Abstract
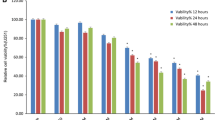
Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthaquinone), an active component present in the root and rhizome of Rheum palmatum L. (Polygonaceae) has anti-bacterial, anti-tumor, diuretic and vasorelaxant effects. However, its mechanism of action on the cell migration and invasion of human neuroblastoma cancer SH-SY5Y cells is not fully understood. In this study, firstly, the effects of emodin on the percentage of viable cells were examined by using MTT assay and it was found that emodin induced dose-and time-dependent inhibition in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Second, the effects of emodin on the migration and invasion of SH-SY5Y cells were examined by using wound assay and matrigel counting and the results showed that emodin suppressed the migration and invasion of SH-SY5Y cells. Third, we examined the effect of emodin on the levels of associated proteins by using Western blotting and the results indicated that emodin inhibited the levels of GRB2, RhoA, HIF-1α, VEGF, FAK, iNOS, COX2, p-p38, p-c-jun, MMP2, MMP9 and MMP7 but promoted the levels of PKC, PI3K, MEKK3 and NF-κB p65 that led to the inhibition of migration and invasion of SH-SY5Y cells in vitro.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Entschladen F, Drell TLt, Lang K, Joseph J, Zaenker KS (2004) Tumour-cell migration, invasion, and metastasis: navigation by neurotransmitters. Lancet Oncol 5:254–258. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(04)01431-7
Sporn MB (1996) The war on cancer. Lancet 347:1377–1381. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)91015-6
Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J, Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E, Peeper DS (2004) Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature 430:1034–1039
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M (2003) Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol 21:1624–1636. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.05.063
Haga A, Funasaka T, Niinaka Y, Raz A, Nagase H (2003) Autocrine motility factor signaling induces tumor apoptotic resistance by regulations Apaf-1 and Caspase-9 apoptosome expression. Int J Cancer 107:707–714. doi:10.1002/ijc.11449
Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R (2005) Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol 23:2411–2422. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.089
Liang JW, Hsiu SL, Huang HC, Lee Chao PD (1993) HPLC analysis of emodin in serum, herbs and Chinese herbal prescriptions. J Food Drug Anal 09:251–257
Tsai TH, Chen CF (1992) Ultraviolet spectrum identification of emodin in rabbit plasma by HPLC and its pharmacokinetics application Asia Pacific. J Pharmacol 7:53–56
Huang HC, Chu SH, Chao PD (1991) Vasorelaxants from Chinese herbs, emodin and scoparone, possess immunosuppressive properties. Eur J Pharmacol 198:211–213. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90624-Y
Koyama M, Kelly TR, Watanabe KA (1988) Novel type of potential anticancer agents derived from chrysophanol and emodin. Some structure-activity relationship studies. J Med Chem 31:283–284. doi:10.1021/jm00397a002
Zhou XM, Chen QH (1988) Biochemical study of Chinese rhubarb. XXII. Inhibitory effect of anthraquinone derivatives on Na+-K+-ATPase of the rabbit renal medulla and their diuretic action. Yao Xue Xue Bao 23:17–20
Huang Q, Shen HM, Ong CN (2004) Inhibitory effect of emodin on tumor invasion through suppression of activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB. Biochem Pharmacol 68:361–371. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2004.03.032
Wang C, Wu X, Chen M, Duan W, Sun L, Yan M et al (2007) Emodin induces apoptosis through caspase 3-dependent pathway in HK-2 cells. Toxicology 231:120–128. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.11.064
Brown M, Bellon M, Nicot C (2007) Emodin and DHA potently increase arsenic trioxide interferon-alpha-induced cell death of HTLV-I-transformed cells by generation of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of Akt and AP-1. Blood 109:1653–1659
Wang R, Wan Q, Zhang Y, Huang F, Yu K, Xu D et al (2007) Emodin suppresses interleukin-1beta induced mesangial cells proliferation and extracellular matrix production via inhibiting P38 MAPK. Life Sci 80:2481–2488. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.04.010
Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Lin JP, Lee JH, Lin CC, Su CC et al (2007) Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana radix inhibit invasion and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 27:2377–2384
Fishman DA, Liu Y, Ellerbroek SM, Stack MS (2001) Lysophosphatidic acid promotes matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activation and MMP-dependent invasion in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:3194–3199
Huang YT, Hwang JJ, Lee LT, Liebow C, Lee PP, Ke FC et al (2002) Inhibitory effects of a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist on basal and epidermal growth factor-induced cell proliferation and metastasis-associated properties in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Int J Cancer 99:505–513. doi:10.1002/ijc.10373
Pilcher BK, Dumin JA, Sudbeck BD, Krane SM, Welgus HG, Parks WC (1997) The activity of collagenase-1 is required for keratinocyte migration on a type I collagen matrix. J Cell Biol 137:1445–1457. doi:10.1083/jcb.137.6.1445
Kwak HJ, Park MJ, Park CM, Moon SI, Yoo DH, Lee HC et al (2006) Emodin inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-A-induced angiogenesis by blocking receptor-2 (KDR/Flk-1) phosphorylation. Int J Cancer 118:2711–2720. doi:10.1002/ijc.21641
