal rat tongue suggest guidance of developing somatosensory nerves to their final targets. Cell Tissue Research 292, 619–623.
NOSRAT, I. V., LINDSKOG, S., SEIGER, Å. & NOSRAT, C. A. (2000) Lingual BDNF and NT-3 mRNA expression patterns and their relation to innervation in the human tongue: similarities and differences compared with rodents. Journal of Comparative Neurology 417, 133– 152.
RINGSTEDT, T., IBÁÑTEZ, C. F. & NOSRAT, C. A. (1999) Role of BDNF in target invasion in the gustatory system. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 3507–3518.
ROCHLIN, M. W., O'CONNOR, R., GIGER, R. J., VERHAAGEN, J. & FARBMAN, A. I. (2000) Comparison of neurotrophin and repellent sensitivities of early embryonic geniculate and trigeminal axons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 422, 579–593.
SEGAL, R. A. (2003) Selectivity in Neurotrophin Signaling: Theme and Variations. Annual Reviews in Neuroscience 18, 18.
STONE, L. M., FINGER, T. E., TAM, P. & TAN, S. S. (1995) Taste receptor cells arise from local epithelium, not neurogenic ectoderm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 92, 1916–1920.
TAKEDA, M., SUZUKI, Y., OBARA, N., UCHIDA, N. & KAWAKOSHI, K. (2004) Expression of GDNF and GFR alpha 1 in mouse taste bud cells. Journal of Comparative Neurology 479, 94–102.
UCHIDA, N., KANAZAWA, M., SUZUKI, Y. & TAKEDA, M. (2003) Expression of BDNF and TrkB in mouse taste buds after denervation and in circumvallate papillae during development. Archives of Histology and Cytology 66, 17–25.
WILKINSON, G. A., FARINAS, I., BACKUS, C., YOSHIDA, C. K. & REICHARDT, L. F. (1996) Neurotrophin-3 is a survival factor in vivo for early mouse trigeminal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 7661–7669.
YEE, C. L., JONES, K. R. & FINGER, T. E. (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is present in adult mouse taste cells with synapses. Journal of Comparative Neurology 459, 15–24.
ZHANG, C. X., BRANDEMIHL, A., LAU, D., LAWTON, A. & OAKLEY, B. (1997) BDNF is required for the normal development of taste neurons in vivo. Neuroreport 8, 1013–1017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nosrat, I.V., Agerman, K., Marinescu, A. et al. Lingual deficits in neurotrophin double knockout mice. J Neurocytol 33, 607–615 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-3330-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-3330-2