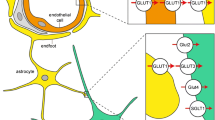
Abstract
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter that plays a major role in the pathogenesis of ischemia brain injury. The regulation of glutamate neurotransmission is carried out by excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs) that act through reuptake of glutamate into cells. EAATs may also release glutamate into the extracellular space in a calcium-independent manner during ischemia and dysfunction of EAATs is specifically implicated in the pathology of cerebral ischemia. Recent studies show that up-regulation of EAAT2 provides neuroprotection during ischemic insult. This review summarizes current knowledge regarding the role of EAATs in cerebral ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farso MC, O’Shea RD, Beart PM (2009) Evidence group I mGluR drugs modulate the activation profile of lipopolysaccharide-exposed microglia in culture. Neurochem Res 34:1721–1728
Xiang Y, Gao H, Zhu H, Sun N, Ma Y, Lei H (2006) Neurochemical changes in brain induced by chronic morphine treatment: NMR studies in thalamus and somatosensory cortex of rats. Neurochem Res 31:1255–1261
Albrecht J, Hilgier W, Zielińska M, Januszewski S, Hesselink M, Quack G (2000) Extracellular concentrations of taurine, glutamate, and aspartate in the cerebral cortex of rats at the asymptomatic stage of thioacetamide-induced hepatic failure: modulation by ketamine anesthesia. Neurochem Res 25:1497–1502
Barbour B, Brew H, Attwell D (1988) Electrogenic glutamate uptake in glial cells is activated by intracellular potassium. Nature 335:433–435
Kanai Y, Nussberger S, Romero MF, Boron WF, Hebert SC, Hediger MA (1995) Electrogenic properties of the epithelial and neuronal high-affinity glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem 270:16561–16568
Zerangue N, Kavanaugh MP (1996) Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 383:634–637
Marcaggi P, Attwell D (2004) Role of glial amino acid transporters in synaptic transmission and brain energetics. Glia 47:217–225
Bruijn LI, Miller TM, Cleveland DW (2004) Unraveling the mechanisms involved in motor neuron degeneration in ALS. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:723–749
Schwartz M, Shaked I, Fisher J, Mizrahi T, Schori H (2003) Protective autoimmunity against the enemy within: fighting glutamate toxicity. Trends Neurosci 26:297–302
Shashidharan P, Plaitakis A (1993) Cloning and characterization of a glutamate transporter cDNA from human cerebellum. Biochim J Biophys 1216:161–164
Storck T, Schulte S, Hofmann K, Stoffel W (1992) Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na+ -dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10955–10959
Shashidharan P, Wittenberg I, Plaitakis A (1994) Molecular cloning of human brain glutamate/aspartate transporter II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1191:393–396
Perego C, Vanoni C, Bossi M, Massari S, Basudev H, Longhi R, Pietrini G (2000) The GLT-1 and GLAST glutamate transporters are expressed on morphologically distinct astrocytes and regulated by neuronal activity in primary hippocampal cocultures. J Neurochem 75:1076–1084
Plachez C, Danbolt NC, Recasens M (2000) Transient expression of the glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT in hippocampal neurons in primary culture. J Neurosci Res 59:587–593
Liang JF et al (2008) Excitatory amino acid transporter expression by astrocytes is neuroprotective against microglial excitotoxicity. Brain Res 1210:11–19
Schmitt A, Asan E, Lesch KP, Kugler P (2002) A splice variant of glutamate transporter GLT1/EAAT2 expressed in neurons: cloning and localization in rat nervous system. Neuroscience 109:45–61
Yamada T, Kawahara K, Kosugi T, Tanaka M (2006) Nitric oxide produced during sublethal ischemia is crucial for the preconditioning-induced down regulation of glutamate transporter GLT-1 in neuron/astrocyte co-cultures. J Neurochem Res 31:49–56
Yernool D, Boudker O, Folta-Stogniew E, Gouaux E (2003) Trimeric subunit stoichiometry of the glutamate transporters from Bacillus caldotenax and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem 42:12981–12988
