Abstract
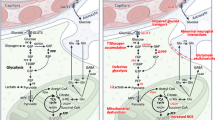
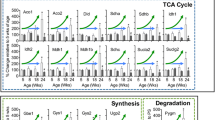
This review summarises the recent findings on metabolic treatments for epilepsy and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) in honour of Professor Ursula Sonnewald. The metabolic impairments in rodent models of these disorders as well as affected patients are being discussed. In both epilepsy and ALS, there are defects in glucose uptake and reduced tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycling, at least in part due to reduced amounts of C4 TCA cycle intermediates. In addition there are impairments in glycolysis in ALS. A reduction in glucose uptake can be addressed by providing the brain with alternative fuels, such as ketones or medium-chain triglycerides. As anaplerotic fuels, such as the triglyceride of heptanoate, triheptanoin, refill the TCA cycle C4/C5 intermediate pool that is deficient, they are ideal to boost TCA cycling and thus the oxidative metabolism of all fuels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan KN, McDonald TS, Borges K (2015) Metabolic dysfunctions in epilepsy and novel metabolic treatment approaches. In: Preedy V WR (ed) Bioactive nutraceuticals and dietary supplements in neurological and brain disease: prevention and therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 461–470
Fisher RS, van Emde Boas W, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, Engel J Jr (2005) Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International league against epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46:470–472
French JA, Kanner AM, Bautista J, Abou-Khalil B, Browne T, Harden CL, Theodore WH, Bazil C, Stern J, Schachter SC, Bergen D, Hirtz D, Montouris GD, Nespeca M, Gidal B, Marks WJ, Turk WR, Fischer JH, Bourgeois B, Wilner A, Faught RE, Sachdeo RC, Beydoun A, Glauser TA (2004) Efficacy and tolerability of the new antiepileptic drugs, I: treatment of new-onset epilepsy: report of the TTA and QSS subcommittees of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Epilepsy Society. Epilepsia 45:401–409
Mullen SA, Marini C, Suls A, Mei D, Della Giustina E, Buti D, Arsov T, Damiano J, Lawrence K, De Jonghe P, Berkovic SF, Scheffer IE, Guerrini R (2011) Glucose transporter 1 deficiency as a treatable cause of myoclonic astatic epilepsy. Arch Neurol 68:1152–1155
Scheffer IE (2012) GLUT1 deficiency: a glut of epilepsy phenotypes. Neurology 78:524–525
Zsurka G, Kunz WS (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurological disorders with epileptic phenotypes. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42:443–448
Chugani HT, Chugani DC (1999) Basic mechanisms of childhood epilepsies: studies with positron emission tomography. Adv Neurol 79:883
Kuhl DE, Engel J, Phelps ME, Selin C (1980) Epileptic patterns of local cerebral metabolism and perfusion in humans determined by emission computed tomography of 18FDG and 13NH3. Ann Neurol 8:348–360
Dube C, Boyet S, Marescaux C, Nehlig A (2001) Relationship between neuronal loss and interictal glucose metabolism during the chronic phase of the lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy in the immature and adult rat. Exp Neurol 167:227–241
Hadera MG, Smeland OB, McDonald TS, Tan KN, Sonnewald U, Borges K (2013) Triheptanoin partially restores levels of tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates in the mouse pilocarpine model of epilepsy. J Neurochem 129(1):107–119
Melo TM, Nehlig A, Sonnewald U (2005) Metabolism is normal in astrocytes in chronically epileptic rats: a (13)C NMR study of neuronal-glial interactions in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1254–1264
Smeland OB, Meisingset TW, Sonnewald U (2012) Dietary supplementation with acetyl-l-carnitine in seizure treatment of pentylenetetrazole kindled mice. Neurochem Int 61:444–454
Hadera MG, Faure JB, Berggaard N, Tefera TW, Nehlig A, Sonnewald U (2014) The anticonvulsant actions of carisbamate associate with alterations in astrocyte glutamine metabolism in the lithium-pilocarpine epilepsy model. J Neurochem 132:532–545
