Abstract
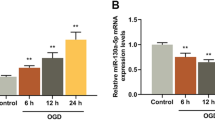
Ischemic stroke (IS) is a common disease that seriously endangers human health. Patients with IS present with increased death of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). MALAT1 is found to be upregulated in IS patients. However, the function of MALAT1 in IS pathogenesis still remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the role of MALAT1 in IS in vitro model and the related molecular mechanisms. The expressions of MALAT1 and miR-126 were detected by qPCR. The in vitro IS model was established by treating BMECs with oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). Cell viability and cell apoptosis were assessed by MTT assay and flow cytometry, respectively. Luciferase assay was conducted to examine the interplay between MALAT1 and miR-126. Western blotting was used to determine the protein levels of apoptosis-associated proteins (e.g. caspase 3, Bax and Bcl-2) and PI3K/Akt pathway-related proteins (e.g. PI3K, Akt, p-PI3K, p-Akt). OGD induced upregulation of MALAT1 and downregulation of miR-126 in HBMECs. MALAT1 knockdown promoted the proliferation of HBMECs and reduced the proportion of apoptotic HBMECs by regulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins. MALAT1 targeted and negatively regulated miR-126 expression. Overexpression of miR-126 activated the PI3K/Akt pathway, which in turn affected the proliferation and apoptosis of HBMECs. MALAT1 negatively regulated PI3K/Akt pathway. MALAT1 inhibited the proliferation and induced the apoptosis of OGD-induced HBMECs through suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway by sponging miR-126, providing a potential therapeutic target for IS.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IS:
-
Ischemic stroke
- BMECs:
-
Brain microvascular endothelial cells
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- miRNA:
-
microRNA
- MALAT1:
-
Metastasis-associate lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1
- HBMECs:
-
Human brain microvascular endothelial cells
- ATCC:
-
American type culture collection
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- CST:
-
Cell signaling technology
- OGD:
-
Oxygen-glucose deprivation
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- RIPA buffer:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
References
Munshi A, Das S, Kaul S (2015) Genetic determinants in ischaemic stroke subtypes: seven year findings and a review. Gene 555:250–259
Liu LP, Wong LK, Wang DZ, Miao ZR (2014) Current status of endovascular procedures in management of ischemic stroke in China. CNS Neurosci Ther 20:483–484
Ronning OM (2013) Very long-term mortality after ischemic stroke: predictors of cardiovascular death. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 196:69–72
Zhang Y, Wang T, Yang K, Xu J, Ren L, Li W, Liu W (2016) Cerebral microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis after ischemia: role of enolase-phosphatase 1 activation and aci-reductone dioxygenase 1 translocation. Front Mol Neurosci 9:79
Guo L, Carraro M, Sartori G, Minervini G, Eriksson O, Petronilli V, Bernardi P (2018) Arginine 107 of yeast ATP synthase subunit g mediates sensitivity of the mitochondrial permeability transition to phenylglyoxal. J Biol Chem 293:14632–14645
Yu QJ, Tao H, Wang X, Li MC (2015) Targeting brain microvascular endothelial cells: a therapeutic approach to neuroprotection against stroke. Neural Regen Res 10:1882–1891
Zhao W, Li L (2019) SP1-induced upregulation of long non-coding RNA HCP5 promotes the development of osteosarcoma. Pathol Res Pract 215:439–445
Zhang J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Zhu T, Meng F, Li Y, Chen YE, Yin KJ (2016) Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 277:162–170
Zhang T, Wang H, Li Q, Fu J, Huang J, Zhao Y (2018) MALAT1 activates the P53 signaling pathway by regulating MDM2 to promote ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem 50:2216–2228
Ren L, Wei C, Li K, Lu Z (2019) LncRNA MALAT1 up-regulates VEGF-A and ANGPT2 to promote angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation via targetting miR-145. Biosci Rep 39:BSR20180226
Tan W, Liu B, Qu S, Liang G, Luo W, Gong C (2018) MicroRNAs and cancer: key paradigms in molecular therapy. Oncol Lett 15:2735–2742
Wang H, Peng R, Wang J, Qin Z, Xue L (2018) Circulating microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers: the advantage and disadvantage. Clin Epigenetics 10:59
Chen J, Cui C, Yang X, Xu J, Venkat P, Zacharek A, Yu P, Chopp M (2017) MiR-126 affects brain-heart interaction after cerebral ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 8:374–385
