Abstract
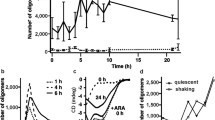
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, like arachidonic acid, can bind proteins and affect their function. The 14-3-3 proteins bind phosphorylated sites on a diverse array of client proteins and, in this way, are involved in many intracellular signaling pathways. In this study, we used a novel approach to discover that 14-3-3ζ is able to directly bind arachidonic acid. Furthermore, arachidonic acid, at physiological concentrations, reduced the binding of 14-3-3ζ to phosphorylated BAD, an interaction that is important in regulating apoptosis. In addition, high concentrations of arachidonic acid caused the polymerization of 14-3-3ζ, an event observed in neurodegenerative disorders. Taken together, these results indicate that arachidonic acid directly interacts with 14-3-3ζ and that this interaction may be important in both normal and pathological cellular events. If so, then factors that mediate the release, metabolism and reacylation of arachidonic acid into membranes represent key points of regulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Arachidonic acid
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- LDH-A:
-
l-Lactate dehydrogenase A chain
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight
- pBAD:
-
Phosphorylated BAD
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
- RBL:
-
Rat basophilic leukemia
References
Tzivion G, Avruch J (2002) 14-3-3 proteins: active cofactors in cellular regulation by serine/threonine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 277:3061–3064
Bridges D, Moorhead GB (2005) 14-3-3 proteins: a number of functions for a numbered protein. Sci STKE re10/DC2
Darling DL, Yingling J, Wynshaw-Boris A (2005) Role of 14-3-3 proteins in eukaryotic signaling and development. Curr Top Dev Biol 68:281–315
Dougherty MK, Morrison DK (2004) Unlocking the code of 14-3-3. J Cell Sci 117:1875–1884
Masters SC, Fu H (2001) 14-3-3 proteins mediate an essential anti-apoptotic signal. J Biol Chem 276:45193–45200
Porter GW, Khuri FR, Fu H (2006) Dynamic 14-3-3/client protein interactions integrate survival and apoptotic pathways. Semin Cancer Biol 16:193–202
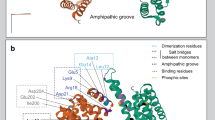
Yang H, Masters SC, Wang H, Fu H (2001) The proapoptotic protein Bad binds the amphipathic groove of 14-3-3zeta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1547:313–319
Subramanian R, Masters S, Zhang H, Fu H (2001) Functional conservation of 14-3-3 isoforms in inhibiting bad-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 271:142–151
Chiang CW, Kanies C, Kim KW et al (2003) Protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylation of phosphoserine 112 plays the gatekeeper role for BAD-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 23:6350–6362
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ (1996) Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L). Cell 87:619–628
Maslyar DJ, Aoki M, Vogt PK (2001) The growth-promoting activity of the Bad protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts requires binding to protein 14-3-3. Oncogene 20:5087–5092
Berg D, Holzmann C, Riess O (2003) 14-3-3 proteins in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:752–762
Layfield R, Fergusson J, Aitken A, Lowe J, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1996) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease brains contain 14-3-3 proteins. Neurosci Lett 209:57–60
Fountoulakis M, Cairns N, Lubec G (1999) Increased levels of 14-3-3 gamma and epsilon proteins in brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome. J Neural Transm Suppl 57:323–335
Umahara T, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K et al (2004) 14-3-3 proteins and zeta isoform containing neurofibrillary tangles in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 108:279–286
Soulié C, Nicole A, Delacourte A, Ceballos-Picot I (2004) Examination of stress-related genes in human temporal versus occipital cortex in the course of neurodegeneration: involvement of 14-3-3ζ in this dynamic process. Neurosci Lett 365:1–5
Waelter S, Boeddrich A, Lurz R et al (2001) Accumulation of mutant huntingtin fragments in aggresome-like inclusion bodies as a result of insufficient protein degradation. Mol Biol Cell 12:1393–1407
Umahara T, Uchihara T, Tsuchiya K et al (2001) Immunolocalization of 14-3-3 isoforms in brains with Pick body disease. Neurosci Lett 371:215–219
Wiltfang J, Otto M, Baxter HC et al (1999) Isoform pattern of 14-3-3 proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurochem 73:2485–2490
Krasnianski A, Meissner B, Schulz-Schaeffer W et al (2006) Clinical features and diagnosis of the MM2 cortical subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol 63:876–880
Hayakawa M, Ishida N, Takeuchi K et al (1993) Arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic phospholipase A2 is crucial in the cytotoxic action of tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem 268:11290–11295