Smeland OB, Hadera MG, McDonald TS, Sonnewald U, Borges K (2013) Brain mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction and glutamate level reduction in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1090–1097
Barnerias C, Saudubray JM, Touati G, De Lonlay P, Dulac O, Ponsot G, Marsac C, Brivet M, Desguerre I (2010) Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency: four neurological phenotypes with differing pathogenesis. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:e1–e9
Kang HC, Kwon JW, Lee YM, Kim HD, Lee HJ, Hahn SH (2007) Nonspecific mitochondrial disease with epilepsy in children: diagnostic approaches and epileptic phenotypes. Childs Nerv Syst 23:1301–1307
Bonnefont JP, Chretien D, Rustin P, Robinson B, Vassault A, Aupetit J, Charpentier C, Rabier D, Saudubray JM, Munnich A (1992) Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase deficiency presenting as congenital lactic acidosis. J Pediatr 121:255–258
Elpeleg O, Miller C, Hershkovitz E, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Bondi-Rubinstein G, Rahman S, Pagnamenta A, Eshhar S, Saada A (2005) Deficiency of the ADP-forming succinyl-CoA synthase activity is associated with encephalomyopathy and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Am J Hum Genet 76:1081–1086
Bourgeron T, Rustin P, Chretien D, Birch-Machin M, Bourgeois M, Viegas-Pequignot E, Munnich A, Rotig A (1995) Mutation of a nuclear succinate dehydrogenase gene results in mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency. Nat Genet 11:144–149
Burgeois M, Goutieres F, Chretien D, Rustin P, Munnich A, Aicardi J (1992) Deficiency in complex II of the respiratory chain, presenting as a leukodystrophy in two sisters with Leigh syndrome. Brain Dev 14:404–408
Horváth R, Abicht A, Holinski-Feder E, Laner A, Gempel K, Prokisch H, Lochmüller H, Klopstock T, Jaksch M (2006) Leigh syndrome caused by mutations in the flavoprotein (Fp) subunit of succinate dehydrogenase (SDHA). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:74–76
Parfait B, Chretien D, Rotig A, Marsac C, Munnich A, Rustin P (2000) Compound heterozygous mutations in the flavoprotein gene of the respiratory chain complex II in a patient with Leigh syndrome. Hum Genet 106:236–243
Ezgu F, Krejci P, Wilcox WR (2013) Mild clinical presentation and prolonged survival of a patient with fumarase deficiency due to the combination of a known and a novel mutation in FH gene. Gene 524:403–406
Kerrigan JF, Aleck KA, Tarby TJ, Bird CR, Heidenreich RA (2000) Fumaric aciduria: clinical and imaging features. Ann Neurol 47:583–588
Alvestad S, Hammer J, Eyjolfsson E, Qu H, Ottersen OP, Sonnewald U (2008) Limbic structures show altered glial-neuronal metabolism in the chronic phase of kainate induced epilepsy. Neurochem Res 33:257–266
Willis S, Stoll J, Sweetman L, Borges K (2010) Anticonvulsant effects of a triheptanoin diet in two mouse chronic seizure models. Neurobiol Dis 40:565–572
Eid T, Hammer J, Runden-Pran E, Roberg B, Thomas MJ, Osen K, Davanger S, Laake P, Torgner IA, Lee TS, Kim JH, Spencer DD, Ottersen OP, de Lanerolle NC (2007) Increased expression of phosphate-activated glutaminase in hippocampal neurons in human mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 113:137–152
Wilder RM (1921) The effects of ketonemia on the course of epilepsy. Mayo Clin Proc 2:307–308
Kossoff EH, Krauss GL, McGrogan JR, Freeman JM (2003) Efficacy of the Atkins diet as therapy for intractable epilepsy. Neurology 61:1789–1791
Huttenlocher PR (1976) Ketonemia and seizures: metabolic and anticonvulsant effects of two ketogenic diets in childhood epilepsy. Pediatr Res 10:536–540
Coppola G, D’Aniello A, Messana T, Di Pasquale F, della Corte R, Pascotto A, Verrotti A (2011) Low glycemic index diet in children and young adults with refractory epilepsy: first Italian experience. Seizure 20:526–528
Muzykewicz DA, Lyczkowski DA, Memon N, Conant KD, Pfeifer HH, Thiele EA (2009) Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of the low glycemic index treatment in pediatric epilepsy. Epilepsia 50:1118–1126
