Abstract
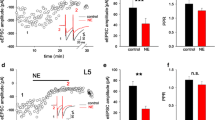
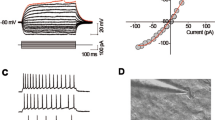
The primary auditory cortex is subject to the modulation of numerous neurotransmitters including norepinephrine (NE), which has been shown to decrease cellular excitability by yet unclear mechanisms. We investigated the possibility that NE directly affects excitatory glutamatergic synapses. We found that bath applications of NE (20 μM) decreased glutamatergic excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) in all cortical layers. Changes in the kinetics of synaptic EPSCs, invariance of pair pulse ratio and of the coefficient-of-variation, together with the decrease of responses to pressure-application of AMPA (500 μM), indicated the postsynaptic nature of the adrenergic effect. Pharmacological experiments suggested that the NE-induced depression of EPSCs is caused by the activation of α1 adrenoceptors, PLC, and a Ca2+-independent PKC. We speculate that the decrease in temporal cortex excitability might promote a posterior-to-anterior shift in cortical activation together with a decrease in spontaneous background activity, resulting eventually in more effective sensory processing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie ED, Jacobs BL (1987) Single-unit response of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus of freely moving cats. I. Acutely presented stressful and nonstressful stimuli. J Neurosci 7:2837–2843
Aoki C, Venkatesan C, Go CG, Forman R, Kurose H (1998) Cellular and subcellular sites for noradrenergic action in the monkey dorsolateral prefrontal cortex as revealed by the immunocytochemical localization of noradrenergic receptors and axons. Cereb Cortex 8:269–277. doi:10.1093/cercor/8.3.269
Araneda RC, Firestein S (2006) Adrenergic enhancement of inhibitory transmission in the accessory olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 26:3292–3298. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4768-05.2006
Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS (1985) Catecholamines and cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Ann N Y Acad Sci 444:218–234. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb37592.x
Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Goldman-Rakic PS (1988) The alpha-2 adrenergic agonist guanfacine improves memory in aged monkeys without sedative or hypotensive side effects: evidence for alpha-2 receptor subtypes. J Neurosci 8:4287–4298
Asnis GM, Halbreich U, Rabinovich H, Ryan ND, Sachar EJ, Nelson B, Puig-Antich J, Novacenko H (1985) The cortisol response to desipramine in endogenous depressives and normal controls: preliminary findings. Psychiatry Res 14:225–233. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(85)90017-4
Asnis GM, Sanderson WC, van Praag HM (1992) Cortisol response to intramuscular desipramine in patients with major depression and normal control subjects: a replication study. Psychiatry Res 44:237–250. doi:10.1016/0165-1781(92)90027-Z
Aston-Jones G, Chiang C, Alexinsky T (1991) Discharge of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats and monkeys suggests a role in vigilance. Prog Brain Res 88:501–520. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63830-3
Atzori M, Lei S, Evans DI, Kanold PO, Phillips-Tansey E, McIntyre O, McBain CJ (2001) Differential synaptic processing separates stationary from transient inputs to the auditory cortex. Nat Neurosci 4:1230–1237. doi:10.1038/nn760
Barth DS (2003) Submillisecond synchronization of fast electrical oscillations in neocortex 1. J Neurosci 23:2502–2510
Behl P, Bocti C, Swartz RH, Gao F, Sahlas DJ, Lanctot KL, Streiner DL, Black SE (2007) Strategic subcortical hyperintensities in cholinergic pathways and executive function decline in treated Alzheimer patients. Arch Neurol 64:266–272. doi:10.1001/archneur.64.2.266
Bengzon J, Kalen P, Lindvall O (1990) Evidence for long-term reduction of noradrenaline release after kindling in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 535:353–357. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)91624-P