Yernool D, Boudker O, Jin Y, Gouaux E (2004) Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature 431:811–818
Koch HP, Larsson HP (2005) Small-scale molecular motions accomplish glutamate uptake in human glutamate transporters. J Neurosci 25:1730–1736
Mennerick S et al (1998) Neuronal expression of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in hippocampal microcultures. J Neurosci 18:4490–4499
Conti F, Dibiasi S, Minelli A, Rothstein JD, Melone M (1998) EAAC1, a high-affinity glutamate transporter, is localized to astrocytes and gabaergic neurons besides pyramidal cells in the rat cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 8:108–116
Dunlop J, Beal MH, Lou Z, Franco R (1998) The pharmacological profile of L-glutamate transport in human NT2 neurones is consistent with excitatory amino acid transporter 2. Eur J Pharmacol 360:249–256
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (1992) Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 360:467–471
Dowd LA, Robinson MB (1996) Rapid stimulation of EAAC1-mediated Na+ -dependent L-glutamate transport activity in C6 glioma by phorbol ester. J Neurochem 67:508–516
Palos TP, Ramachandran B, Boado R, Howard BD (1996) Rat C6 and human astrocytic tumor cells express a neuronal type of glutamate transporter. Mol Brain Res 37:297–303
Dunlop J, Lou Z, McIlvain HB (1999) Properties of excitatory amino acid transport in the human U373 astrocytoma cell line. Brain Res 839:235–242
Barpeled O, BenHur H, Biegon A, Groner Y, Dewhurst S, Furuta A, Rothstein JD (1997) Distribution of glutamate transporter subtypes during human brain development. J Neurochem 69:2571–2580
Fairman WA, Vandenberg RJ, Arriza JL, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG (1995) An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 375:599–603
Furuta A, Martin LJ, Lin CLG, DykesHoberg M, Rothstein JD (1997) Cellular and synaptic localization of the neuronal glutamate transporters excitatory amino acid transporter 3 and 4. Neurosci 81:1031–1042
Schlag BD, Vondrasek JR, Munir M, Kalandadze A, Zelenaia OA, Rothstein JD, Robinson MB (1998) Regulation of the glial Na+ -dependent glutamate transporters by cyclic AMP analogs and neurons. J Mol Pharmacol 53:355–369
Hu WH, Walters WM, Xia XM, Karmally SA, Bethea JR (2003) Neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT4 is expressed in astrocytes. Glia 44:13–25
Arriza JL, Eliasof S, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG (1997) Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4155–4160
Pow DV, Barnett NL (2000) Developmental expression of excitatory amino acid transporter 5: a photoreceptor and bipolar cell glutamate transporter in rat retina. Neurosci Lett 280:21–24
Rothstein JD et al (1996) Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16:675–686
Rao VL, Dogan A, Bowen KK, Todd KG, Dempsey RJ (2001) Antisense knockdown of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 exacerbates hippocampal neuronal damage following traumatic injury to rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 13:119–128
Vizi ES (2000) Role of high-affinity receptors and membrane transporters in nonsynaptic communication and drug action in the central nervous system. Pharmacol 52:63–89
Rossi DJ, Oshima T, Attwell D (2000) Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 403:316–321
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (2003) The glutamate and neutral amino acid transporter family: physiological and pharmacological implications. Eur J Pharmacol 479:237–247
Shigeri Y, Seal RP, Shimamoto K (2004) Molecular pharmacology of glutamate transporters, EAATs and VGLUTs. Brain Res 45:250–265
Grewer C, Rauen T (2005) Electrogenic glutamate transporters in the CNS: molecular mechanism, pre-steady-state kinetics, and their impact on synaptic signaling. J Membr Biol 203:1–20
Sepkuty JP, Cohen AS, Eccles C, Rafiq A, Behar K, Ganel R, Coulter DA, Rothstein JD (2002) A neuronal glutamate transporter contributes to neurotransmitter GABA synthesis and epilepsy. J Neurosci 22:6372–6379
