Abstract
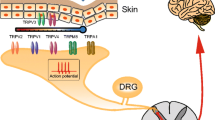
Transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) is specifically expressed in the nociceptive receptors and can detect a variety of noxious stimuli, thus potentiating pain sensitization. While peripheral delivery of capsaicin causes the desensitization of sensory neurons, thus alleviating pain. Therefore capsaicin is used in the clinical treatment of various types of pain; however, these treatments will bring many side effects, such as a strong burning pain in the early stages of treatment which hampers the further use of capsaicin. Thus, the studies of the functional regulation of TRPV1 are mainly focused on two aspects: to develop more potent analogues of capsaicin with less side effects; or to elucidate the mechanisms of TRPV1 in pain sensitivity, especially of that TRPV1 as a target of various protein kinases such as PKD1 and Cdk5 is involved pain hypersensitivity. Thus we would summarize the progress of these two aspects in this mini review.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadesi S, Cottrell GS, Divino L, Chapman K, Grady EF, Bautista F, Karanjia R, Barajas-Lopez C, Vanner S, Vergnolle N, Bunnett NW (2006) Protease-activated receptor 2 sensitizes TRPV1 by protein kinase Cepsilon- and A-dependent mechanisms in rats and mice. J Physiol 575:555–571
Bevan S, Szolcsanyi J (1990) Sensory neuron-specific actions of capsaicin: mechanisms and applications. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:330–333
Carrasquillo Y, Gereau RW (2007) Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the amygdala modulates pain perception. J Neurosci 27:1543–1551
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389:816–824
Davis JB, Gray J, Gunthorpe MJ, Hatcher JP, Davey PT, Overend P, Harries MH, Latcham J, Clapham C, Atkinson K, Hughes SA, Rance K, Grau E, Harper AJ, Pugh PL, Rogers DC, Bingham S, Randall A, Sheardown SA (2000) Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature 405:183–187
De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V (2005) Lipids as regulators of the activity of transient receptor potential type V1 (TRPV1) channels. Life Sci 77:1651–1666
Dhavan R, Tsai LH (2001) A decade of CDK5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:749–759
Diaz Anel AM, Malhotra V (2005) PKCeta is required for beta1gamma2/beta3gamma2- and PKD-mediated transport to the cell surface and the organization of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol 169:83–91
Haworth RS, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E, Avkiran M (1999) Protein kinase D inhibits plasma membrane Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activity. Am J Physiol 277:C1202–C1209
Hellmich MR, Pant HC, Wada E, Battey JF (1992) Neuronal cdc2-like kinase: a cdc2-related protein kinase with predominantly neuronal expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10867–10871
Holzer P (1988) Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience 24:739–768
Hwang SW, Cho H, Kwak J, Lee SY, Kang CJ, Jung J, Cho S, Min KH, Suh YG, Kim D, Oh U (2000) Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6155–6160
Jamora C, Yamanouye N, Van Lint J, Laudenslager J, Vandenheede JR, Faulkner DJ, Malhotra V (1999) Gbetagamma-mediated regulation of Golgi organization is through the direct activation of protein kinase D. Cell 98:59–68
Ji RR, Kawasaki Y, Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang YQ (2007) Protein kinases as potential targets for the treatment of pathological pain. Handb Exp Pharmacol 359–389
Ji RR, Samad TA, Jin SX, Schmoll R, Woolf CJ (2002) p38 MAPK activation by NGF in primary sensory neurons after inflammation increases TRPV1 levels and maintains heat hyperalgesia. Neuron 36:57–68
Ji RR, Strichartz G (2004) Cell signaling and the genesis of neuropathic pain. Sci STKE 2004:reE14
Ji RR, Woolf CJ (2001) Neuronal plasticity and signal transduction in nociceptive neurons: implications for the initiation and maintenance of pathological pain. Neurobiol Dis 8:1–10
Johannes FJ, Prestle J, Eis S, Oberhagemann P, Pfizenmaier K (1994) PKCu is a novel, atypical member of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem 269:6140–6148
Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH (2000) Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by calpain. Nature 405:360–364
Lew J, Huang QQ, Qi Z, Winkfein RJ, Aebersold R, Hunt T, Wang JH (1994) A brain-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371:423–426
Lew J, Winkfein RJ, Paudel HK, Wang JH (1992) Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem 267:25922–25926
Li BS, Sun MK, Zhang L, Takahashi S, Ma W, Vinade L, Kulkarni AB, Brady RO, Pant HC (2001) Regulation of NMDA receptors by cyclin-dependent kinase-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12742–12747
Liljedahl M, Maeda Y, Colanzi A, Ayala I, Van Lint J, Malhotra V (2001) Protein kinase D regulates the fission of cell surface destined transport carriers from the trans-Golgi network. Cell 104:409–420
Matta JA, Miyares RL, Ahern GP (2007) TRPV1 is a novel target for omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Physiol 57:397–411
Morenilla-Palao C, Planells-Cases R, Garcia-Sanz N, Ferrer-Montiel A (2004) Regulated exocytosis contributes to protein kinase C potentiation of vanilloid receptor activity. J Biol Chem 279:25665–25672