Lu Y, Zhang J, Qian J (2008) The effect of emodin on VEGF receptors in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:222–228. doi:10.1089/cbr.2007.0425
Cha TL, Qiu L, Chen CT, Wen Y, Hung MC (2005) Emodin down-regulates androgen receptor and inhibits prostate cancer cell growth. Cancer Res 65:2287–2295. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3250
Huang HC, Lee CR, Chao PD, Chen CC, Chu SH (1991) Vasorelaxant effect of emodin, an anthraquinone from a Chinese herb. Eur J Pharmacol 205:289–294. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90912-A
Cai J, Razzak A, Hering J, Saed A, Babcock TA, Helton S et al (2008) Feasibility evaluation of emodin (rhubarb extract) as an inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation in vitro. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 32:190–196. doi:10.1177/0148607108314371
Guo J, Xiao B, Liu Q, Gong Z, Le Y (2008) Suppression of C-myc expression associates with anti-proliferation of aloe-emodin on gastric cancer cells. Cancer Invest 26:369–374. doi:10.1080/07357900701788130
Kim HR, Kim K, Lee KH, Kim SJ, Kim J (2008) Inhibition of casein kinase 2 enhances the death ligand- and natural kiler cell-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell death. Clin Exp Immunol 152:336–344
Wang XD, Gu LQ, Wu JY (2007) Apoptosis-inducing activity of new pyrazole emodin derivatives in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 30:1113–1116. doi:10.1248/bpb.30.1113
Huang Q, Shen HM, Ong CN (2005) Emodin inhibits tumor cell migration through suppression of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Cdc42/Rac1 pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:1167–1175. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5050-2
Kim JH, Na HJ, Kim CK, Kim JY, Ha KS, Lee H et al (2008) The non-provitamin A carotenoid, lutein, inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression through redox-based regulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/Akt and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase pathways: role of H(2)O(2) in NF-kappaB activation. Free Radic Biol Med 45:885–896. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.06.019
Mathes E, O’Dea EL, Hoffmann A, Ghosh G (2008) NF-kappaB dictates the degradation pathway of IkappaBalpha. EMBO J 27:1357–1367. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.73
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev 2:563–572
Morozevich GE, Kozlova NI, Cheglakov IB, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, Berman AE (2008) Implication of alpha5beta1 integrin in invasion of drug-resistant MCF-7/ADR breast carcinoma cells: a role for MMP-2 collagenase. Biochemistry 73:791–796
Nagase H, Woessner JF Jr (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 274:21491–21494. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.31.21491
Stetler-Stevenson WG (1996) Dynamics of matrix turnover during pathologic remodeling of the extracellular matrix. Am J Pathol 148:1345–1350
Rydlova M, Holubec L Jr, Ludvikova M Jr, Kalfert D, Franekova J, Povysil C et al (2008) Biological activity and clinical implications of the matrix metalloproteinases. Anticancer Res 28:1389–1397
Park SK, Han SB, Lee K, Lee HJ, Kho YH, Chun H et al (2006) Gelastatins and their hydroxamates as dual functional inhibitors for TNF-alpha converting enzyme and matrix metalloproteinases: synthesis, biological evaluation, and mechanism studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:627–634. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.219
Chantrain CF, Shimada H, Jodele S, Groshen S, Ye W, Shalinsky DR et al (2004) Stromal matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulates the vascular architecture in neuroblastoma by promoting pericyte recruitment. Cancer Res 64:1675–1686. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-0160
Ribatti D, Marimpietri D, Pastorino F, Brignole C, Nico B, Vacca A et al (2004) Angiogenesis in neuroblastoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1028:133–142. doi:10.1196/annals.1322.014
Ara T, Fukuzawa M, Kusafuka T, Komoto Y, Oue T, Inoue M et al (1998) Immunohistochemical expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and TIMP-2 in neuroblastoma: association with tumor progression and clinical outcome. J Pediatr Surg 33:1272–1278. doi:10.1016/S0022-3468(98)90167-1
Cheng Y, Dong Q, Sun LR, Yang CM, Jiang BX (2005) Correlation between expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-2, TIMP-1 and metastasis of neuroblastoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 27:164–166
Sugiura Y, Shimada H, Seeger RC, Laug WE, DeClerck YA (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 are expressed in human neuroblastoma: contribution of stromal cells to their production and correlation with metastasis. Cancer Res 58:2209–2216
Heslin MJ, Yan J, Johnson MR, Weiss H, Diasio RB, Urist MM (2001) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal carcinogenesis. Ann Surg 233:786–792. doi:10.1097/00000658-200106000-00008
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant CMU97-086 from China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, HF., Lai, KC., Hsu, SC. et al. Involvement of Matrix Metalloproteinases on the Inhibition of Cells Invasion and Migration by Emodin in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurochem Res 34, 1575–1583 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9946-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9946-3