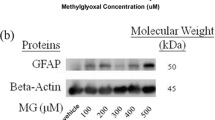
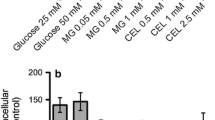
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is a disease associated with several changes in the central nervous system, including oxidative stress and abnormal glutamatergic neurotransmission, and the astrocytes play an essential role in these alterations. In vitro studies of astroglial function have been performed using cultures of primary astrocytes or C6 glioma cells. Herein, we investigated glutamate uptake, glutamine synthetase and S100B secretion in C6 glioma cells cultured in a high-glucose environment, as well as some parameters of oxidative stress and damage. C6 glioma cells, cultured in 12 mM glucose medium, exhibited signals of oxidative and nitrosative stress similar to those found in diabetes mellitus and other models of diabetic disease (decrease in glutathione, elevated NO, DNA damage). Interestingly, we found an increase in glutamate uptake and S100B secretion, and a decrease in glutamine synthetase, which might be linked to the altered glutamatergic communication in diabetes mellitus. Moreover, glutamate uptake in C6 glioma cells, like primary astrocytes, was stimulated by extracellular S100B. Aminoguanidine partially prevented the glial alterations induced by the 12 mM glucose medium. Together, these data emphasize the relevance of astroglia in diabetes mellitus, as well as the importance of glial parameters in the evaluation of diabetic disease progression and treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardoni F, Kamal A, Bellone C, Biessels GJ, Ramakers GM, Cattabeni F, Gispent WH, Di Luca M (2002) Effects of streptozotocin-diabetes on the hippocampal NMDA receptor complex in rats. J Neurochem 80:438–447
Kroner Z (2009) The relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes: Type 3 diabetes? Altern Med Rev 14:373–379
Biessels GJ, Gispen WH (2005) The impact of diabetes on cognition: what can be learned from rodent models? Neurobiol Aging 26(Suppl 1):36–41
Dringen R, Hirrlinger J (2003) Glutathione pathways in the brain. Biol Chem 384:505–516
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Donato R, Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Arcuri C, Bianchi R, Brozzi F, Tubaro C, Giambanco I (2009) S100B’s double life: intracellular regulator and extracellular signal. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:1008–1022
Garcia-Espinosa MA, Garcia-Martin ML, Cerdan S (2003) Role of glial metabolism in diabetic encephalopathy as detected by high resolution 13C NMR. NMR Biomed 16:440–449
Coleman ES, Dennis JC, Braden TD, Judd RL, Posner P (2010) Insulin treatment prevents diabetes-induced alterations in astrocyte glutamate uptake and GFAP content in rats at 4 and 8 weeks of diabetes duration. Brain Res 1306:131–141
Pinto SS, Gottfried C, Mendez A, Goncalves D, Karl J, Goncalves CA, Wofchuk S, Rodnight R (2000) Immunocontent and secretion of S100B in astrocyte cultures from different brain regions in relation to morphology. FEBS Lett 486:203–207
Davey GE, Murmann P, Heizmann CW (2001) Intracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ levels regulate the alternative cell density-dependent secretion of S100B in human glioblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:30819–30826
Castets F, Griffin WS, Marks A, Van Eldik LJ (1997) Transcriptional regulation of the human S100 beta gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 46:208–216
Tabernero A, Medina JM, Giaume C (2006) Glucose metabolism and proliferation in glia: role of astrocytic gap junctions. J Neurochem 99:1049–1061
Haghighat N, McCandless DW (1997) Effect of ammonium chloride on energy metabolism of astrocytes and C6-glioma cells in vitro. Metab Brain Dis 12:287–298
Nardin P, Tramontina F, Leite MC, Tramontina AC, Quincozes-Santos A, de Almeida LM, Battastini AM, Gottfried C, Goncalves CA (2007) S100B content and secretion decrease in astrocytes cultured in high-glucose medium. Neurochem Int 50:774–782
Tramontina F, Tramontina AC, Souza DF, Leite MC, Gottfried C, Souza DO, Wofchuk ST, Goncalves CA (2006) Glutamate uptake is stimulated by extracellular S100B in hippocampal astrocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:81–86