Bennett BD, Huguenard JR, Prince DA (1997) Adrenoceptor-mediated elevation of ambient GABA levels activates presynaptic GABA(B) receptors in rat sensorimotor cortex. J Neurophysiol 78:561–566
Bennett BD, Huguenard JR, Prince DA (1998) Adrenergic modulation of GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in rat sensorimotor cortex. Neurophysiol 79:937–946
Berts A, Zhong H, Minneman KP (1999) No role for Ca++ or protein kinase C in alpha-1A adrenergic receptor activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in transfected PC12 cells. Mol Pharmacol 55:296–303
Bloom FE, Hoffer BJ, Siggins GR (1971) Studies on norepinephrine-containing afferents to Purkinje cells of art cerebellum. I. Localization of the fibers and their synapses. Brain Res 25:501–521. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(71)90457-4
Bockhorst KH, Narayana PA, Liu R, Ahobila-Vijjula P, Ramu J, Kamel M, Wosik J, Bockhorst T, Hahn K, Hasan KM, Perez P (2008) Early postnatal development of rat brain: in vivo diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurosci Res 86:1520–1528. doi:10.1002/jnr.21607
Borsini F, Rolls ET (1984) Role of noradrenaline and serotonin in the basolateral region of the amygdala in food preferences and learned taste aversions in the rat. Physiol Behav 33:37–43. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(84)90010-6
Buffalari DM, Grace AA (2007) Noradrenergic modulation of basolateral amygdala neuronal activity: opposing influences of alpha-2 and beta receptor activation. J Neurosci 27:12358–12366. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2007-07.2007
Cameron NM, Carey P, Erskine MS (2004) Medullary noradrenergic neurons release norepinephrine in the medial amygdala in females in response to mating stimulation sufficient for pseudopregnancy. Brain Res 1022:137–147. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.022
Carr DB, Andrews GD, Glen WB, Lavin A (2007) alpha2-Noradrenergic receptors activation enhances excitability and synaptic integration in rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons via inhibition of HCN currents. J Physiol 584:437–450. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141671
Chamberlain SR, Muller U, Blackwell AD, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2006) Noradrenergic modulation of working memory and emotional memory in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 188:397–407. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0391-6
Chauvel P, Trottier S (1986) Role of noradrenergic ascending system in extinction of epileptic phenomena. Adv Neurol 44:475–487
Cohen RI, Almazan G (1993) Norepinephrine-stimulated PI hydrolysis in oligodendrocytes is mediated by alpha 1A-adrenoceptors. NeuroReport 4:1115–1118. doi:10.1097/00001756-199308000-00014
Crow TJ, Cross AJ, Cooper SJ, Deakin JF, Ferrier IN, Johnson JA, Joseph MH, Owen F, Poulter M, Lofthouse R et al (1984) Neurotransmitter receptors and monoamine metabolites in the brains of patients with Alzheimer-type dementia and depression, and suicides. Neuropharmacology 23:1561–1569. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(84)90100-X
Debiec J, LeDoux JE (2006) Noradrenergic signaling in the amygdala contributes to the reconsolidation of fear memory: treatment implications for PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1071:521–524. doi:10.1196/annals.1364.056
Doze VA, Cohen GA, Madison DV (1991) Synaptic localization of adrenergic disinhibition in the rat hippocampus. Neuron 6:889–900. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(91)90229-S
Faber DS, Korn H (1991) Applicability of the coefficient of variation method for analyzing synaptic plasticity. Biophys J 60:1288–1294. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82162-2
Fallon S, Shearman E, Sershen H, Lajtha A (2007) Food reward-induced neurotransmitter changes in cognitive brain regions. Neurochem Res 32:1772–1782. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9343-8
Franowicz JS, Arnsten AF (1998) The alpha-2a noradrenergic agonist, guanfacine, improves delayed response performance in young adult rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 136:8–14. doi:10.1007/s002130050533