Nurse P (1990) Univerasl control mechanism regultion onset of M-phase. Nature 344:503–508
Pareek TK, Keller J, Kesavapany S, Agarwal N, Kuner R, Pant HC, Iadarola MJ, Brady RO, Kulkarni AB (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates nociceptive signaling through direct phosphorylation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:660–665
Pareek TK, Keller J, Kesavapany S, Pant HC, Iadarola MJ, Brady RO, Kulkarni AB (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity regulates pain signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:791–796
Rains C, Bryson HM (1995) Topical capsaicin. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and osteoarthritis. Drugs Aging 7:317–328
Robbins W (2000) Clinical applications of capsaicinoids. Clin J Pain 16:S86–S89
Shin J, Cho H, Hwang SW, Jung J, Shin CY, Lee SY, Kim SH, Lee MG, Choi YH, Kim J, Haber NA, Reichling DB, Khasar S, Levine JD, Oh U (2002) Bradykinin-12-lipoxygenase-VR1 signaling pathway for inflammatory hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10150–10155
Storz P, Doppler H, Toker A (2004) Protein kinase Cdelta selectively regulates protein kinase D-dependent activation of NF-kappaB in oxidative stress signaling. Mol Cell Biol 24:2614–2626
Storz P, Toker A (2003) Protein kinase D mediates a stress-induced NF-kappaB activation and survival pathway. EMBO J 22:109–120
Sugiura T, Tominaga M, Katsuya H, Mizumura K (2002) Bradykinin lowers the threshold temperature for heat activation of vanilloid receptor 1. J Neurophysiol 88:544–548
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1989) Resiniferatoxin, a phorbol-related diterpene, acts as an ultrapotent analog of capsaicin, the irritant constituent in red pepper. Neuroscience 30:515–520
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1993) Mechanisms and therapeutic potential of vanilloids (capsaicin-like molecules). Adv Pharmacol 24:123–155
Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O, Wang JH (1995) An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator. J Biol Chem 270:26897–26903
Tominaga M, Caterina MJ, Malmberg AB, Rosen TA, Gilbert H, Skinner K, Raumann BE, Basbaum AI, Julius D (1998) The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron 21:531–543
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness VS Jr, Chae T, Harlow E (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371:419–423
Valverde AM, Sinnett-Smith J, Van Lint J, Rozengurt E (1994) Molecular cloning and characterization of protein kinase D: a target for diacylglycerol and phorbol esters with a distinctive catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8572–8576
Wahl P, Foged C, Tullin S, Thomsen C (2001) Iodo-resiniferatoxin, a new potent vanilloid receptor antagonist. Mol Pharmacol 59:9–15
Wang Y, Kedei N, Wang M, Wang QJ, Huppler AR, Toth A, Tran R, Blumberg PM (2004) Interaction between protein kinase Cmu and the vanilloid receptor type 1. J Biol Chem 279:53674–53682
Wang Y, Szabo T, Welter JD, Toth A, Tran R, Lee J, Kang SU, Suh YG, Blumberg PM, Lee J (2002) High affinity antagonists of the vanilloid receptor. Mol Pharmacol 62:947–956
Wang Y, Toth A, Tran R, Szabo T, Welter JD, Blumberg PM, Lee J, Kang SU, Lim JO, Lee J (2003) High-affinity partial agonists of the vanilloid receptor. Mol Pharmacol 64:325–333
Woolf CJ, Salter MW (2000) Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science 288:1765–1769
Yang YR, He Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Li Y, Han Y, Zhu H, Wang Y (2007) Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) in primary sensory and dorsal horn neurons by peripheral inflammation contributes to heat hyperalgesia. Pain 127:109–120
Zhang H, Cang CL, Kawasaki Y, Liang LL, Zhang YQ, Ji RR, Zhao ZQ (2007) Neurokinin-1 receptor enhances TRPV1 activity in primary sensory neurons via PKCepsilon: a novel pathway for heat hyperalgesia. J Neurosci 27:12067–12077
Zhu H, Yang Y, Zhang H, Han Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Yin D, He Q, Zhao Z, Blumberg PM, Han J, Wang Y (2007) Interaction between protein kinase D1 and transient receptor potential V1 in primary sensory neurons is involved in heat hypersensitivity. Pain
Zhuang ZY, Xu H, Clapham DE, Ji RR (2004) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activates ERK in primary sensory neurons and mediates inflammatory heat hyperalgesia through TRPV1 sensitization. J Neurosci 24:8300–8309
Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA, Chuang H, Sorgard M, Di Marzo V, Julius D, Hogestatt ED (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400:452–457
Acknowledgments
All the works were supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30371635, 303330230 and 30770703), a grant from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7072040), and a grant from the specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20060001121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue article in honor of Dr. Ji-Sheng Han.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y. The Functional Regulation of TRPV1 and Its Role in Pain Sensitization. Neurochem Res 33, 2008–2012 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9750-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9750-5