Abstract
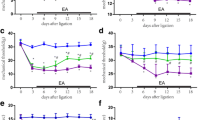
Electro-acupuncture (EA) has been used for clinic analgesia for many years. However, its mechanisms are not fully understood. We recently reported that AXL, a tyrosine kinase receptor, contributes to the peripheral mechanism of neuropathic pain. We here aim to figure out the significance of EA on neuropathic pain mediated by AXL in dorsal root ganglion (DRG). Spinal nerve ligation (SNL) was used as a neuropathic pain model. EA was applied at ‘‘Huantiao’’ (GB-30) and ‘‘Yanglingquan’’ (GB-34) acupoints for 30 min daily from day 7 to day 10 after SNL. EA not only gradually attenuated SNL-induced mechanical allodynia, but also suppressed the expression of phosphorylated AXL (p-AXL) and AXL in injured DRGs of SNL rats examined by western blotting and immunofluorescence. Moreover, intrathecal injection of the subthreshold dose of AXL inhibitor TP0903, significantly prolonged the analgesic time of single EA treatment and enhanced the analgesic effect of repeated EA treatments, suggesting a synergic effect of EA and AXL inhibitor. These results indicate that AXL signaling underlies EA analgesia and combination of AXL inhibitor and EA might be a new strategy for clinic analgesia on neuropathic pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, L. Liang. The data are not publicly available.
References
Dworkin RH, O’Connor AB, Backonja M, Farrar JT, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, Kalso EA, Loeser JD, Miaskowski C, Nurmikko TJ, Portenoy RK, Rice AS, Stacey BR, Treede RD, Turk DC, Wallace MS (2007) Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain 132:237–251
Bouhassira D, Lanteri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C (2008) Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 136:380–387
Harifi G, Amine M, Ait OM, Boujemaoui A, Ouilki I, Rekkab I, Belkhou A, El B, Niamane I, R., and El HS (2013) Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the Moroccan general population: a national survey. Pain Med 14:287–292
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32
Liem L van, Huygen DE, Staats FJ, P., and Kramer J (2016) The Dorsal Root Ganglion as a Therapeutic Target for Chronic Pain. Reg Anesth. Pain Med 41:511–519
Nakahashi Y, Kamiya Y, Funakoshi K, Miyazaki T, Uchimoto K, Tojo K, Ogawa K, Fukuoka T, Goto T (2014) Role of nerve growth factor-tyrosine kinase receptor A signaling in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:415–419
Fukuoka T, Kondo E, Dai Y, Hashimoto N, Noguchi K (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases in the uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons in selective spinal nerve ligation model. J Neurosci 21:4891–4900
Unger JW, Klitzsch T, Pera S, Reiter R (1998) Nerve growth factor (NGF) and diabetic neuropathy in the rat: morphological investigations of the sural nerve, dorsal root ganglion, and spinal cord. Exp Neurol 153:23–34
Yao P, Ding Y, Wang Z, Ma J, Hong T, Zhu Y, Li H, Pan S (2016) Impacts of anti-nerve growth factor antibody on pain-related behaviors and expressions of opioid receptor in spinal dorsal horn and dorsal root ganglia of rats with cancer-induced bone pain. Mol Pain 12:1744806916644928
Tender GC, Li YY, Cui JG (2013) The role of nerve growth factor in neuropathic pain inhibition produced by resiniferatoxin treatment in the dorsal root ganglia. Neurosurgery 73:158–165
Tender GC, Kaye AD, Li YY, Cui JG (2011) Neurotrophin-3 and tyrosine kinase C have modulatory effects on neuropathic pain in the rat dorsal root ganglia. Neurosurgery 68:1048–1055
Rivat C, Sar C, Mechaly I, Leyris JP, Diouloufet L, Sonrier C, Philipson Y, Lucas O, Mallie S, Jouvenel A, Tassou A, Haton H, Venteo S, Pin JP, Trinquet E, Charrier-Savournin F, Mezghrani A, Joly W, Mion J, Schmitt M, Pattyn A, Marmigere F, Sokoloff P, Carroll P, Rognan D, Valmier J (2018) Inhibition of neuronal FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinase alleviates peripheral neuropathic pain in mice. Nat Commun 9:1042
Liang L, Zhang J, Tian L, Wang S, Xu L, Wang Y, Guo-Shuai Q, Dong Y, Chen Y, Jia H, Yang X, Yuan C (2020) AXL signaling in primary sensory neurons contributes to chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Mol Pain 16:1744806919900814
Liang L, Tao B, Fan L, Yaster M, Zhang Y, Tao YX (2013) mTOR and its downstream pathway are activated in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord after peripheral inflammation, but not after nerve injury. Brain Res 1513:17–25
Xu JT, Tu HY, Xin WJ, Liu XG, Zhang GH, Zhai CH (2007) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase B/Akt in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord contributes to the neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Exp Neurol 206:269–279
Xu JT, Zhao X, Yaster M, Tao YX (2010) Expression and distribution of mTOR, p70S6K, 4E-BP1, and their phosphorylated counterparts in rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord dorsal horn. Brain Res 1336:46–57
Xu JT, Sun L, Lutz BM, Bekker A, Tao YX (2015) Intrathecal rapamycin attenuates morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia in rats with neuropathic pain. Transl Perioper Pain Med 2:27–34
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85:355–375
Gim GT, Lee JH, Park E, Sung YH, Kim CJ, Hwang WW, Chu JP, Min BI (2011) Electroacupuncture attenuates mechanical and warm allodynia through suppression of spinal glial activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Brain Res Bull 86:403–411
Manni L, Florenzano F, Aloe L (2011) Electroacupuncture counteracts the development of thermal hyperalgesia and the alteration of nerve growth factor and sensory neuromodulators induced by streptozotocin in adult rats. Diabetologia 54:1900–1908