Pfeifer HH, Thiele EA (2005) Low-glycemic-index treatment: a liberalized ketogenic diet for treatment of intractable epilepsy. Neurology 65:1810–1812
Neal EG, Chaffe H, Schwartz RH, Lawson MS, Edwards N, Fitzsimmons G, Whitney A, Cross JH (2008) The ketogenic diet for the treatment of childhood epilepsy: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 7:500–506
Sharma S, Sankhyan N, Gulati S, Agarwala A (2013) Use of the modified Atkins diet for treatment of refractory childhood epilepsy: a randomized controlled trial. Epilepsia 54:481–486
Martin K, Jackson CF, Levy RG, Cooper PN (2016) Ketogenic diet and other dietary treatments for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD001903
Klein P, Tyrlikova I, Mathews GC (2014) Dietary treatment in adults with refractory epilepsy: a review. Neurology 83:1978–1985
Kashiwaya Y, Pawlosky R, Markis W, King MT, Bergman C, Srivastava S, Murray A, Clarke K, Veech RL (2010) A ketone ester diet increases brain malonyl-CoA and Uncoupling proteins 4 and 5 while decreasing food intake in the normal Wistar Rat. J Biol Chem 285:25950–25956
D’Agostino DP, Pilla R, Held HE, Landon CS, Puchowicz M, Brunengraber H, Ari C, Arnold P, Dean JB (2013) Therapeutic ketosis with ketone ester delays central nervous system oxygen toxicity seizures in rats. Am J Physiol Reg Integr Comp Physiol 304:R829–R836
Viggiano A, Pilla R, Arnold P, Monda M, D’Agostino D, Coppola G (2015) Anticonvulsant properties of an oral ketone ester in a pentylenetetrazole-model of seizure. Brain Res 1618:50–54
Ciarlone SL, Grieco JC, D’Agostino DP, Weeber EJ (2016) Ketone ester supplementation attenuates seizure activity, and improves behavior and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in an Angelman syndrome mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 96:38–46
Courchesne-Loyer A, Croteau E, Castellano CA, St-Pierre V, Hennebelle M, Cunnane SC (2016) Inverse relationship between brain glucose and ketone metabolism in adults during short-term moderate dietary ketosis: A dual tracer quantitative positron emission tomography study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. doi:10.1177/0271678X16669366
Zhang Y, Kuang Y, Xu K, Harris D, Lee Z, LaManna J, Puchowicz MA (2013) Ketosis proportionately spares glucose utilization in brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1307–1311
Garriga-Canut M, Schoenike B, Qazi R, Bergendahl K, Daley TJ, Pfender RM, Morrison JF, Ockuly J, Stafstrom C, Sutula T (2006) 2-Deoxy-d-glucose reduces epilepsy progression by NRSF-CtBP–dependent metabolic regulation of chromatin structure. Nat Neurosci 9:1382–1387
Gasior M, Yankura J, Hartman AL, French A, Rogawski MA (2010) Anticonvulsant and proconvulsant actions of 2-deoxy-d-glucose. Epilepsia 51:1385–1394
Stafstrom CE, Ockuly JC, Murphree L, Valley MT, Roopra A, Sutula TP (2009) Anticonvulsant and antiepileptic actions of 2,deoxy-d-glucose in epilepsy models. Ann Neurol 65:435–447
Potter WB, O’Riordan KJ, Barnett D, Osting SM, Wagoner M, Burger C, Roopra A (2010) Metabolic regulation of neuronal plasticity by the energy sensor AMPK. PLoS One 5:e8996
Achanta LB, Rae CD (2016) β-Hydroxybutyrate in the brain: one molecule, multiple mechanisms. Neurochem Res. doi:10.1007/s11064-016-2099-2
Yudkoff M, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Horyn O, Lazarow A, Luhovyy B, Wehrli S, Nissim I (2005) Response of brain amino acid metabolism to ketosis. Neurochem Int 47:119–128
Yudkoff M, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Grunstein R, Nissim I (1997) Effects of ketone bodies on astrocyte amino acid metabolism. J Neurochem 69:682–692
Yudkoff M, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Lazarow A, Nissim I (2004) Ketogenic diet, brain glutamate metabolism and seizure control. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty acids 70:277–285
Melo TM, Nehlig A, Sonnewald U (2006) Neuronal-glial interactions in rats fed a ketogenic diet. Neurochem Int 48:498–507
Bough KJ, Rho JM (2007) Anticonvulsant mechanisms of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 48:43–58
