Abstract
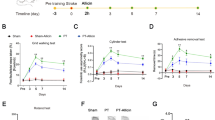
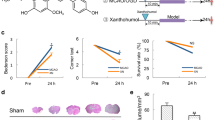
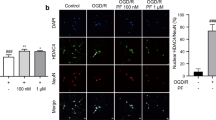
An herb-derived phenolic compound, 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol (4-HBA), exhibits beneficial effects in cerebral ischemic injury. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this observation remain unclear. Here we used an in vitro ischemic model of oxygen–glucose deprivation followed by reperfusion (OGD/R) and an in vivo ischemic model of middle cerebral artery occlusion to investigate the relevant neuroprotective mechanisms. We demonstrated that 4-HBA reduced the neuronal injury, LDH release, and up-regulation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) induced by OGD/R. Furthermore, 4-HBA reduced the cerebral infarct size and improved the behavioral parameters after cerebral ischemia. These neuroprotective effects may be conferred by the 4-HBA mediated upregulation of the transcription factor nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), peroxiredoxin 6 (Prdx6) and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) by the use of 4-HBA. Interestingly, LY294002, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, blocked the increase in phosphorylation of Akt and abolished the neuroprotection associated with 4-HBA. Our results suggested that 4-HBA protects neurons against cerebral ischemic injury, and this neuroprotection may occur through upregulation of Nrf2, Prdx6, and PDI expression via the PI3K/Akt pathway.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang T, Gu J, Wu PF et al (2009) Protection by tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against cerebral ischemia: involvement of JNK, SIRT1, and NF-κB pathways and inhibition of intracellular ROS/RNS generation. Free Radic Biol Med 47:229–240
Doyle KP, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP (2008) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 55:310–318
Ahsan H, Ali A, Ali R (2003) Oxygen free radicals and systemic autoimmunity. Clin Exp Immunol 131:398–404
Das L, Vinayak M (2011) Anticarcinogenic action of curcumin by activation of antioxidant defence system and inhibition of NF-κB signaling in lymphoma bearing mice. Biosci Rep 32:161–170
Danilov CA, Chandrasekaran K, Racz J et al (2009) Sulforaphane protects astrocytes against oxidative stress and delayed death caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation. Glia 57:645–656
Kam KY, Yu SJ, Jeong N et al (2011) P-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol prevents brain injury and behavioral impairment by activating Nrf2, PDI, and neurotrophic factor genes in a rat model of brain ischemia. Mol Cells 31:209–215
Descamps E, Petrault-Laprais M, Maurois P et al (2009) Experimental stroke protection induced by 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol is cancelled by bacitracin. Neurosci Res 64:137–142
Kim HJ, Hwang IK, Won MH (2007) Vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzyl aldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol prevent hippocampal CA1 cell death following global ischemia. Brain Res 1181:130–141
Yu SS, Zhao J, Lei SP et al (2011) 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol ameliorates cerebral injury in rats by antioxidant action. Neurochem Res 36:339–346
Yu SJ, Kim JR, Lee CK et al (2005) Gastrodia elata blume and an active component, p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol reduce focal ischemic brain injury through antioxidant related gene expressions. Biol Pharm Bull 28:1016–1020
Gu J, Sun X, Wang G et al (2011) Icariside II enhances Nrf2 nuclear translocation to upregulate phase II detoxifying enzyme expression coupled with the ERK, Akt and JNK signaling pathways. Molecules 16:9234–9244
Hwang YP, Jeong HG (2010) “Ginsenoside Rb1 protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by increasing heme oxygenase-1 expression through an estrogen receptor-related PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway in human dopaminergic cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 242(1):18–28
Calkins MJ, Johnson DA, Townsend JA et al (2009) The Nrf2/ARE pathway as a potential therapeutic target in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:497–508
Alfieri A, Srivastava S, Siow RC et al (2011) Targeting the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant defence pathway for neurovascular protection in stroke. J Physiol 589:4125–4136
Fisher AB (2011) Peroxiredoxin 6: a bifunctional enzyme with gutathione peroxidase and phospholipase A2 activities. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:831–844
Tasanen K, Oikarinen J, Kivirikko K et al (1992) Promoter of the gene for the multifunctional protein disulfide isomerase polypeptide. J Biol Chem 267:11513–11519