Su ZZ, Leszczyniecka M, Kang DC, Sarkar D, Chao W, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB (2003) Insights into glutamate transport regulation in human astrocytes: cloning of the promoter for excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1955–1960
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2004) Glutamate transporters: animal models to neurologic disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:461–473
Beart PM, O’Shea RD (2007) Transporters for L-glutamate: an update on their molecular pharmacology and pathological involvement. Br J Pharmacol 150:5–17
Naskar R, Vorwerk CK, Dreyer E (2000) Concurrent downregulation of a glutamate transporter and receptor in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:1940–1944
Rozyczka J, Figiel M, Engele J (2004) Endothelins negatively regulate glial glutamate transporter expression. Brain Pathol 14:406–414
Escartin C et al (2006) Ciliary neurotrophic factor activates astrocytes, redistributes their glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 to raft microdomains, and improves glutamate handling in vivo. J Neurosci 26:5978–5989
Grintal B et al (2009) Inhibition of astroglial glutamate transport by polyunsaturated fatty acids: evidence for a signalling role of docosahexaenoic acid. J Neurochem 54:535–543
Huang Y, Zuo Z (2005) Isoflurane induces a protein kinase C a-dependent increase in cell surface protein level and activity of glutamate transporter type 3. Mol Pharmacol 67:1522–1533
Rothstein JD et al (2005) β-Lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 433:73–77
Do SH, Ham BM, Zuo Z (2003) Effects of propofol on the activity of rat glutamate transporter type 3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes: the role of protein kinase C. Neurosci Lett 343:113–116
Yun JY, Park KS, Kim JH, Do SH, Zuo ZY (2007) Propofol reverses oxidative stress-attenuated glutamate transporter EAAT3 activity: evidence of protein kinase C involvement. Eur J Pharmacol 565:83–88
Romera C et al (2007) Ischemic preconditioning reveals that GLT1/EAAT2 glutamate transporter is a novel PPARgamma target gene involved in neuroprotection. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1327–1338
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (1997) Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: global burden of disease study. Lancet 349:1498–1504
Fei Z, Zhang X, Bai HM, Jiang XF, Li X, Zhang W, Hu W (2007) Posttraumatic secondary brain insults exacerbates neuronal injury by altering metabotropic glutamate receptors. BMC Neurosci 8:96–99
Romera C et al (2004) In vitro ischemic tolerance involves upregulation of glutamate transport partly mediated by the TACE/ADAM17-tumor necrosis factor-alpha pathway. J Neurosci 24:1350–1357
Inage YW, Itoh M, Wada K, Takashima S (1998) Expression of two glutamate transporters, GLAST and EAAT4, in the human cerebellum—their correlation in development and neonatal hypoxic–ischemic damage. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:554–562
Martin LJ et al (1997) Hypoxia–ischemia causes abnormalities in glutamate transporters and death of astroglia and neurons in newborn striatum. Ann Neurol 42:335–348
Fukamachi S, Furuta A, Ikeda T, Ikenoue T, Kaneoka T, Rothstein JD, Iwaki T (2001) Altered expressions of glutamate transporter subtypes in rat model of neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Res Dev 132:131–139
Munch C et al (2003) Differential regulation of 50 splice variants of the glutamate transporter EAAT2 in an in vivo model of chemical hypoxia induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. Neurosci Res 71:819–825
Pow DV et al (2004) Loss of glial glutamate transporters and induction of neuronal expression of GLT-1B in the hypoxic neonatal pig brain. Dev Brain Res 153:1–11
Chen JC, Hsu-Chou H, Lu JL, Chiang YC, Huang HM, Wang HL, Wu T, Liao JJ, Yeh TS (2005) Down-regulation of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in rat hippocampus and striatum and its modulation by a group III metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist following transien global forebrain ischemia. Neuropharmacol 49:703–714