Chen J, Qi JG, Zhang W, Zhou X, Meng QS, Zhang WM, Wang XY, Wang TH (2007) Electro-acupuncture induced NGF, BDNF and NT-3 expression in spared L6 dorsal root ganglion in cats subjected to removal of adjacent ganglia. Neurosci Res 59:399–405
Liang L, Tao YX (2018) Expression of acetyl-histone H3 and acetyl-histone H4 in dorsal root ganglion and spinal dorsal horn in rat chronic pain models. Life Sci 211:182–188
Wang S, Liu S, Xu L, Zhu X, Liu W, Tian L, Chen Y, Wang Y, Nagendra BVP, Jia S, Liang L, Huo FQ (2019) The upregulation of EGFR in the dorsal root ganglion contributes to chronic compression of dorsal root ganglions-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Mol Pain 15:1744806919857297
Liang LL, Yang JL, Lu N, Gu XY, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ (2010) Synergetic analgesia of propentofylline and electroacupuncture by interrupting spinal glial function in rats. Neurochem Res 35:1780–1786
Sun S, Chen WL, Wang PF, Zhao ZQ, Zhang YQ (2006) Disruption of glial function enhances electroacupuncture analgesia in arthritic rats. Exp Neurol 198:294–302
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Liang L, Wu S, Lin C, Chang YJ, Tao YX (2020) Alternative Splicing of Nrcam Gene in Dorsal Root Ganglion Contributes to Neuropathic Pain. J Pain 21:892–904
Lemke G, Burstyn-Cohen T (2010) TAM receptors and the clearance of apoptotic cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1209:23–29
van der Meer JH, van der Poll T, and van, ‘. V (2014) TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 123:2460–2469
Gruber RC, Ray AK, Johndrow CT, Guzik H, Burek D, de Frutos PG, Shafit-Zagardo B (2014) Targeted GAS6 delivery to the CNS protects axons from damage during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurosci 34:16320–16335
Weinger JG, Brosnan CF, Loudig O, Goldberg MF, Macian F, Arnett HA, Prieto AL, Tsiperson V, Shafit-Zagardo B (2011) Loss of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl leads to enhanced inflammation in the CNS and delayed removal of myelin debris during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation 8:49
Prieto AL, Weber JL, Lai C (2000) Expression of the receptor protein-tyrosine kinases Tyro-3, Axl, and mer in the developing rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 425:295–314
Lindqvist N, Lonngren U, Agudo M, Napankangas U, Vidal-Sanz M, Hallbook F (2010) Multiple receptor tyrosine kinases are expressed in adult rat retinal ganglion cells as revealed by single-cell degenerate primer polymerase chain reaction. Ups J Med Sci 115:65–80
Li R, Chen J, Hammonds G, Phillips H, Armanini M, Wood P, Bunge R, Godowski PJ, Sliwkowski MX, Mather JP (1996) Identification of Gas6 as a growth factor for human Schwann cells. J Neurosci 16:2012–2019
Funakoshi H, Yonemasu T, Nakano T, Matumoto K, Nakamura T (2002) Identification of Gas6, a putative ligand for Sky and Axl receptor tyrosine kinases, as a novel neurotrophic factor for hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res 68:150–160
Zou Z, Sun J, Kang Z, Wang Y, Zhao H, Zhu K, Wang J (2020) Tyrosine kinase receptors Axl and MerTK mediate the beneficial effect of electroacupuncture in a Cuprizone-induced demyelinating model. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2020:3205176
Linger RM, Keating AK, Earp HS, Graham DK (2008) TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res 100:35–83
Wu S, Marie LB, Miao X, Liang L, Mo K, Chang YJ, Du P, Soteropoulos P, Tian B, Kaufman AG, Bekker A, Hu Y, Tao YX (2016) Dorsal root ganglion transcriptome analysis following peripheral nerve injury in mice. Mol Pain 12:1744806916629048
Wang Q, Lu QJ, Xiao B, Zheng Y, Wang XM (2011) Expressions of Axl and Tyro-3 receptors are under regulation of nerve growth factor and are involved in differentiation of PC12 cells. Neurosci Bull 27:15–22
Terada Y, Morita-Takemura S, Isonishi A, Tanaka T, Okuda H, Tatsumi K, Shinjo T, Kawaguchi M, Wanaka A (2018) NGF and BDNF expression in mouse DRG after spared nerve injury. Neurosci Lett 686:67–73
Wu JR, Chen H, Yao YY, Zhang MM, Jiang K, Zhou B, Zhang DX, Wang J (2017) Local injection to sciatic nerve of dexmedetomidine reduces pain behaviors, SGCs activation, NGF expression and sympathetic sprouting in CCI rats. Brain Res Bull 132:118–128
Nori SL, Rocco ML, Florenzano F, Ciotti MT, Aloe L, Manni L (2013) Increased nerve growth factor signaling in sensory neurons of early diabetic rats is corrected by electroacupuncture. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:652735
Dong ZQ, Ma F, Xie H, Wang YQ, Wu GC (2005) Changes of expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor in dorsal root ganglions and spinal dorsal horn during electroacupuncture treatment in neuropathic pain rats. Neurosci Lett 376:143–148
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Projects of National Health and Family Planning Commission of Tianjin, China (16KG157), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701112, 31871065), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2019JM-128), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M633527), the Shaanxi Province Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018BSHEDZZ147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, S., Chang, S., Dong, Y. et al. Electro-acupuncture Suppresses AXL Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons and Enhances Analgesic Effect of AXL Inhibitor in Spinal Nerve Ligation Induced-Neuropathic Pain Rats. Neurochem Res 46, 504–512 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03185-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03185-x