Abstract
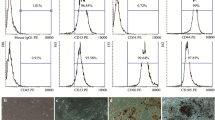
Evidence suggests that apoptosis contributes significantly to cell death after cerebral ischemia. Our recent studies that utilized human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUCBSCs) demonstrated the potential of hUCBSCs to inhibit neuronal apoptosis in a rat model of CNS injury. Therefore, we hypothesize that intravenous administration of hUCBSCs after focal cerebral ischemia would reduce brain damage by inhibiting apoptosis and downregulating the upregulated apoptotic pathway molecules. Male Sprague–Dawley rats were obtained and randomly assigned to various groups. After the animals reached a desired weight, they were subjected to a 2 h middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) procedure followed by 7 days of reperfusion. The hUCBSCs were obtained, cultured, and intravenously injected (0.25 × 106 cells or 1 × 106 cells) via the tail vein to separate groups of animals 24 h post-MCAO procedure. We performed various techniques including PCR microarray, hematoxylin and eosin, and TUNEL staining in addition to immunoblot and immunofluorescence analysis in order to investigate the effect of our treatment on regulation of apoptosis after focal cerebral ischemia. Most of the apoptotic pathway molecules which were upregulated after focal cerebral ischemia were downregulated after hUCBSCs treatment. Further, the staining techniques revealed a prominent reduction in brain damage and the extent of apoptosis at even the lowest dose of hUCBSCs tested in the present study. In conclusion, our treatment with hUCBSCs after cerebral ischemia in the rodent reduces brain damage by inhibiting apoptosis and downregulating the apoptotic pathway molecules.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner RC, Dodson SC, Rosen CL, Huber JD (2013) The science of cerebral ischemia and the quest for neuroprotection: navigating past failure to future success. J Neurosurg 118:1072–1085
Banerjee S, Williamson D, Habib N, Gordon M, Chataway J (2011) Human stem cell therapy in ischaemic stroke: a review. Age Ageing 40:7–13
Sinden JD, Vishnubhatla I, Muir KW (2012) Prospects for stem cell-derived therapy in stroke. Prog Brain Res 201:119–167
Buhnemann C, Scholz A, Bernreuther C, Malik CY, Braun H, Schachner M et al (2006) Neuronal differentiation of transplanted embryonic stem cell-derived precursors in stroke lesions of adult rats. Brain 129:3238–3248
Hicks A, Jolkkonen J (2009) Challenges and possibilities of intravascular cell therapy in stroke. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 69:1–11
Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, Lee PH, Ahn YH, Bang OY (2010) A long-term follow-up study of intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells 28:1099–1106
Veeravalli KK, Dasari VR, Fassett D, Dinh DH, Rao JS (2011) Human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells upregulate myelin basic protein in shiverer mice. Stem Cells Dev 20:881–891
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Willing AE et al (2001) Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 32:2682–2688
Vendrame M, Cassady J, Newcomb J, Butler T, Pennypacker KR, Zigova T et al (2004) Infusion of human umbilical cord blood cells in a rat model of stroke dose-dependently rescues behavioral deficits and reduces infarct volume. Stroke 35:2390–2395
Chung DJ, Choi CB, Lee SH, Kang EH, Lee JH, Hwang SH et al (2009) Intraarterially delivered human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in canine cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 87:3554–3567
Riegelsberger UM, Deten A, Posel C, Zille M, Kranz A, Boltze J et al (2011) Intravenous human umbilical cord blood transplantation for stroke: impact on infarct volume and caspase-3-dependent cell death in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Neurol 227:218–223
Lim JY, Jeong CH, Jun JA, Kim SM, Ryu CH, Hou Y et al (2011) Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells after intrathecal administration by lumbar puncture in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Stem Cell Res Ther 2:38
Kim ES, Ahn SY, Im GH, Sung DK, Park YR, Choi SH et al (2012) Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates severe brain injury by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in newborn rats. Pediatr Res 72:277–284
Dasari VR, Veeravalli KK, Tsung AJ, Gondi CS, Gujrati M, Dinh DH et al (2009) Neuronal apoptosis is inhibited by cord blood stem cells after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 26:2057–2069
Chelluboina B, Klopfenstein JD, Gujrati M, Rao JS, Veeravalli KK (2014) Temporal regulation of apoptotic and anti-apoptotic molecules after middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by reperfusion. Mol Neurobiol 49:50–65
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:e331–e339
Yuan J (2009) Neuroprotective strategies targeting apoptotic and necrotic cell death for stroke. Apoptosis 14:469–477
Akpan N, Serrano-Saiz E, Zacharia BE, Otten ML, Ducruet AF, Snipas SJ et al (2011) Intranasal delivery of caspase-9 inhibitor reduces caspase-6-dependent axon/neuron loss and improves neurological function after stroke. J Neurosci 31:8894–8904
Dasari VR, Spomar DG, Gondi CS, Sloffer CA, Saving KL, Gujrati M et al (2007) Axonal demyelination by cord blood stem cells after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 24:391–410
Dasari VR, Spomar DG, Li L, Gujrati M, Rao JS, Dinh DH (2008) Umbilical cord blood stem cell mediated downregulation of Fas improves functional recovery of rats after spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res 33:134–149
Veeravalli KK, Dasari VR, Tsung AJ, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, Fassett D et al (2009) Human umbilical cord blood stem cells upregulate matrix metalloproteinase-2 in rats after spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis 36:200–212
Loddick SA, MacKenzie A, Rothwell NJ (1996) An ICE inhibitor, z-VAD-DCB attenuates ischaemic brain damage in the rat. NeuroReport 7:1465–1468
Hara H, Friedlander RM, Gagliardini V, Ayata C, Fink K, Huang Z et al (1997) Inhibition of interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme family proteases reduces ischemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2007–2012
Endres M, Namura S, Shimizu-Sasamata M, Waeber C, Zhang L, Gomez-Isla T et al (1998) Attenuation of delayed neuronal death after mild focal ischemia in mice by inhibition of the caspase family. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:238–247
Cheng Y, Deshmukh M, D’Costa A, Demaro JA, Gidday JM, Shah A et al (1998) Caspase inhibitor affords neuroprotection with delayed administration in a rat model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Clin Invest 101:1992–1999
Krupinski J, Lopez E, Marti E, Ferrer I (2000) Expression of caspases and their substrates in the rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 7:332–342
Li H, Colbourne F, Sun P, Zhao Z, Buchan AM, Iadecola C (2000) Caspase inhibitors reduce neuronal injury after focal but not global cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 31:176–182
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1999) Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10964–10967
Thorburn A (2004) Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 16:139–144
Acknowledgments
We thank Noorjehan Ali for technical assistance, Debbie McCollum for manuscript preparation, and Diana Meister for manuscript review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chelluboina, B., Klopfenstein, J.D., Pinson, D.M. et al. Stem Cell Treatment After Cerebral Ischemia Regulates the Gene Expression of Apoptotic Molecules. Neurochem Res 39, 1511–1521 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1341-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1341-z