Galvez R, Mesches MH, McGaugh JL (1996) Norepinephrine release in the amygdala in response to footshock stimulation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 66:253–257. doi:10.1006/nlme.1996.0067
Gerber U, Greene RW, McCarley RW, Haas HL (1990) Excitation of brain stem neurons by noradrenaline and histamine. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 1:71–76
Grant SJ, Aston-Jones G, Redmond DE Jr (1988) Responses of primate locus coeruleus neurons to simple and complex sensory stimuli. Brain Res Bull 21:401–410. doi:10.1016/0361-9230(88)90152-9
Gross-Isseroff R, Dillon KA, Fieldust SJ, Biegon A (1990) Autoradiographic analysis of alpha 1-noradrenergic receptors in the human brain postmortem. Effect of suicide. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:1049–1053
Hatfield T, Spanis C, McGaugh JL (1999) Response of amygdalar norepinephrine to footshock and GABAergic drugs using in vivo microdialysis and HPLC. Brain Res 835:340–345. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01566-8
Hieble JP, Bylund DB, Clarke DE, Eikenburg DC, Langer SZ, Lefkowitz RJ, Minneman KP, Ruffolo RR Jr (1995) International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev 47:267–270
Hokfelt T, Fuxe K (1969) Cerebellar monoamine nerve terminals, a new type of afferent fibers to the cortex cerebelli. Exp Brain Res Exp Hirnforsch 9:63–72
Hull EM, Dominguez JM (2007) Sexual behavior in male rodents. Horm Behav 52:45–55. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.03.030
Hunt RD, Arnsten AF, Asbell MD (1995) An open trial of guanfacine in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 34:50–54. doi:10.1097/00004583-199501000-00013
Ji XH, Ji JZ, Zhang H, Li BM (2008) Stimulation of alpha2-adrenoceptors suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex of rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2263–2271. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301603
Kawaguchi Y, Shindou T (1998) Noradrenergic excitation and inhibition of GABAergic cell types in rat frontal cortex. J Neurosci 18:6963–6976
Kim J, Alger BE (2001) Random response fluctuations lead to spurious paired-pulse facilitation. J Neurosci 21:9608–9618
Kossl M, Vater M (1989) Noradrenaline enhances temporal auditory contrast and neuronal timing precision in the cochlear nucleus of the mustached bat. J Neurosci 9:4169–4178
Kulik A, Haentzsch A, Luckermann M, Reichelt W, Ballanyi K (1999) Neuron-glia signaling via alpha(1) adrenoceptor-mediated Ca(2+) release in Bergmann glial cells in situ. J Neurosci 19:8401–8408
Law-Tho D, Crepel F, Hirsch JC (1993) Noradrenaline decreases transmission of NMDA- and non-NMDA-receptor mediated monosynaptic EPSPs in rat prefrontal neurons in vitro. Eur J NeuroSci 5:1494–1500. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00217.x
Lehmenkuhler C, Walden J, Speckmann EJ (1991) Decrease of N-methyl-d-aspartate responses by noradrenaline in the rat motorcortex in vivo. Neurosci Lett 121:5–8. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(91)90635-7
Lei S, Deng PY, Porter JE, Shin HS (2007) Adrenergic facilitation of GABAergic transmission in rat entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 98:2868–2877. doi:10.1152/jn.00679.2007
Lepretre N, Mironneau J, Morel JL (1994) Both alpha 1A- and alpha 2A-adrenoreceptor subtypes stimulate voltage-operated l-type calcium channels in rat portal vein myocytes. Evidence for two distinct transduction pathways. J Biol Chem 269:29546–29552
Levy F (2008) Pharmacological and therapeutic directions in ADHD: specificity in the PFC. Behav Brain Funct 4:12. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-4-12
Li BM, Mei ZT (1994) Delayed-response deficit induced by local injection of the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine into the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in young adult monkeys. Behav Neural Biol 62:134–139. doi:10.1016/S0163-1047(05)80034-2
Liu X, Lonart G, Sanford LD (2007) Transient fear-induced alterations in evoked release of norepinephrine and GABA in amygdala slices. Brain Res 1142:46–53. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.038