Masino SA, Rho JM (2012) Mechanisms of ketogenic diet action. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV (eds) Jasper’s basic mechanisms of the epilepsies, 4th edn., Bethesda
Dean HG, Bonser JC, Gent JP (1989) HPLC analysis of brain and plasma for octanoic and decanoic acids. Clin Chem 35:1945–1948
Haidukewych D, Forsythe WI, Sills M (1982) Monitoring octanoic and decanoic acids in plasma from children with intractable epilepsy treated with medium-chain triglyceride diet. Clin Chem 28:642–645
Sills MA, Forsythe WI, Haidukewych D, MacDonald A, Robinson M (1986a) The medium chain triglyceride diet and intractable epilepsy. Arch Dis Child 61:1168–1172
Kuge Y, Yajima K, Kawashima H, Yamazaki H, Hashimoto N, Miyake Y (1995) Brain uptake and metabolism of [1-11C] octanoate in rats: pharmacokinetic basis for its application as a radiopharmaceutical for studying brain fatty acid metabolism. Ann Nucl Med 9:137–142
Oldendorf WH (1973) Carrier-mediated blood–brain barrier transport of short-chain monocarboxylic organic acids. Am J Physiol 224:1450–1453
Chang P, Terbach N, Plant N, Chen PE, Walker MC, Williams RS (2013) Seizure control by ketogenic diet-associated medium chain fatty acids. Neuropharmacology 69:105–114
Perlman BJ, Goldstein DB (1984) Membrane-disordering potency and anticonvulsant action of valproic acid and other short-chain fatty acids. Mol Pharmacol 26:83–89
Wlaz P, Socala K, Nieoczym D, Luszczki JJ, Zarnowska I, Zarnowski T, Czuczwar SJ, Gasior M (2012) Anticonvulsant profile of caprylic acid, a main constituent of the medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) ketogenic diet, in mice. Neuropharmacology 62:1882–1889
Wlaz P, Socala K, Nieoczym D, Zarnowski T, Zarnowska I, Czuczwar SJ, Gasior M (2015) Acute anticonvulsant effects of capric acid in seizure tests in mice. Prog NeuroPsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 57:110–116
McDonald TS, Tan KN, Hodson MP, Borges K (2014) Alterations of hippocampal glucose metabolism by even versus uneven medium chain triglycerides. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:153–160
Tan KN, Carrasco-Pozo C, McDonald TS, Puchowicz M, Borges K (2016) Tridecanoin is anticonvulsant, antioxidant, and improves mitochondrial function. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. doi:10.1177/0271678X16659498
Edmond J, Robbins R, Bergstrom J, Cole R, De Vellis J (1987) Capacity for substrate utilization in oxidative metabolism by neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes from developing brain in primary culture. J Neurosci Res 18:551–561
Cremer JE, Teal HM, Heath DF, Cavanagh JB (1977) The Influence of portocaval anastomosis on the metabolism of labeled octanoate, butyrate and leucine in rat brain. J Neurochem 28:215–222
Ebert D, Haller RG, Walton ME (2003) Energy contribution of octanoate to intact rat brain metabolism measured by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurosci 23:5928–5935
Roe CR, Mochel F (2006) Anaplerotic diet therapy in inherited metabolic disease: therapeutic potential. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:332–340
Vockley J, Marsden D, McCracken E, DeWard S, Barone A, Hsu K, Kakkis E (2015) Long-term major clinical outcomes in patients with long chain fatty acid oxidation disorders before and after transition to triheptanoin treatment: a retrospective chart review. Mol Genet Metab 116:53–60
Mochel F, Duteil S, Marelli C, Jauffret C, Barles A, Holm J, Sweetman L, Benoist JF, Rabier D, Carlier PG, Durr A (2010) Dietary anaplerotic therapy improves peripheral tissue energy metabolism in patients with Huntington’s disease. Eur J Hum Genet 18:1057–1060
Adanyeguh IM, Rinaldi D, Henry PG, Caillet S, Valabregue R, Durr A, Mochel F (2015) Triheptanoin improves brain energy metabolism in patients with Huntington disease. Neurology 84(5):490–495
Mochel F, Hainque E, Gras D, Adanyeguh IM, Caillet S, Heron B, Roubertie A, Kaphan E, Valabregue R, Rinaldi D, Vuillaumier S, Schiffmann R, Ottolenghi C, Hogrel JY, Servais L, Roze E (2016) Triheptanoin dramatically reduces paroxysmal motor disorder in patients with GLUT1 deficiency. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87:550–553
