Abstract
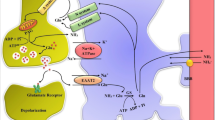
Brain edema is a severe clinical complication in a number of pathologies and is a major cause of increased morbidity and death. The swelling of astrocytes caused by a disruption of water and ion homeostasis, is the primary event contributing to the cytotoxic form of brain edema. Astrocyte cytotoxic swelling ultimately leads to transcapillary fluxes of ions and water into the brain parenchyma. This review focuses on the implication of transporters and channels in cytotoxic astrocyte swelling in hyponatremia, ischemia, trauma and hepatic encephalopathy. Emphasis is put on some salient features of the astrocyte physiology, all related to cell swelling, i.e. predominance of aquaporins, control of K+ homeostasis and ammonia accumulation during the brain ammonia-detoxifying process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walz W (2000) Role of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extra-cellular potassium. Neurochem Int 36:291–300
Leis JA, Bekar LK, Walz W (2005) Potassium homeostasis in the ischemic brain. Glia 50:407–416
Kofuji P, Newman EA (2004) Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 129:1045–1056
Päsler D, Gabriel S, Heinemann U (2007) Two-pore-domain potassium channels contribute to neuronal potassium release and glial potassium buffering in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1173:14–26
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85(2):423–493
Sun D, Kintner D, Pond BB (2009) The role of cation-chloride cotransporters in brain ischemia. In: Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Delpire E (eds) Physiology and pathology of chloride transporters and channels in the nervous system, 1st edn. Elsevier, San Diego, CA, pp 501–517
Kahle KT, Simard JM, Staley KJ, Nahed BV, Jones PS, Sun D (2009) Molecular mechanisms of ischemic cerebral edema: role of electroneutral ion transport. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:257–265
Jayakumar AR, Norenberg MD (2010) The Na-K-Cl Co-transporter in astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 25:31–38
Yan Y, Dempsey RJ, Flemmer A, Forbush B, Sun D (2003) Inhibition of Na+-K+-Cl− cotransporter during focal cerebral ischemia decreases edema and neuronal damage. Brain Res 961:22–31
Chen H, Luo J, Kintner DB, Shull GE, Sun D (2005) Na+-dependent chloride transporter (NKCC1)-null mice exhibit less gray and white matter damage after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:54–66
Su G, Kintner DB, Sun D (2002) Contribution of Na+-K+-Cl− cotransporter to high-[K+](o)-induced swelling and EAA release in astrocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1136–C1146
Vázquez-Juárez E, Hernández-Benítez R, López-Domínguez A, Pasantes-Morales H (2009) Thrombin potentiates D-aspartate efflux from cultured astrocytes under conditions of K+ homeostasis disruption. J Neurochem 111:1398–1408
Su G, Kintner DB, Flagella M, Shull GE, Sun D (2002) Astrocytes from Na(+)-K(+)-Cl(−) cotransporter-null mice exhibit absence of swelling and decrease in EAA release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1147–C1160
Koyama Y, Ishibashi T, Okamoto T, Matsuda T, Hashimoto H, Baba A (2000) Transient treatments with L-glutamate and threo-beta-hydroxyaspartate induce swelling of rat cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Int 36:167–173
Marmarou A (2003) Pathophysiology of traumatic brain edema: current concepts. Acta Neurochir Suppl 86:7–10
Jayakumar AR, Rao KV, Panickar KS, Moriyama M, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) Trauma-induced cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:417–427
Migliati E, Meurice N, DuBois P, Fang JS, Somasekharan S, Beckett E, Flynn G, Yool AJ (2009) Inhibition of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 water permeability by a derivative of the loop diuretic bumetanide acting at an internal pore-occluding binding site. Mol Pharmacol 76:105–112
Benesova J, Rusnakova V, Honsa P, Pivonkova H, Dzamba D, Kubista M, Anderova M (2012) Distinct expression/function of potassium and chloride channels contributes to the diverse volume regulation in cortical astrocytes of GFAP/EGFP mice. PLoS ONE 7:e29725
Chen M, Simard JM (2001) Cell swelling and a nonselective cation channel regulated by internal Ca2+ and ATP in native reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain. J Neurosci 21:6512–6521
Simard JM, Kahle KT, Gerzanich V (2010) Molecular mechanisms of microvascular failure in central nervous system injury—synergistic roles of NKCC1 and SUR1/TRPM4. J Neurosurg 113:622–629
