Abstract
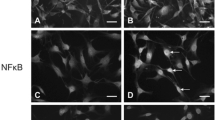
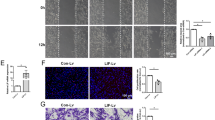
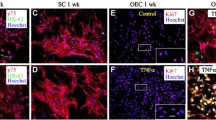
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) derived from activated Schwann cells (SCs) play a critical role as a pleiotropic mediator. In this study, we examined the function of TNF-α as an inflammatory mediator in SCs activation. TNF-α exhibits its biological effect through two distinct surface receptors, TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) and TNFR2. We show here that cultured SCs express both TNFR1 and TNFR2, and that activation of these receptors by TNF-α promotes expression of TNF-α. Meanwhile, TNF-α also increased the production of other inflammatory mediators. Furthermore, TNF-α is involved in the induction of apoptosis through binding to TNFR in SCs. The activation of SCs by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is partially mediated by SCs-derived TNF-α. These findings suggest the existence of a positive feedback loop in the activation of SC via TNF-α. This loop may be involved in the prolonged activation of SCs. Acute or chronic stimulation of TNF-α by SC at sites of PNS inflammation may be critical in determining whether TNF-α has activational, inflammatory, or cytotoxic effects on these cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raine CS, Bonetti B, Cannella B (1998) Multiple sclerosis: expression of molecules of the tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptor families in relationship to the demyelinated plaque. Rev Neurol (Paris) 154 (8–9):577–585
MacEwan DJ (2002) TNF receptor subtype signalling: differences and cellular consequences. Cell Signal 14(6):477–492
McFarlane SM, Pashmi G, Connell MC, Littlejohn AF, Tucker SJ, Vandenabeele P, MacEwan DJ (2002) Differential activation of nuclear factor-kappaB by tumour necrosis factor receptor subtypes TNFR1 predominates whereas TNFR2 activates transcription poorly. FEBS Lett 515(1–3):119–126
Baud V, Karin M (2001) Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 11(9):372–377
Hu S, Peterson PK, Chao CC (1997) Cytokine-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Neurochem Int 30(4–5):427–431
Bruck W, Stadelmann C (2003) Inflammation and degeneration in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci 24(Suppl. 5):S265–S267
Melton LM, Keith AB, Davis S, Oakley AE, Edwardson JA, Morris CM (2003) Chronic glial activation, neurodegeneration, and APP immunoreactive deposits following acute administration of double-stranded RNA. Glia 44(1):1–12
Banati RB, Newcombe J, Gunn RN, Cagnin A, Turkheimer F, Heppner F, Price G, Wegner F, Giovannoni G, Miller DH, Perkin GD, Smith T, Hewson AK, Bydder G, Kreutzberg GW, Jones T, Cuzner ML, Myers R (2000) The peripheral benzodiazepine binding site in the brain in multiple sclerosis: quantitative in vivo imaging of microglia as a measure of disease activity. Brain 123(Pt 11):2321–2337
Armati PJ, Pollard JD (1996) Immunology of the Schwann Cell. Baillieres Clin Neurol 5(1):47–64
Lisak P, Skundric D, Bealmear B, Ragheb S (1997) The role of cytokines in Schwann cell damage, protection, and repair. J Infect Dis 176(Suppl.2):S173–S179
Orlikowski D, Chazaud B, Plonquet A, Poron F, Sharshar T, Maison P, Raphael JC, Gherardi RK, Creange A (2003) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and chemokine receptor CCR2 productions in Guillain-Barre syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis. J Neuroimmunol 134(1–2):118–127
Cheng C, Qin Y, Shao X, Wang H, Gao Y, Cheng M, Shen A (2007) Induction of TNF-α by LPS in Schwann cell is regulated by MAPK activation signals, Cell Mol Neurobiol doi:10.1007/s10571-007-9215-4
Brockes JP, Fields KL, Raff MC (1979) Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res 165(1):105–118
Muñoz-Fernández MA, Fresno M (1998) The role of tumour necrosis factor, interleukin6, interferon-gamma and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the development and pathology of the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 56(3):307–340
Ronet C, Darche S, Leite de Moraes M, Miyake S, Yamamura T, Louis JA, Kasper LH, Buzoni-Gatel D (2005) NKT cells are critical for the initiation of an inflammatory bowel response against Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 175(2):899–908
Murray PJ (2005) The primary mechanism of the IL-10-regulated anti-inflammatory response is to selectively inhibit transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(24):8686–8691
Ware CF, Crowe PD, Vanarsdale TL, Andrews JL, Grayson MH, Jerzy R, Smith CA, Goodwin RG (1991) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor expression in T lymphocytes: Differential regulation of the type 1 TNF receptor during activation of resting and effector T cells. J Immunol 147(12):4229–4238
Vilcek J, Lee TH (1991) Tumor necrosis factor: new insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem 266(12):7313–7316
Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV (1994) A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78(4):681–692
Hsu H, Shu HB, Pan MG, Goeddel DV (1996) TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 84(2):299–308
Tartaglia LA, Weber RF, Figari IS, Reynolds C, Palladino MA Jr, Goeddel DV (1991) The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(20):9292–9296
Pan W, Zadina JE, Harlan RE, Weber JT, Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a neuromodulator in the CNS. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21(5):603–613
Merrill JE, Ignarro LJ, Sherman MP, Melinek J, Lane TE (1993) Microglial cell cytotoxicity of oligodendrocytes is mediated through nitric oxide. J Immunol 151(4):2132–2141
Nishie M, Mori F, Ogawa M, Sannohe S, Tanno K, Kurahashi K, Kuroda N, Wakabayashi K (2004) Multinucleated astrocytes in old demyelinated plaques in a patient with multiple sclerosis. Neuropathology 24(3):248–253
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); Grant numbers: 30300099, 30500153, 30770488.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yongwei Qin and Chun Cheng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Cheng, C., Wang, H. et al. TNF-α as an Autocrine Mediator and its Role in the Activation of Schwann Cells. Neurochem Res 33, 1077–1084 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9552-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9552-1