Pascual JM, Liu P, Mao D, Kelly DI, Hernandez A, Sheng M, Good LB, Ma Q, Marin-Valencia I, Zhang X, Park JY, Hynan LS, Stavinoha P, Roe CR, Lu H (2014) Triheptanoin for glucose transporter type I deficiency (G1D): modulation of human ictogenesis, cerebral metabolic rate, and cognitive indices by a food supplement. JAMA Neurol 71:1255–1265
Marin-Valencia I, Good LB, Ma Q, Malloy CR, Pascual JM (2013) Heptanoate as a neural fuel: energetic and neurotransmitter precursors in normal and glucose transporter I-deficient (G1D) brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:175–182
Kinman RP, Kasumov T, Jobbins KA, Thomas KR, Adams JE, Brunengraber LN, Kutz G, Brewer WU, Roe CR, Brunengraber H (2006) Parenteral and enteral metabolism of anaplerotic triheptanoin in normal rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E860–E866
Brunengraber H, Roe CR (2006) Anaplerotic molecules: current and future. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:327–331
Kim TH, Borges K, Petrou S, Reid CA (2013) Triheptanoin reduces seizure susceptibility in a syndrome-specific mouse model of generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 103:101–105
Thomas NK, Willis S, Sweetman L, Borges K (2012) Triheptanoin in acute mouse seizure models. Epilepsy Res 99:312–317
Baumer D, Talbot K, Turner MR (2014) Advances in motor neurone disease. J R Soc Med 107:14–21
Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A, Donaldson D, Goto J, O’Regan JP, Deng HX et al (1993) Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362:59–62
Kabashi E, Valdmanis PN, Dion P, Spiegelman D, McConkey BJ, Vande Velde C, Bouchard JP, Lacomblez L, Pochigaeva K, Salachas F, Pradat PF, Camu W, Meininger V, Dupre N, Rouleau GA (2008) TARDBP mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 40:572–574
Kwiatkowski TJ Jr, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL, Tamrazian E, Vanderburg CR, Russ C, Davis A, Gilchrist J, Kasarskis EJ, Munsat T, Valdmanis P, Rouleau GA, Hosler BA, Cortelli P, de Jong PJ, Yoshinaga Y, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Yan J, Ticozzi N, Siddique T, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Horvitz HR, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323:1205–1208
Deng HX, Chen W, Hong ST, Boycott KM, Gorrie GH, Siddique N, Yang Y, Fecto F, Shi Y, Zhai H, Jiang H, Hirano M, Rampersaud E, Jansen GH, Donkervoort S, Bigio EH, Brooks BR, Ajroud K, Sufit RL, Haines JL, Mugnaini E, Pericak-Vance MA, Siddique T (2011) Mutations in UBQLN2 cause dominant X-linked juvenile and adult-onset ALS and ALS/dementia. Nature 477:211–215
DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Nicholson AM, Finch NA, Flynn H, Adamson J, Kouri N, Wojtas A, Sengdy P, Hsiung GY, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Josephs KA, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Wszolek ZK, Feldman H, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Dickson DW, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R (2011) Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 72:245–256
Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simon-Sanchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Schymick JC, Laaksovirta H, van Swieten JC, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Mok K, Ryten M, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister JB, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita VM, Kaivorinne AL, Holtta-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chio A, Restagno G, Borghero G, Sabatelli M, Consortium I, Heckerman D, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rothstein JD, Sendtner M, Drepper C, Eichler EE, Alkan C, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Dutra A, Pak E, Hardy J, Singleton A, Williams NM, Heutink P, Pickering-Brown S, Morris HR, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ (2011) A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 72:257–268
Rothstein JD, Tsai G, Kuncl RW, Clawson L, Cornblath DR, Drachman DB, Pestronk A, Stauch BL, Coyle JT (1990) Abnormal excitatory amino acid metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 28:18–25