Miralles VJ, Martinez-Lopez I, Zaragoza R, Borras E, Garcia C, Pallardo FV, Vina JR (2001) Na+ dependent glutamate transporters (EAAT1, EAAT2, and EAAT3) in primary astrocyte cultures: effect of oxidative stress. Brain Res 922:21–29
Matos M, Augusto E, Oliveira CR, Agostinho P (2008) Amyloid-beta peptide decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes: involvement of oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Neuroscience 156:898–910
Hansson E, Muyderman H, Leonova J, Allansson L, Sinclair J, Blomstrand F, Thorlin T, Nilsson M, Ronnback L (2000) Astroglia and glutamate in physiology and pathology: aspects on glutamate transport, glutamate-induced cell swelling and gap-junction communication. Neurochem Int 37:317–329
Ward MM, Jobling AI, Kalloniatis M, Fletcher EL (2005) Glutamate uptake in retinal glial cells during diabetes. Diabetologia 48:351–360
Duarte AI, Santos MS, Seica R, Oliveira CR (2004) Oxidative stress affects synaptosomal gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate transport in diabetic rats: the role of insulin. Diabetes 53:2110–2116
dos Santos AQ, Nardin P, Funchal C, de Almeida LM, Jacques-Silva MC, Wofchuk ST, Goncalves CA, Gottfried C (2006) Resveratrol increases glutamate uptake and glutamine synthetase activity in C6 glioma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 453:161–167
Abib RT, Quincozes-Santos A, Nardin P, Wofchuk ST, Perry ML, Goncalves CA, Gottfried C (2008) Epicatechin gallate increases glutamate uptake and S100B secretion in C6 cell lineage. Mol Cell Biochem 310:153–158
de Almeida LM, Pineiro CC, Leite MC, Brolese G, Tramontina F, Feoli AM, Gottfried C, Goncalves CA (2007) Resveratrol increases glutamate uptake, glutathione content, and S100B secretion in cortical astrocyte cultures. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:661–668
de Arriba SG, Stuchbury G, Yarin J, Burnell J, Loske C, Munch G (2007) Methylglyoxal impairs glucose metabolism and leads to energy depletion in neuronal cells—protection by carbonyl scavengers. Neurobiol Aging 28:1044–1050
Nardin P, Tramontina AC, Quincozes-Santos A, Tortorelli LS, Lunardi P, Klein PR, Wartchow KM, Bobermin LD, Gottfried C, Elisabetsky E, Goncalves CA (2011) In vitro S100B secretion is reduced by apomorphine: effects of antipsychotics and antioxidants. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1291–1296
Gottfried C, Tramontina F, Goncalves D, Goncalves CA, Moriguchi E, Dias RD, Wofchuk ST, Souza DO (2002) Glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes depends on age: a study about the effect of guanosine and the sensitivity to oxidative stress induced by H(2)O(2). Mech Ageing Dev 123:1333–1340
Leite MC, Galland F, Brolese G, Guerra MC, Bortolotto JW, Freitas R, Almeida LM, Gottfried C, Goncalves CA (2008) A simple, sensitive and widely applicable ELISA for S100B: methodological features of the measurement of this glial protein. J Neurosci Methods 169:93–99
Hu J, Castets F, Guevara JL, Van Eldik LJ (1996) S100 beta stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase activity and mRNA levels in rat cortical astrocytes. J Biol Chem 271:2543–2547
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Hartmann A, Agurell E, Beevers C, Brendler-Schwaab S, Burlinson B, Clay P, Collins A, Smith A, Speit G, Thybaud V, Tice RR (2003) Recommendations for conducting the in vivo alkaline Comet assay. 4th International Comet Assay Workshop. Mutagenesis 18:45–51
Collins AR, Dusinska M, Gedik CM, Stetina R (1996) Oxidative damage to DNA: do we have a reliable biomarker? Environ Health Perspect 104(Suppl 3):465–469
Collins A, Dusinska M, Franklin M, Somorovska M, Petrovska H, Duthie S, Fillion L, Panayiotidis M, Raslova K, Vaughan N (1997) Comet assay in human biomonitoring studies: reliability, validation, and applications. Environ Mol Mutagen 30:139–146
Quincozes-Santos A, Andreazza AC, Nardin P, Funchal C, Goncalves CA, Gottfried C (2007) Resveratrol attenuates oxidative-induced DNA damage in C6 Glioma cells. Neurotoxicology 28:886–891
Andreazza AC, Frey BN, Erdtmann B, Salvador M, Rombaldi F, Santin A, Goncalves CA, Kapczinski F (2007) DNA damage in bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res 153:27–32
