Abstract
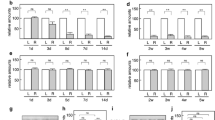
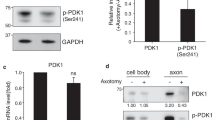
The ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways play important role in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. However, the relative importance and degree of functional overlap of the two pathways are still debated due to lack of in-vivo data. We used rats which underwent a facial nerve axotomy, and examined subsequent ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling activity by quantifying phosphorylation of ERK and Akt. We also assessed the survival rate of facial neurons, number of regenerated axons, and the length of axonal regrowth in axotomized animals treated with an inhibitor of ERK/MAPK (U0126) or PI3K/Akt (LY294002) phosphorylation, or with vehicle. Axotomy increased phosphorylation of ERK and Akt in the facial nucleus 7 days after injury. The inhibition of ERK phosphorylation significantly reduced the length of regenerated axons, but not the other parameters. Inhibition of Akt phosphorylation significantly reduced the survival rate of facial neurons and the number of new axons, as well as the length of regenerated axons. The results indicate that facial nerve injury activates the ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in the facial nerve nucleus and its axons. However, the pathways promoted aspects of regeneration with only slight overlap: PI3K/Akt signaling improved the survival of neurons, as well as axonal growth and branching, whereas ERK/MAPK signaling promoted only axonal extension.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chierzi S, Ratto GM, Verma P, Fawcett JW (2005) The ability of axons to regenerate their growth cones depends on axonal type and age, and is regulated by calcium, cAMP and ERK. Eur J Neurosci 21(8):2051–2062. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04066.x
Dai CF, Kanoh N, Li KY, Wang Z (2000) Study on facial motoneuronal death after proximal or distal facial nerve transection. Am J Otol 21(1):115–118
Mattsson P, Meijer B, Svensson M (1999) Extensive neuronal cell death following intracranial transection of the facial nerve in the adult rat. Brain Res Bull 49(5):333–341
Mattsson P, Delfani K, Janson AM, Svensson M (2006) Motor neuronal and glial apoptosis in the adult facial nucleus after intracranial nerve transection. J Neurosurg 104(3):411–418. doi:10.3171/jns.2006.104.3.411
Schmid RS, Pruitt WM, Maness PF (2000) A MAP kinase-signaling pathway mediates neurite outgrowth on L1 and requires Src-dependent endocytosis. J Neurosci 20(11):4177–4188
Forcet C, Stein E, Pays L, Corset V, Llambi F, Tessier-Lavigne M, Mehlen P (2002) Netrin-1-mediated axon outgrowth requires deleted in colorectal cancer-dependent MAPK activation. Nature 417(6887):443–447. doi:10.1038/nature748
Carter AN, Downes CP (1992) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 267(21):14563–14567
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Dai Y, Tachibana T, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Yoshikawa H, Noguchi K (2003) Differential activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in primary afferent neurons regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression after peripheral inflammation and nerve injury. J Neurosci 23(10):4117–4126
Orike N, Middleton G, Borthwick E, Buchman V, Cowen T, Davies AM (2001) Role of PI 3-kinase, Akt and Bcl-2-related proteins in sustaining the survival of neurotrophic factor-independent adult sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol 154(5):995–1005. doi:10.1083/jcb.200101068
Edstrom A, Ekstrom PA (2003) Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in neuronal survival and axonal outgrowth of adult mouse dorsal root ganglia explants. J Neurosci Res 74(5):726–735. doi:10.1002/jnr.10686
Kimpinski K, Mearow K (2001) Neurite growth promotion by nerve growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 in cultured adult sensory neurons: role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and mitogen activated protein kinase. J Neurosci Res 63(6):486–499. doi:10.1002/jnr.1043
Johanson SO, Crouch MF, Hendry IA (1995) Retrograde axonal transport of signal transduction proteins in rat sciatic nerve. Brain Res 690(1):55–63
Zhou FQ, Snider WD (2006) Intracellular control of developmental and regenerative axon growth. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 361(1473):1575–1592. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1882
Smith DS, Skene JH (1997) A transcription-dependent switch controls competence of adult neurons for distinct modes of axon growth. J Neurosci 17(2):646–658
Hobson SA, Holmes FE, Kerr NC, Pope RJ, Wynick D (2006) Mice deficient for galanin receptor 2 have decreased neurite outgrowth from adult sensory neurons and impaired pain-like behaviour. J Neurochem 99(3):1000–1010. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04143.x
Yamazaki T, Sabit H, Oya T, Ishii Y, Hamashima T, Tokunaga A, Ishizawa S, Jie S, Kurashige Y, Matsushima T, Furuta I, Noguchi M, Sasahara M (2009) Activation of MAP kinases, Akt and PDGF receptors in injured peripheral nerves. J Peripher Nerv Syst 14(3):165–176. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2009.00228.x
Sheu JY, Kulhanek DJ, Eckenstein FP (2000) Differential patterns of ERK and STAT3 phosphorylation after sciatic nerve transection in the rat. Exp Neurol 166(2):392–402. doi:10.1006/exnr.2000.7508
Huang X, Hu J, Li Y, Yang ZZ, Zhu H, Zhou L, Ma K, Schachner M, Xiao Z, Li Y (2013) The cell adhesion molecule L1 regulates the expression of FGF21 and enhances neurite outgrowth. Brain Res 1530:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2013.07.043
Sagot Y, Dubois-Dauphin M, Tan SA, de Bilbao F, Aebischer P, Martinou JC, Kato AC (1995) Bcl-2 overexpression prevents motoneuron cell body loss but not axonal degeneration in a mouse model of a neurodegenerative disease. J Neurosci 15(11):7727–7733