Simard JM, Chen M, Tarasov KV, Bhatta S, Ivanova S, Melnitchenko L, Tsymbalyuk N, West GA, Gerzanich V (2006) Newly expressed SUR1-regulated NC(Ca-ATP) channel mediates cerebral edema after ischemic stroke. Nat Med 12:433–440
Simard JM, Yurovsky V, Tsymbalyuk N, Melnichenko L, Ivanova S, Gerzanich V (2009) Protective effect of delayed treatment with low-dose glibenclamide in three models of ischemic stroke. Stroke 40:604–609
Simard JM, Kilbourne M, Tsymbalyuk O, Tosun C, Caridi J, Ivanova S, Keledjian K, Bochicchio G, Gerzanich V (2009) Key role of sulfonylurea receptor 1 in progressive secondary hemorrhage after brain contusion. J Neurotrauma 26:2257–2267
Simard JM, Woo SK, Bhatta S, Gerzanich V (2008) Drugs acting on SUR1 to treat CNS ischemia and trauma. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:42–49
Norenberg MD, Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Panickar KS (2007) New concepts in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 22:219–234
Vaquero J, Butterworth RF (2007) Mechanisms of brain edema in acute liver failure and impact of novel therapeutic interventions. Neurol Res 29:683–690
Chastre A, Jiang W, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF (2010) Ammonia and proinflammatory cytokines modify expression of genes coding for astrocytic proteins implicated in brain edema in acute liver failure. Metab Brain Dis 25:17–21
Jayakumar AR, Liu M, Moriyama M, Ramakrishnan R, Forbush B III, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) Na-K-Cl Cotransporter-1 in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. J Biol Chem 283:33874–33882
Sinke AP, Jayakumar AR, Panickar KS, Moriyama M, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) NFkappaB in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in culture. J Neurochem 106:2302–2311
Lichter-Konecki U, Mangin JM, Gordish-Dressman H, Hoffman EP, Gallo V (2008) Gene expression profiling of astrocytes from hyperammonemic mice reveals altered pathways for water and potassium homeostasis in vivo. Glia 56:365–377
Obara-Michlewska M, Pannicke T, Karl A, Bringmann A, Reichenbach A, Szeliga M, Hilgier W, Wrzosek A, Szewczyk A, Albrecht J (2011) Down-regulation of Kir4.1 in the cerebral cortex of rats with liver failure and in cultured astrocytes treated with glutamine: Implications for astrocytic dysfunction in hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurosci Res 89:2018–2027
Obara-Michlewska M, Jiang H, Aschner M, Albrecht J (2010) Gain of function of Kir4.1 channel increases cell resistance to changes of potassium fluxes and cell volume evoked by ammonia and hypoosmotic stress. Pharmacol Rep 62:1237–1242
Jalan R, Olde Damink SW, Hayes PC, Deutz NE, Lee A (2004) Pathogenesis of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: inflammation, ammonia and cerebral blood flow. J Hepatol 41:613–620
Skowrońska M, Albrecht J (2012) Alterations of blood brain barrier function in hyperammonemia: an overview. Neurotox Res 21:236–244
Okada Y, Sato K, Toychiev AH, Suzuki M, Dutta AK, Inoue H, Sabirov RZ (2009) The puzzles of volume-activated anion channels. In: Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Delpire E (eds) Physiology and pathology of chloride transporters and channels in the nervous system, 1st edn. Elsevier, San Diego, CA, pp 283–306
Jalonen T (1993) Single-channel characteristics of the large-conductance anion channel in rat cortical astrocytes in primary culture. Glia 9:227–237
Liu HT, Toychiev AH, Takahashi N, Sabirov RZ, Okada Y (2008) Maxi-anion channel as a candidate pathway for osmosensitive ATP release from mouse astrocytes in primary culture. Cell Res 18:558–565
Tait MJ, Saadoun S, Bell BA, Papadopoulos MC (2008) Water movements in the brain: role of aquaporins. Trends Neurosci 31:37–43
Neely JD, Christensen BM, Nielsen S, Agre P (1999) Heterotetrameric composition of aquaporin-4 water channels. Biochemistry 38:911156–911163
Nagelhus EA, Lehmann A, Ottersen OP (1993) Neuronal-glial exchange of taurine during hypo-osmotic stress: a combined immunocytochemical and biochemical analysis in rat cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience 54:615–631
Vajda Z, Promeneur D, Dóczi T, Sulyok E, Frøkiaer J, Ottersen OP, Nielsen S (2000) Increased aquaporin-4 immunoreactivity in rat brain in response to systemic hyponatremia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:495–503
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6:159–163
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP (2004) Alphasyntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but not endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J 18:542–544