Browne RW, Armstrong D (1998) Reduced glutathione and glutathione disulfide. Methods Mol Biol 108:347–352
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Bauduceau B, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Brocker P, Taillia H (2005) The brain of the elderly diabetic patient. Diabetes Metab 31 Spec No 2:5S92–95S97
Gispen WH, Biessels GJ (2000) Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci 23:542–549
Biessels GJ, Deary IJ, Ryan CM (2008) Cognition and diabetes: a lifespan perspective. Lancet Neurol 7:184–190
Sango K, Saito H, Takano M, Tokashiki A, Inoue S, Horie H (2006) Cultured adult animal neurons and schwann cells give us new insights into diabetic neuropathy. Curr Diabetes Rev 2:169–183
Tan AL, Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2007) AGE, RAGE, and ROS in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27:130–143
Gowda K, Zinnanti WJ, LaNoue KF (2011) The influence of diabetes on glutamate metabolism in retinas. J Neurochem 117:309–320
Coleman E, Judd R, Hoe L, Dennis J, Posner P (2004) Effects of diabetes mellitus on astrocyte GFAP and glutamate transporters in the CNS. Glia 48:166–178
Palos TP, Ramachandran B, Boado R, Howard BD (1996) Rat C6 and human astrocytic tumor cells express a neuronal type of glutamate transporter. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 37:297–303
Wilkinson-Berka JL, Kelly DJ, Koerner SM, Jaworski K, Davis B, Thallas V, Cooper ME (2002) ALT-946 and aminoguanidine, inhibitors of advanced glycation, improve severe nephropathy in the diabetic transgenic (mREN-2)27 rat. Diabetes 51:3283–3289
Cockroft KM, Meistrell M, Zimmerman GA, Risucci D, Bloom O, Cerami A, Tracey KJ (1996) Cerebroprotective effects of aminoguanidine in a rodent model of stroke. Stroke 27:6
Schimchowitsch SCJ (2006) Polyamine and aminoguanidine treatments to promote structural and functional recovery in the adult mammalian brain after injury: a brief literature review and preliminary data about their combined administration. J Physiol Paris 99:11
Kamboj SSCK, Sandhir R (2008) Neuroprotective effect of N-acetylcysteine in the development of diabetic encephalopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Metab Brain Dis 23:16
Goodarzi MT, Navidi AA, Rezaei M, Babahmadi-Rezaei H Oxidative damage to DNA and lipids: correlation with protein glycation in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Lab Anal 24:72–76
Powell LA, Nally SM, McMaster D, Catherwood MA, Trimble ER (2001) Restoration of glutathione levels in vascular smooth muscle cells exposed to high glucose conditions. Free Radic Biol Med 31:1149–1155
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54:1615–1625
Goncalves D, Karl J, Leite M, Rotta L, Salbego C, Rocha E, Wofchuk S, Goncalves CA (2002) High glutamate decreases S100B secretion stimulated by serum deprivation in astrocytes. Neuroreport 13:1533–1535
Buyukuysal RL (2005) Protein S100B release from rat brain slices during and after ischemia: comparison with lactate dehydrogenase leakage. Neurochem Int 47:580–588
Hu J, Ferreira A, Van Eldik LJ (1997) S100beta induces neuronal cell death through nitric oxide release from astrocytes. J Neurochem 69:2294–2301
Allen DA, Yaqoob MM, Harwood SM (2005) Mechanisms of high glucose-induced apoptosis and its relationship to diabetic complications. J Nutr Biochem 16:705–713
Kosenko E, Llansola M, Montoliu C, Monfort P, Rodrigo R, Hernandez-Viadel M, Erceg S, Sanchez-Perez AM, Felipo V (2003) Glutamine synthetase activity and glutamine content in brain: modulation by NMDA receptors and nitric oxide. Neurochem Int 43:493–499
Lieth E, LaNoue KF, Antonetti DA, Ratz M (2000) Diabetes reduces glutamate oxidation and glutamine synthesis in the retina. The Penn State Retina Research Group. Exp Eye Res 70:723–730
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), FINEP (IBN 01.06.0842-00) and INCT-National Institute of Science and Technology for Excitotoxicity and Neuroprotection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tramontina, A.C., Nardin, P., Quincozes-Santos, A. et al. High-Glucose and S100B Stimulate Glutamate Uptake in C6 Glioma Cells. Neurochem Res 37, 1399–1408 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0722-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0722-4