Levrat C, Louisot P (1996) Increase of mitochondrial PLA2-released fatty acids is an early event in tumor necrosis factor alpha-treated WEHI-164 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 221:531–538
Baskin DS, Ngo H, Didenko V (2003) Thimerosal induces DNA breaks, caspase-3 activation, membrane damage, and cell death in cultured human neurons and fibroblasts. Toxicol Sci 74:361–368
Woo KJ, Lee TJ, Bae JH et al (2006) Thimerosal induces apoptosis and G2/M phase arrest in human leukemia cells. Mol Carcinogen 45:657–666
Pérez R, Matabosch X, Llebaria A, Balboa MA, Balsinde J (2006) Blockade of arachidonic acid incorporation into phospholipids induces apoptosis in U937 promonocytic cells. J Lipid Res 47:484–491
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79:1431–1568
Wilson DM, Binder LI (1997) Free fatty acids stimulate the polymerization of tau and amyloid beta peptides. In vitro evidence for a common effector of pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 150:2181–2195
King ME, Gamblin TC, Kuret J, Binder LI (2000) Differential assembly of human tau isoforms in the presence of arachidonic acid. J Neurochem 74:1749–1757
Luo ZJ, Zhang XF, Rapp U, Avruch J (1995) Identification of the 14.3.3 zeta domains important for self-association and Raf binding. J Biol Chem 270:23681–23687
Brock TG, Paine RI, Peters-Golden M (1994) Localization of 5-lipoxygenase to the nucleus of unstimulated rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 269:22059–22066
Raza H, Pongubala J, Sorof S (1989) Specific high affinity binding of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid by liver fatty acid binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:448–455
Roth D, Morgan A, Martin H et al (1994) Characterization of 14-3-3 proteins in adrenal chromaffin cells and demonstration of isoform-specific phospholipid binding. Biochem J 301:305–310
Jones DH, Martin H, Madrazo J et al (1995) Expression and structural analysis of 14-3-3 proteins. J Mol Biol 245:375–384
Lawrence JW, Kroll DJ, Eacho PI (2000) Ligand-dependent interaction of hepatic fatty acid-binding protein with the nucleus. J Lipid Res 41:1390–1401
Huang H, Starodub O, McIntosh A, Kier AB, Schroeder F (2002) Liver fatty acid-binding protein targets fatty acids to the nucleus. Real time confocal and multiphoton fluorescence imaging in living cells. J Biol Chem 277:29139–23151
Phillis JW, O’Regan MH (2004) A potentially critical role of phospholipases in central nervous system ischemic, traumatic, and neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 44:13–47
Baethmann A, Maier-Hauff K, Schürer L et al (1989) Release of glutamate and of free fatty acids in vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg 70:578–291
Siesjö BK, Ingvar M, Westerberg E (1982) The influence of bicuculline-induced seizures on free fatty acid concentrations in cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. J Neurochem 39:796–802
Yoshida S, Harik SI, Busto R, Santiso M, Martinez E, Ginsberg MD (1984) Free fatty acids and energy metabolites in ischemic cerebral cortex with noradrenaline depletion. J Neurochem 42:711–717
Meller R, Schindler CK, Chu XP et al (2003) Seizure-like activity leads to the release of BAD from 14-3-3 protein and cell death in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Cell Death Differ 10:539–547
Chen XQ, Fung YW, Yu AC (2005) Association of 14-3-3gamma and phosphorylated bad attenuates injury in ischemic astrocytes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:338–347
Perrin RJ, Woods WS, Clayton DF, George JM (2001) Exposure to long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids triggers rapid multimerization of synucleins. J Biol Chem 276:41958–41962
Hashiguchi M, Sobue K, Paudel H (2000) 14-3-3ζ is an effector of tau protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 275:25247–25254
Hernández F, Cuadros R, Avila J (2004) Zeta 14-3-3 protein favours the formation of human tau fibrillar polymers. Neurosci Lett 357:143–146
Sugimori K, Kobayashi K, Kitamura T, Sudo S, Koshino Y (2007) 14-3-3 protein beta isoform is associated with 3-repeat tau neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 61:159–167
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by generous funding from the Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program at the University of Michigan, as well as by National Institutes of Health Grant R01 AI43574. The technical expertise of John Allard is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brock, T.G. Arachidonic Acid Binds 14-3-3ζ, Releases 14-3-3ζ from Phosphorylated BAD and Induces Aggregation of 14-3-3ζ. Neurochem Res 33, 801–807 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9498-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9498-3