Nicchia GP, Frigeri A, Liuzzi GM, Santacroce MP, Nico B, Procino G, Quondamatteo F, Herken R, Roncali L, Svelto M (2000) Aquaporin-4-containing astrocytes sustain a temperature- and mercury-insensitive swelling in vitro. Glia 31:29–38
Solenov E, Watanabe H, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2004) Sevenfoldreduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C426–C432
Taniguchi M, Yamashita T, Kumura E, Tamatani M, Kobayashi A, Yokawa T, Maruno M, Kato A, Ohnishi T, Kohmura E, Tohyama M, Yoshimine T (2000) Induction of aquaporin-4 water channel mRNA after focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 78:131–137
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A (2003) An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2106–2111
Morishima T, Aoyama M, Iida Y, Yamamoto N, Hirate H, Arima H, Fujita Y, Sasano H, Tsuda T, Katsuya H, Asai K, Sobue K (2008) Lactic acid increases aquaporin 4 expression on the cell membrane of cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci Res 61:18–26
Yang M, Gao F, Liu H, Yu WH, Sun SQ (2009) Temporal changes in expression of aquaporin-3, -4, -5 and -8 in rat brains after permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1290:121–132
Neal CJ, Lee EY, Gyorgy A, Ecklund JM, Agoston DV, Ling GS (2007) Effect of penetrating brain injury on aquaporin-4 expression using a rat model. J Neurotrauma 24:1609–1617
Hu H, Yao HT, Zhang WP, Zhang L, Ding W, Zhang SH, Chen Z, Wei EQ (2005) Increased expression of aquaporin-4 in human traumatic brain injury and brain tumors. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 6:33–37
Taya K, Gulsen S, Okuno K, Prieto R, Marmarou CR, Marmarou A (2008) Modulation of AQP4 expression by the selective V1a receptor antagonist, SR49059, decreases trauma-induced brain edema. Acta Neurochir Suppl 102:425–429
Badaut J, Ashwal S, Adami A, Tone B, Recker R, Spagnoli D, Ternon B, Obenaus A (2011) Brain water mobility decreases after astrocytic aquaporin-4 inhibition using RNA interference. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:819–831
Rao KV, Reddy PV, Curtis KM, Norenberg MD (2011) Aquaporin-4 expression in cultured astrocytes after fluid percussion injury. J Neurotrauma 28:371–381
Nesic O, Lee J, Ye Z, Unabia GC, Rafati D, Hulsebosch CE, Perez-Polo JR (2006) Acute and chronic changes in aquaporin 4 expression after spinal cord injury. Neuroscience 143:779–792
Saadoun S, Bell BA, Verkman AS, Papadopoulos MC (2008) Greatly improved neurological outcome after spinal cord compression injury in AQP4-deficient mice. Brain 131:1087–1098
Margulies JE, Thomson RC, Demetriou AA (1999) Aquaporin-4-water channel is upregulated in the brain in fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 30:395ª (Abstract)
Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Tong X, Curtis KM, Norenberg MD (2010) Brain aquaporin-4 in experimental acute liver failure. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:869–879
Eefsen M, Jelnes P, Schmidt LE, Vainer B, Bisgaard HC, Larsen FS (2010) Brain expression of the water channels aquaporin-1 and -4 in mice with acute liver injury, hyperammonemia and brain edema. Metab Brain Dis 25:315–323
Rama Rao KV, Chen M, Simard JM, Norenberg MD (2003) Increased aquaporin-4 expression in ammonia-treated cultured astrocytes. NeuroReport 14:2379–2382
Chastre A, Jiang W, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF (2010) Ammonia and proinflammatory cytokines modify expression of genes coding for astrocytic proteins implicated in brain edema in acute liver failure. Metab Brain Dis 25:17–21
Zelenina M (2010) Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neurochem Int 57:468–488
Tanaka K, Koyama Y (2011) Endothelins decrease the expression of aquaporins and plasma membrane water permeability in cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 89:320–328
Gunnarson E, Zelenina M, Axehult G, Song Y, Bondar A, Krieger P, Brismar H, Zelenin S, Aperia A (2008) Identification of a molecular target for glutamate regulation of astrocyte water permeability. Glia 56:587–596
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico (DGAPA), Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM) [grant number IN203410], and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) [grant number 98952].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In honor of Leif Hertz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasantes-Morales, H., Vázquez-Juárez, E. Transporters and Channels in Cytotoxic Astrocyte Swelling. Neurochem Res 37, 2379–2387 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0777-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0777-2