Abstract
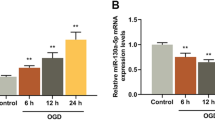
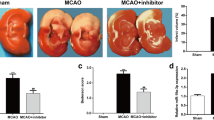
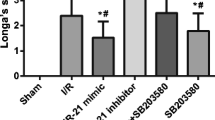
Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury severely threatens human life, while the potential mechanism underlying it is still need further exploration. The rat model of cerebral I/R injury was established using middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The rat microvascular endothelial cell line bEND.3 was exposed to oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) to mimic ischemic condition in vitro. Evans blue was performed to determine the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Real-time PCR and western blot were performed to determine gene expression in mRNA and protein level, individually. Luciferase reporter assay was conducted to determine the relationship between miR-539 and MMP-9. The infarct volume and BBB permeability of cerebral (I/R) rats were significantly greater than Sham group. The expression of miR-539 was decreased, while MMP-9 was increased in the brain tissues of I/R injury rats and OGD/R pretreated bEND.3. Up-regulated miR-539 in OGD/R pretreated bEND.3 significantly promoted the BBB permeability. MiR-539 targets MMP-9 to regulate its expression. OGD/R treatment significantly promoted the BBB permeability in bEND.3, miR-539 mimic transfection abolished the effects of OGD/R, while co-transfected with pcDNA-MMP-9 abolished the effects of miR-539 mimic. MiR-539 targets MMP-9 and further regulates the BBB permeability in cerebral I/R injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsai CF, Thomas B, Sudlow CL (2013) Epidemiology of stroke and its subtypes in Chinese vs white populations: a systematic review. Neurology 81:264–272
Lou Z, Wang AP, Duan XM, Hu GH, Song GL, Zuo ML, Yang ZB (2018) Upregulation of NOX2 and NOX4 mediated by TGF-beta signaling pathway exacerbates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion oxidative stress injury. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:2103–2113
Zhang YS, Liu B, Luo XJ, Li TB, Zhang JJ, Peng JJ, Zhang XJ, Ma QL, Hu CP, Li YJ, Peng J, Li Q (2015) Nuclear cardiac myosin light chain 2 modulates NADPH oxidase 2 expression in myocardium: a novel function beyond muscle contraction. Basic Res Cardiol 110:38
Khatri R, McKinney AM, Swenson B, Janardhan V (2012) Blood-brain barrier, reperfusion injury, and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 79:S52–S57
Wang Z, Leng Y, Tsai LK, Leeds P, Chuang DM (2011) Valproic acid attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia: the roles of HDAC and MMP-9 inhibition. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:52–57
Jin G, Arai K, Murata Y, Wang S, Stins MF, Lo EH, van Leyen K (2008) Protecting against cerebrovascular injury: contributions of 12/15-lipoxygenase to edema formation after transient focal ischemia. Stroke 39:2538–2543
Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W, Rosenberg GA (2007) Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:697–709
Kamada H, Yu F, Nito C, Chan PH (2007) Influence of hyperglycemia on oxidative stress and matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats: relation to blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Stroke 38:1044–1049
Magnoni S, Baker A, George SJ, Duncan WC, Kerr LE, McCulloch J, Horsburgh K (2004) Differential alterations in the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurobiol Dis 17:188–197
Asahi M, Wang X, Mori T, Sumii T, Jung JC, Moskowitz MA, Fini ME, Lo EH (2001) Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 21:7724–7732
Gu Z, Cui J, Brown S, Fridman R, Mobashery S, Strongin AY, Lipton SA (2005) A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 25:6401–6408
Quan J, Qu J, Zhou L (2017) MicroRNA-539 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion by targeting DIXDC1. Biomed Pharmacother 93:746–753
Liu Y, Hong W, Zhou C, Jiang Z, Wang G, Wei G, Li X (2017) miR-539 inhibits FSCN1 expression and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma migration and invasion. Oncol Rep 37:2593–2602
Wen D, Li S, Jiang W, Zhu J, Liu J, Zhao S (2017) miR-539 inhibits human colorectal cancer progression by targeting RUNX2. Biomed Pharmacother 95:1314–1320
Feng Y, Wang J, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Shen M, Yuan F (2018) miR-539-5p inhibits experimental choroidal neovascularization by targeting CXCR7. FASEB J 32:1626–1639
Shen J, Ma S, Chan P, Lee W, Fung PC, Cheung RT, Tong Y, Liu KJ (2006) Nitric oxide down-regulates caveolin-1 expression in rat brains during focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Neurochem 96:1078–1089
Jiang Y, Li L, Tan X, Liu B, Zhang Y, Li C (2015) miR-210 mediates vagus nerve stimulation-induced antioxidant stress and anti-apoptosis reactions following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurochem 134:173–181
Diaz-Canestro C, Merlini M, Bonetti NR, Liberale L, Wust P, Briand-Schumacher S, Klohs J, Costantino S, Miranda M, Schoedon-Geiser G, Kullak-Ublick GA, Akhmedov A, Paneni F, Beer JH, Luscher TF, Camici GG (2018) Sirtuin 5 as a novel target to blunt blood-brain barrier damage induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol 260:148–155
Zhao H, Wang J, Gao L, Wang R, Liu X, Gao Z, Tao Z, Xu C, Song J, Ji X, Luo Y (2013) MiRNA-424 protects against permanent focal cerebral ischemia injury in mice involving suppressing microglia activation. Stroke 44:1706–1713
Tu Y, Wan L, Fan Y, Wang K, Bu L, Huang T, Cheng Z, Shen B (2013) Ischemic postconditioning-mediated miRNA-21 protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via PTEN/Akt pathway. PLoS One 8:e75872
Zeng L, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang L, Weng S, Tang Y, Zheng C, Cheng Q, Chen S, Yang GY (2011) MicroRNA-210 as a novel blood biomarker in acute cerebral ischemia. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 3:1265–1272
Hamzei Taj S, Kho W, Riou A, Wiedermann D, Hoehn M (2016) MiRNA-124 induces neuroprotection and functional improvement after focal cerebral ischemia. Biomaterials 91:151–165
Deng X, Zhong Y, Gu L, Shen W, Guo J (2013) MiR-21 involve in ERK-mediated upregulation of MMP9 in the rat hippocampus following cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Bull 94:56–62
Siegel C, Li J, Liu F, Benashski SE, McCullough LD (2011) miR-23a regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) contributes to sex differences in the response to cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:11662–11667
Ouyang YB, Lu Y, Yue S, Xu LJ, Xiong XX, White RE, Sun X, Giffard RG (2012) miR-181 regulates GRP78 and influences outcome from cerebral ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Neurobiol Dis 45:555–563
Su WS, Tsai ML, Huang SL, Liu SH, Yang FY (2015) Controllable permeability of blood-brain barrier and reduced brain injury through low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation. Oncotarget 6:42290–42299
Malik R, Dichgans M (2018) Challenges and opportunities in stroke genetics. Cardiovasc Res 114(9):1226–1240
Miyazaki T, Kimura Y, Ohata H, Hashimoto T, Shibata K, Hasumi K, Honda K (2011) Distinct effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator and SMTP-7 on cerebrovascular inflammation following thrombolytic reperfusion. Stroke 42:1097–1104
Durukan A, Tatlisumak T (2007) Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 87:179–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, F., Yang, J., Xu, Y. et al. MiR-539 Targets MMP-9 to Regulate the Permeability of Blood–Brain Barrier in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of Brain. Neurochem Res 43, 2260–2267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2646-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2646-0