Bruijn LI, Houseweart MK, Kato S, Anderson KL, Anderson SD, Ohama E, Reaume AG, Scott RW, Cleveland DW (1998) Aggregation and motor neuron toxicity of an ALS-linked SOD1 mutant independent from wild-type SOD1. Science 281:1851–1854
Julien JP, Beaulieu JM (2000) Cytoskeletal abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: beneficial or detrimental effects? J Neurol Sci 180:7–14
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2002) Inflammatory processes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 26:459–470
Barber SC, Mead RJ, Shaw PJ (2006) Oxidative stress in ALS: a mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:1051–1067
Nagai M, Re DB, Nagata T, Chalazonitis A, Jessell TM, Wichterle H, Przedborski S (2007) Astrocytes expressing ALS-linked mutated SOD1 release factors selectively toxic to motor neurons. Nat Neurosci 10:615–622
Dupuis L, Oudart H, Rene F, Gonzalez de Aguilar JL, Loeffler JP (2004) Evidence for defective energy homeostasis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: benefit of a high-energy diet in a transgenic mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11159–11164
Dupuis L, Pradat PF, Ludolph AC, Loeffler JP (2011) Energy metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 10:75–82
Paganoni S, Deng J, Jaffa M, Cudkowicz ME, Wills AM (2011) Body mass index, not dyslipidemia, is an independent predictor of survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 44:20–24
Korner S, Hendricks M, Kollewe K, Zapf A, Dengler R, Silani V, Petri S (2013) Weight loss, dysphagia and supplement intake in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): impact on quality of life and therapeutic options. BMC Neurol 13:84
Desport JC, Preux PM, Magy L, Boirie Y, Vallat JM, Beaufrere B, Couratier P (2001) Factors correlated with hypermetabolism in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Clin Nutr 74:328–334
Dalakas MC, Hatazawa J, Brooks RA, Di Chiro G (1987) Lowered cerebral glucose utilization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 22:580–586
Hatazawa J, Brooks RA, Dalakas MC, Mansi L, Di Chiro G (1988) Cortical motor-sensory hypometabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a PET study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12:630–636
Ludolph AC, Langen KJ, Regard M, Herzog H, Kemper B, Kuwert T, Bottger IG, Feinendegen L (1992) Frontal lobe function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a neuropsychologic and positron emission tomography study. Acta Neurol Scand 85:81–89
Browne SE, Yang L, DiMauro JP, Fuller SW, Licata SC, Beal MF (2006) Bioenergetic abnormalities in discrete cerebral motor pathways presage spinal cord pathology in the G93A SOD1 mouse model of ALS. Neurobiol Dis 22:599–610
Cistaro A, Valentini MC, Chio A, Nobili F, Calvo A, Moglia C, Montuschi A, Morbelli S, Salmaso D, Fania P, Carrara G, Pagani M (2012) Brain hypermetabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a FDG PET study in ALS of spinal and bulbar onset. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:251–259
Niessen HG, Debska-Vielhaber G, Sander K, Angenstein F, Ludolph AC, Hilfert L, Willker W, Leibfritz D, Heinze HJ, Kunz WS, Vielhaber S (2007) Metabolic progression markers of neurodegeneration in the transgenic G93A-SOD1 mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci 25:1669–1677
Wiedemann FR, Manfredi G, Mawrin C, Beal MF, Schon EA (2002) Mitochondrial DNA and respiratory chain function in spinal cords of ALS patients. J Neurochem 80:616–625
Jung C, Higgins CM, Xu Z (2002) Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 83:535–545
Mattiazzi M, D’Aurelio M, Gajewski CD, Martushova K, Kiaei M, Beal MF, Manfredi G (2002) Mutated human SOD1 causes dysfunction of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 277:29626–29633
Menzies FM, Cookson MR, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM, Dong L, Figlewicz DA, Shaw PJ (2002) Mitochondrial dysfunction in a cell culture model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 125:1522–1533