Sun Z, Ou C, Liu J, Chen C, Zhou Q, Yang S, Li G, Wang G, Song J, Li Z, Zhang Z, Yuan W, Li X (2019) YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 38:2627–2644
Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Liu XS, Hozeska-Solgot A, Chopp M (2007) The PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the neuroprotective effect of atorvastatin in extending thrombolytic therapy after embolic stroke in the rat. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2470–2475
Pan Q, Zheng J, Du D, Liao X, Ma C, Yang Y, Chen Y, Zhong W, Ma X (2018) MicroRNA-126 priming enhances functions of endothelial progenitor cells under physiological and hypoxic conditions and their therapeutic efficacy in cerebral ischemic damage. Stem Cells Int 2018:2912347
Tasca CI, Dal-Cim T, Cimarosti H (2015) In vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation to study ischemic cell death. Methods Mol Biol 1254:197–210
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS, Feng ZP (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9:281
Li HB, You QS, Xu LX, Sun LX, Abdul Majid AS, Xia XB, Ji D (2017) Long non-coding RNA-MALAT1 mediates retinal ganglion cell apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats with glaucoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:2117–2132
Cao DW, Liu MM, Duan R, Tao YF, Zhou JS, Fang WR, Zhu JR, Niu L, Sun JG (2019) The lncRNA Malat1 functions as a ceRNA to contribute to berberine-mediated inhibition of HMGB1 by sponging miR-181c-5p in poststroke inflammation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41:22
Guo D, Ma J, Yan L, Li T, Li Z, Han X, Shui S (2017) Down-regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 attenuates neuronal cell death through suppressing Beclin1-dependent autophagy by regulating Mir-30a in cerebral ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:182–194
Li Z, Li J, Tang N (2017) Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression. Neuroscience 354:1–10
Sun Z, Ou C, Liu J, Chen C, Zhou Q, Yang S, Li G, Wang G, Song J, Li Z (2019) YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 38:2627–2644
Schober A, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Wei Y, Bidzhekov K, Gremse F, Grommes J, Megens RT, Heyll K, Noels H, Hristov M, Wang S, Kiessling F, Olson EN, Weber C (2014) MicroRNA-126-5p promotes endothelial proliferation and limits atherosclerosis by suppressing Dlk1. Nat Med 20:368–376
Villain G, Poissonnier L, Noueihed B, Bonfils G, Rivera JC, Chemtob S, Soncin F, Mattot V (2018) miR-126-5p promotes retinal endothelial cell survival through SetD5 regulation in neurons. Development 145:dev156232
Lei H, Li H, Tian L, Li M, Xin Z, Zhang X, Guan R (2018) Icariside II ameliorates endothelial dysfunction by regulating the MAPK pathway via miR-126/SPRED1 in diabetic human cavernous endothelial cells. Drug Des Dev Ther 12:1743–1751
Long G, Wang F, Li H, Yin Z, Wang DW (2013) Circulating miR-30a, miR-126 and let-7b as biomarker for ischemic stroke in humans. BMC Neurol 13:178
Chen J-J, Zhou S-H (2011) Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing MiR-126 enhance ischemic angiogenesis via the AKT/ERK-related pathway. Cardiol J 18:675–681
Chen L, Wang J, Wang B, Yang J, Gong Z, Zhao X, Zhang C, Du K (2016) MiR-126 inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt signaling. Ann Hematol 95:365–374
Zhang B, Liu Y, Li Y, Zhe X, Zhang S, Zhang L (2018) Neuroglobin promotes the proliferation and suppresses the apoptosis of glioma cells by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep 17:2757–2763
Hynes NE (2016) Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors blocks PI3K/AKT signaling, induces apoptosis, and impairs mammary tumor outgrowth and metastasis. Can Res 70:4151–4162
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Guizhou Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration, National Medical Science and Technology Research Project [Grant Number QZYY-2019-021], The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Research projects in the hospital (Grant Number GZEYK[2020]11) and Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2019 Campus Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Yang, H., Li, WJ. et al. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes OGD-Induced Apoptosis of Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Sponging miR-126 to Repress PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res 45, 2091–2099 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03071-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03071-6