Manunta Y, Edeline JM (1997) Effects of noradrenaline on frequency tuning of rat auditory cortex neurons. Eur J NeuroSci 9:833–847. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1997.tb01433.x
Manunta Y, Edeline JM (1998) Effects of noradrenaline on rate-level function of auditory cortex neurons: is there a “gating” effect of noradrenaline? Exp Brain Res Exp Hirnforsch 118:361–372
Manunta Y, Edeline JM (1999) Effects of noradrenaline on frequency tuning of auditory cortex neurons during wakefulness and slow-wave sleep. Eur J NeuroSci 11:2134–2150. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00633.x
Manunta Y, Edeline JM (2004) Noradrenergic induction of selective plasticity in the frequency tuning of auditory cortex neurons. J Neurophysiol 92:1445–1463. doi:10.1152/jn.00079.2004
McCormick DA, Prince DA (1986) Mechanisms of action of acetylcholine in the guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Physiol 375:169–194
McIntyre DC, Giugno L (1988) Effect of clonidine on amygdala kindling in normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-pretreated rats. Exp Neurol 99:96–106. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(88)90130-6
McIntyre DC, Kelly ME, Dufresne C (1991) Suppression of amygdala kindling with massed stimulation: effect of noradrenaline antagonists. Brain Res 561:279–284. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(91)91605-Z
Mouradian RD, Sessler FM, Waterhouse BD (1991) Noradrenergic potentiation of excitatory transmitter action in cerebrocortical slices: evidence for mediation by an alpha 1 receptor-linked second messenger pathway. Brain Res 546:83–95. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(91)91162-T
Mueller AL, Dunwiddie TV (1983) Anticonvulsant and proconvulsant actions of alpha- and beta-noradrenergic agonists on epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus in vitro. Epilepsia 24:57–64. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1983.tb04866.x
Neuman RS (1986) Suppression of penicillin-induced focal epileptiform activity by locus ceruleus stimulation: mediation by an alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Epilepsia 27:359–366. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03554.x
Pan ZZ, Grudt TJ, Williams JT (1994) alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat dorsal raphe neurons: regulation of two potassium conductances. J Physiol 478(Pt 3):437–447
Ramos BP, Arnsten AF (2007) Adrenergic pharmacology and cognition: focus on the prefrontal cortex. Pharmacol Ther 2006(Dec):28. [Epub ahead of print]
Randle JC, Bourque CW, Renaud LP (1986) alpha 1-adrenergic receptor activation depolarizes rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurons in vitro. Am J Physiol 251:R569–R574
Roozendaal B, Hui GK, Hui IR, Berlau DJ, McGaugh JL, Weinberger NM (2006) Basolateral amygdala noradrenergic activity mediates corticosterone-induced enhancement of auditory fear conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 86:249–255. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2006.03.003
Rutkowski RG, Miasnikov AA, Weinberger NM (2003) Characterisation of multiple physiological fields within the anatomical core of rat auditory cortex. Hear Res 181:116–130. doi:10.1016/S0378-5955(03)00182-5
Salgado H, Bellay T, Nichols JA, Bose M, Martinolich L, Perrotti L, Atzori M (2007) Muscarinic M2 and M1 receptors reduce GABA release by Ca2+ channel modulation through activation of PI3 K/Ca2+-independent and PLC/Ca2+-dependent PKC. J Neurophysiol 98:952–965. doi:10.1152/jn.00060.2007
Sato H, Fox K, Daw NW (1989) Effect of electrical stimulation of locus coeruleus on the activity of neurons in the cat visual cortex. J Neurophysiol 62:946–958
Schwinn DA, Page SO, Middleton JP, Lorenz W, Liggett SB, Yamamoto K, Lapetina EG, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Cotecchia S (1991) The alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor: characterization of signal transduction pathways and mammalian tissue heterogeneity. Mol Pharmacol 40:619–626