Rothstein JD, Martin LJ, Kuncl RW (1992) Decreased glutamate transport by the brain and spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 326:1464–1468
Rothstein JD, Van Kammen M, Levey AI, Martin LJ, Kuncl RW (1995) Selective loss of glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 38:73–84
Clement AM, Nguyen MD, Roberts EA, Garcia ML, Boillee S, Rule M, McMahon AP, Doucette W, Siwek D, Ferrante RJ, Brown RH Jr, Julien JP, Goldstein LS, Cleveland DW (2003) Wild-type nonneuronal cells extend survival of SOD1 mutant motor neurons in ALS mice. Science 302:113–117
Ngo S, Steyn F, McCombe P, Borges K (2015) High caloric diets for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: RWaV Preedy (ed) Bioactive nutraceuticals and dietary supplements in neurological and brain disease: prevention and therapy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 461–470
Holness MJ, Sugden MC (2003) Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity by reversible phosphorylation. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1143–1151
Miquel E, Cassina A, Martinez-Palma L, Bolatto C, Trias E, Gandelman M, Radi R, Barbeito L, Cassina P (2012) Modulation of astrocytic mitochondrial function by dichloroacetate improves survival and motor performance in inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 7:e34776
Zhao Z, Lange DJ, Voustianiouk A, MacGrogan D, Ho L, Suh J, Humala N, Thiyagarajan M, Wang J, Pasinetti GM (2006) A ketogenic diet as a potential novel therapeutic intervention in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Neurosci 7:29
Zhao W, Varghese M, Vempati P, Dzhun A, Cheng A, Wang J, Lange D, Bilski A, Faravelli I, Pasinetti GM (2012) Caprylic triglyceride as a novel therapeutic approach to effectively improve the performance and attenuate the symptoms due to the motor neuron loss in ALS disease. PloS one 7:e49191
Group AL, Fournier C, Bedlack B, Hardiman O, Heiman-Patterson T, Gutmann L, Bromberg M, Ostrow L, Carter G, Kabashi E, Bertorini T, Mozaffar T, Andersen P, Dietz J, Gamez J, Dimachkie M, Wang Y, Wicks P, Heywood J, Novella S, Rowland LP, Pioro E, Kinsley L, Mitchell K, Glass J, Sathornsumetee S, Kwiecinski H, Baker J, Atassi N, Forshew D, Ravits J, Conwit R, Jackson C, Sherman A, Dalton K, Tindall K, Gonzalez G, Robertson J, Phillips L, Benatar M, Sorenson E, Shoesmith C, Nash S, Maragakis N, Moore D, Caress J, Boylan K, Armon C, Grosso M, Gerecke B, Wymer J, Oskarsson B, Bowser R, Drory V, Shefner J, Lechtzin N, Leitner M, Miller R, Mitsumoto H, Levine T, Russell J, Sharma K, Saperstein D, McClusky L, MacGowan D, Licht J, Verma A, Strong M, Lomen-Hoerth C, Tandan R, Rivner M, Kolb S, Polak M, Rudnicki S, Kittrell P, Quereshi M, Sachs G, Pattee G, Weiss M, Kissel J, Goldstein J, Rothstein J, Pastula D, Gleb L, Ogino M, Rosenfeld J, Carmi E, Oster C, Barkhaus P, Valor E (2013) ALS Untangled No. 20: the Deanna protocol. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 14:319–323
Ari C, Poff AM, Held HE, Landon CS, Goldhagen CR, Mavromates N, D’Agostino DP (2014) Metabolic therapy with Deanna protocol supplementation delays disease progression and extends survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) mouse model. PLoS One 9:e103526
Tefera TW, Wong Y, Barkl-Luke ME, Ngo ST, Thomas NK, McDonald TS, Borges K (2016) Triheptanoin protect motor neurons and delays symptom onset in a mouse model of ALS model. PLOS One 11(8):e0161816
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for scholarships from UQ international scholarships (KNT, TWT) and APA (TSM) and funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (Grant 1044007 to KB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KB has filed for patents for the use of triheptanoin in seizure disorders and ALS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tefera, T.W., Tan, K.N., McDonald, T.S. et al. Alternative Fuels in Epilepsy and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurochem Res 42, 1610–1620 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2106-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2106-7