Zhou X, Rodriguez WI, Casillas RA, Ma V, Tam J, Hu Z, Lelievre V, Chao A, Waschek JA (1999) Axotomy-induced changes in pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) and PACAP receptor gene expression in the adult rat facial motor nucleus. J Neurosci Res 57(6):953–961
Huang Y, Ren GP, Xu C, Dong SF, Wang Y, Gan Y, Zhu L, Feng TY (2014) Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) as a biomarker for aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 14:479. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-479
Pettmann B, Henderson CE (1998) Neuronal cell death. Neuron 20(4):633–647
Hetman M, Kanning K, Cavanaugh JE, Xia Z (1999) Neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 274(32):22569–22580
Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME (1999) Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 286(5443):1358–1362
Heumann R, Goemans C, Bartsch D, Lingenhohl K, Waldmeier PC, Hengerer B, Allegrini PR, Schellander K, Wagner EF, Arendt T, Kamdem RH, Obst-Pernberg K, Narz F, Wahle P, Berns H (2000) Transgenic activation of Ras in neurons promotes hypertrophy and protects from lesion-induced degeneration. J Cell Biol 151(7):1537–1548
Crowder RJ, Freeman RS (1998) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt protein kinase are necessary and sufficient for the survival of nerve growth factor-dependent sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 18(8):2933–2943
Klesse LJ, Parada LF (1998) p21 ras and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase are required for survival of wild-type and NF1 mutant sensory neurons. J Neurosci 18(24):10420–10428
Creedon DJ, Johnson EM, Lawrence JC (1996) Mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent pathways mediate the effects of nerve growth factor and cAMP on neuronal survival. J Biol Chem 271(34):20713–20718
Agthong S, Koonam J, Kaewsema A, Chentanez V (2009) Inhibition of MAPK ERK impairs axonal regeneration without an effect on neuronal loss after nerve injury. Neurol Res 31(10):1068–1074. doi:10.1179/174313209X380883
Namikawa K, Honma M, Abe K, Takeda M, Mansur K, Obata T, Miwa A, Okado H, Kiyama H (2000) Akt/protein kinase B prevents injury-induced motoneuron death and accelerates axonal regeneration. J Neurosci 20(8):2875–2886
Virdee K, Tolkovsky AM (1996) Inhibition of p42 and p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity by PD98059 does not suppress nerve growth factor-induced survival of sympathetic neurones. J Neurochem 67(5):1801–1805
Yao R, Cooper GM (1995) Requirement for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by nerve growth factor. Science 267(5206):2003–2006
Skaper SD, Floreani M, Negro A, Facci L, Giusti P (1998) Neurotrophins rescue cerebellar granule neurons from oxidative stress-mediated apoptotic death: selective involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Neurochem 70(5):1859–1868
Kishino A, Nakayama C (2003) Enhancement of BDNF and activated-ERK immunoreactivity in spinal motor neurons after peripheral administration of BDNF. Brain Res 964(1):56–66
Shi TJ, Huang P, Mulder J, Ceccatelli S, Hokfelt T (2009) Expression of p-Akt in sensory neurons and spinal cord after peripheral nerve injury. Neurosignals 17(3):203–212. doi:10.1159/000210400
Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27(2):265–277
Traverse S, Gomez N, Paterson H, Marshall C, Cohen P (1992) Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade may be required for differentiation of PC12 cells. Comparison of the effects of nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Biochem J 288(Pt 2):351–355
Liu RY, Snider WD (2001) Different signaling pathways mediate regenerative versus developmental sensory axon growth. J Neurosci 21(17):RC164
Sjogreen B, Wiklund P, Ekstrom PA (2000) Mitogen activated protein kinase inhibition by PD98059 blocks nerve growth factor stimulated axonal outgrowth from adult mouse dorsal root ganglia in vitro. Neuroscience 100(2):407–416
Agthong S, Kaewsema A, Tanomsridejchai N, Chentanez V (2006) Activation of MAPK ERK in peripheral nerve after injury. BMC Neurosci 7:45. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-7-45
Jones DM, Tucker BA, Rahimtula M, Mearow KM (2003) The synergistic effects of NGF and IGF-1 on neurite growth in adult sensory neurons: convergence on the PI 3-kinase signaling pathway. J Neurochem 86(5):1116–1128
Gallo G, Letourneau PC (1998) Localized sources of neurotrophins initiate axon collateral sprouting. J Neurosci 18(14):5403–5414
Markus A, Zhong J, Snider WD (2002) Raf and akt mediate distinct aspects of sensory axon growth. Neuron 35(1):65–76
Napoli I, Noon LA, Ribeiro S, Kerai AP, Parrinello S, Rosenberg LH, Collins MJ, Harrisingh MC, White IJ, Woodhoo A, Lloyd AC (2012) A central role for the ERK-signaling pathway in controlling Schwann cell plasticity and peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo. Neuron 73(4):729–742. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.031
Ogata T, Iijima S, Hoshikawa S, Miura T, Yamamoto S, Oda H, Nakamura K, Tanaka S (2004) Opposing extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt pathways control Schwann cell myelination. J Neurosci 24(30):6724–6732. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5520-03.2004
Funding
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30872898) and Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 7132173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Liu, H., Yan, R. et al. PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK Signaling Promote Different Aspects of Neuron Survival and Axonal Regrowth Following Rat Facial Nerve Axotomy. Neurochem Res 42, 3515–3524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2399-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2399-1