Seguela P, Watkins KC, Geffard M, Descarries L (1990) Noradrenaline axon terminals in adult rat neocortex: an immunocytochemical analysis in serial thin sections. Neuroscience 35:249–264. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(90)90079-J
Stanton PK, Mody I, Zigmond D, Sejnowski T, Heinemann U (1992) Noradrenergic modulation of excitability in acute and chronic model epilepsies. Epilepsy Res Suppl 8:321–334
Stone EA, Quartermain D (1999) alpha-1-noradrenergic neurotransmission, corticosterone, and behavioral depression. Biol Psychiatry 46:1287–1300. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00234-6
Stone EA, Zhang Y, Rosengarten H, Yeretsian J, Quartermain D (1999) Brain alpha 1-adrenergic neurotransmission is necessary for behavioral activation to environmental change in mice. Neuroscience 94:1245–1252. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(99)00394-2
Summers RJ, Papaioannou M, Harris S, Evans BA (1995) Expression of beta 3-adrenoceptor mRNA in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol 116:2547–2548
Thiel CM (2007) Pharmacological modulation of learning-induced plasticity in human auditory cortex. Restor Neurol Neurosci 25:435–443
Timmons SD, Geisert E, Stewart AE, Lorenzon NM, Foehring RC (2004) alpha2-Adrenergic receptor-mediated modulation of calcium current in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Brain Res 1014:184–196. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.025
Tobey EA, Devous MD Sr, Buckley K, Overson G, Harris T, Ringe W, Martinez-Verhoff J (2005) Pharmacological enhancement of aural habilitation in adult cochlear implant users. Ear Hear 26:45S–56S. doi:10.1097/00003446-200508001-00007
Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Kohno Y, Ida Y, Hoaki Y, Iimori K, Nakagawa R, Nishikawa T, Nagasaki N (1983) Daily increase in noradrenaline turnover in brain regions of activity-stressed rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:393–396. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(83)90107-7
Tully K, Li Y, Tsvetkov E, Bolshakov VY (2007) Norepinephrine enables the induction of associative long-term potentiation at thalamo-amygdala synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14146–14150. doi:10.1073/pnas.0704621104
Videen TO, Daw NW, Rader RK (1984) The effect of norepinephrine on visual cortical neurons in kittens and adult cats. J Neurosci 4:1607–1617
Waterhouse BD, Moises HC, Woodward DJ (1980) Noradrenergic modulation of somatosensory cortical neuronal responses to iontophoretically applied putative neurotransmitters. Exp Neurol 69:30–49. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(80)90141-7
Waterhouse BD, Moises HC, Woodward DJ (1981) Alpha-receptor-mediated facilitation of somatosensory cortical neuronal responses to excitatory synaptic inputs and iontophoretically applied acetylcholine. Neuropharmacology 20:907–920. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(81)90020-4
Waterhouse BD, Sessler FM, Cheng JT, Woodward DJ, Azizi SA, Moises HC (1988) New evidence for a gating action of norepinephrine in central neuronal circuits of mammalian brain. Brain Res Bull 21:425–432. doi:10.1016/0361-9230(88)90154-2
Weiss GK, Lewis J, Jimenez-Rivera C, Vigil A, Corcoran ME (1990) Antikindling effects of locus coeruleus stimulation: mediation by ascending noradrenergic projections. Exp Neurol 108:136–140. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(90)90020-S
Zucker RS, Regehr WG (2002) Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 64:355–405. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.092501.114547
Acknowledgments
The study has been funded by NIH/NIDCD R01DC005986-04. We would like to thanks Mr. J. Nichols for critical and English revision of the manuscript, and Mrs. M. Bose for the biocytin development and artwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinh, L., Nguyen, T., Salgado, H. et al. Norepinephrine Homogeneously Inhibits α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate- (AMPAR-) Mediated Currents in All Layers of the Temporal Cortex of the Rat. Neurochem Res 34, 1896–1906 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9966-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9966-z