Robinson MB, Djali S, Buchhalter JR (1993) Inhibition of glutamate uptake with L-trans-pyrrolidine-2, 4-dicarboxylate potentiates glutamate toxicity in primary hippocampal cultures. J Neurochem 61:2099–2103
Dugan LL, Bruno VMG, Amagasu SM, Giffard RG (1995) Glia modulate the response of murine cortical neurons to excitotoxicity: glia exacerbate AMPA neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 15:4545–4555
Guiramand J, Martin A, de Jesus Ferreira MC, Cohen-Solal C, Vignes M, Recasens M (2005) Gliotoxicity in hippocampal cultures is induced by transportable , but not by nontransportable, glutamate uptake inhibitors. J Neurosci Res 81:199–207
Erten SF, Kocak A, Ozdemir I, Aydemir S, Colak A, Reeder BS (2003) Protective effect of melatonin on experimental spinal cord ischemia. Spinal Cord 41:533–538
Hashiguchi A, Yano S, Morioka M et al (2004) Up-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway contributes to ischemic tolerance in the CA1 subfi eld of gerbil hippocampus. Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:271–279
Dallas ML, Boycott HE, Atkinson L, Miller A, Boyle JP, Pearson HA, Peers C (2007) Hypoxia suppresses glutamate transport in astrocytes. J Neurosci 27:3946–3955
Hannah EB, Jenny AW, John PB, Hugh AP, Chris P (2008) Differential involvement of TNF in hypoxic suppression of astrocyte glutamate transporters. Glia 56:998–1004
Lehre KP, Ullensvang K, Wojewodzic M, Zhou Y, Attwell D, Danbolt NC (2008) A quantitative assessment of glutamate uptake into hippocampal synaptic terminals and astrocytes: new insights into a neuronal role for excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2). J Neurosci 157:80–94
Montiel T, Camacho A, Estrada-Sánchez AM, Massieu L (2005) Differential effects of the substrate inhibitor l-trans-pyrrolidine-2, 4-dicarboxylate (PDC) and the non-substrate inhibitor DL-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate (DL-TBOA) of glutamate transporters on neuronal damage and extracellular amino acid levels in rat brain in vivo. Neurosci 133:667–678
Lee SG et al (2008) Mechanism of ceftriaxone induction of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 expression and glutamate uptake in primary human astrocytes. J Biol Chem 283:13116–13123
Weller ML, Stone IM, Goss A, Rau T, Rova C, Poulsen DJ (2008) Selective overexpression of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2) in astrocytes enhances neuroprotection from moderate but not severe hypoxia-ischemia. Neurosci 155:1204–1211
Chu K et al (2007) Pharmacological induction of ischemic tolerance by glutamate transporter-1 (EAAT2) upregulation. Stroke 38:177–182
Tilleux S, Goursaud S, Hermans E (2009) Selective up-regulation of GLT-1 in cultured astrocytes exposed to soluble mediators released by activated microglia. J Neurochem Int 55:35–40
Lewerenz J et al (2009) Induction of Nrf2 and xCT are involved in the action of the neuroprotective antibiotic ceftriaxone in vitro. J Neurochem 111:332–343
Selkirk JV, Stiefel TH, Stone IM, Naeve GS, Foster AC, Poulsen DJ (2005) Over-expression of the human EAAT2 glutamate transporter within neurons of mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures leads to increased vulnerability of CA1 pyramidal cells. Eur J Neurosci 21:2291–2296
Saito Y, Kato A, Hagihara Y, Kaneda Y, Yoshimine T (2003) Gene therapy for ischemic brain diseases. Curr Gene Ther 3:49–58
Tsuboniwa N et al (2001) Safety evaluation of hemagglutinating virus of Japan—artificial viral envelope liposomes in nonhuman primates. Hum Gene Ther 12:469–487
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (30670796, 30930093 and 30700255) of China. We sincerely thank Doctor Yan Qu for his critical review and in-depth comments in preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, Xd., Fei, F. & Fei, Z. The Role of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters in Cerebral Ischemia. Neurochem Res 35, 1224–1230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0178-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0178-3