Hwang YP, Jeong HG (2008) The coffee diterpene kahweol induces heme oxygenase-1 via the PI3K and p38/Nrf2 pathway to protect human dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxydopamine-derived oxidative stress. FEBS Lett 582:2655–2662
Papaiahgari S, Zhang Q, Kleeberger SR et al (2006) Hyperoxia stimulates an Nrf2-ARE transcriptional response via ROS-EGFR-PI3K-Akt/ERK MAP kinase signaling in pulmonary epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:43–52
Nakaso K, Yano H, Fukuhara Y et al (2003) PI3K is a key molecule in the Nrf2-mediated regulation of antioxidative proteins by hemin in human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett 546:181–184
Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT (2003) Erk activation is required for Nrf2 nuclear localization during pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate induction of glutamate cysteine ligase modulatory gene expression in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Sci 73:124–134
Ge QF, Hu X, Ma ZQ et al (2007) Baicalin attenuates oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced injury via inhibiting NMDA receptor-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activation in rat cortical neurons. Pharmacol Res 55:148–157
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S et al (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Yu SS, Zhao J, Zheng WP et al (2010) Neuroprotective effect of 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol against transient focal cerebral ischemia via anti-apoptosis in rats. Brain Res 1308:167–175
Chowdhury I, Mo Y, Gao L et al (2009) Oxidant stress stimulates expression of the human peroxiredoxin 6 gene by a transcriptional mechanism involving an antioxidant response element. Free Radic Biol Med 46:146–153
Jung TY, Suh SI, Lee H et al (2007) Protective effects of several components of Gastrodia elata on lipid peroxidation in gerbil brain homogenates. Phytother Res 21:960–964
Hsieh MT, Wu CR, Hsieh CC (1998) Ameliorating effect of p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol on cycloheximide-induced impairment of passive avoidance response in rats: interactions with compounds acting at 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:337–343
Mishima K, Hayakawa K, Abe K et al (2005) Cannabidiol prevents cerebral infarction via a serotonergic 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor-dependentmechanism. Stroke 36:1077–1082
Parsons CG, Stoffler A, Danysz W (2007) Memantine: a NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system–too little activation is bad, too much is even worse. Neuropharmacology 53:699–723
Soriano FX, Papadia S, Hofmann F et al (2006) Preconditioning doses of NMDA promote neuroprotection by enhancing neuronal excitability. J Neurosci 26:4509–4518
Shibata M, Yamawaki T, Sasaki T et al (2002) Upregulation of Akt phosphorylation at the early stage of middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 942:1–10
Rosenbaum S, Ringseis R, Hillen S et al (2012) The stress signalling pathway nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 is activated in the liver of sows during lactation. Acta Vet Scand 54:59
Manevich Y, Sweitzer T, Pak JH et al (2002) 1-Cys peroxiredoxin overexpression protects cells against phospholipid peroxidation-mediated membrane damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11599–11604
Gruber CW, Cemazar M, Heras B et al (2006) Protein disulfide isomerase: the structure of oxidative folding. Trends Biochem Sci 31:455–464
Uehara T, Nakamura T, Yao D et al (2006) S-Nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature 441:513–517
Barati MT, Rane MJ, Klein JB et al (2006) A proteomic screen identified stress-induced chaperone proteins as targets of Akt phosphorylation in mesangial cells. J Proteome Res 5:1636–1646
Huang NK, Lin YL, Cheng JJ et al (2004) Gastrodia elata prevents rat pheochromocytoma cells from serum-deprived apoptosis: the role of the MAPK family. Life Sci 75:1649–1657
Meller R, Minami M, Cameron JA et al (2005) CREB-mediated Bcl-2 protein expression after ishchemic preconditioning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:234–246
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81070917 and 81271460). The authors wish to thank Dr. Xiu-Wu Bian and Dr You-Hong Cui (Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China) for their support and advice in the cell culture experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, S., Zhao, J., Wang, X. et al. 4-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Confers Neuroprotection Through Up-Regulation of Antioxidant Protein Expression. Neurochem Res 38, 1501–1516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1052-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1052-x