Abstract
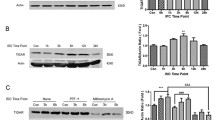
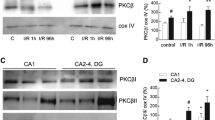
Transient global brain ischemia induces dysfunctions of mitochondria including disturbance in mitochondrial protein synthesis and inhibition of respiratory chain complexes. Due to capacity of mitochondria to release apoptogenic proteins, ischemia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is considered to be a key event coupling cerebral blood flow arrest to neuronal cell death. Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) represents an important phenomenon of adaptation of central nervous system (CNS) to sub-lethal short-term ischemia, which results in increased tolerance of CNS to the lethal ischemia. In this study we have determined the effect of ischemic preconditioning on ischemia/reperfusion-associated inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis and activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I and IV in the hippocampus of rats. Global brain ischemia was induced by 4-vessel occlusion in duration of 15 min. Rats were preconditioned by 5 min of sub-lethal ischemia and 2 days later, 15 min of lethal ischemia was induced. Our results showed that IPC affects ischemia-induced dysfunction of hippocampal mitochondria in two different ways. Repression of mitochondrial translation induced during reperfusion of the ischemic brain is significantly attenuated by IPC. Slight protective effect of IPC was documented for complex IV, but not for complex I. Despite this, protective effect of IPC on ischemia/reperfusion-associated changes in integrity of mitochondrial membrane and membrane proteins were observed. Since IPC exhibited also inhibitory effect on translocation of p53 to mitochondria, our results indicate that IPC affects downstream processes connecting mitochondrial dysfunction to neuronal cell death.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- IPC:
-
Ischemic preconditioning
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate
- TBS-T:
-
Tris-buffered saline with addition of 0.05% of Tween 20
References
Pulsinelli WA (1985) Selective neuronal vulnerability: morphological and molecular characteristics. In: Molecular mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Elsevier, Amsterdam-New York-Oxford, pp 29–37
Kirino T (2000) Delayed neuronal death. Neuropathology 20:S95–S97
Sims NR, Anderson MF (2002) Mitochondrial contributions to tissue damage in stroke. Neurochem Int 40:511–526
Abe K, Aoki M, Kawagoe J, Yoshida T, Hattori A, Kogure K, Itoyama Y (1995) Ischemic delayed neuronal death: a mitochondrial hypothesis. Stroke 26:1478–1489
Fiskum G, Murphy AN, Beal MF (1999) Mitochondria in neurodegeneration: acute ischemia and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:351–369
Hayashi T, Abe K (2004) Ischemic neuronal cell death and organelle damage. Neurol Res 26:827–834
Clayton R, Clark JB, Sharpe M (2005) Cytochrome c release from rat brain mitochondria is proportional to the mitochondrial functional deficit: implications for apoptosis and neurodegenerative disease. J Neurochem 92:840–849
Perier C, Tieu K, Guegan C, Caspersen C, Jackson-Lewis V, Carelli V, Martinuzzi A, Hirano M, Przedborski S, Vila M (2005) Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19126–19131
Cao G, Clark RS, Pei W, Yin W, Zhang F, Sun FY, Graham SH, Chen J (2003) Translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor in vulnerable neurons after transient cerebral ischemia and in neuronal cultures after oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1137–1150
Charriaut-Marlangue C, Aggoun-Zouaoui D, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y (1996) Apoptotic features of selective neuronal death in ischemia, epilepsy and gp 120 toxicity. Trends Neurosci 19:109–114
Endo H, Kamada H, Nito C, Nishi T, Chan PH (2006) Mitochondrial translocation of p53 mediates release of cytochrome c and hippocampal CA1 neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci 26:7974–7983
Hetz C, Vitte PA, Bombrun A, Rostovtseva TK, Montessuit S, Hiver A, Schwarz MK, Church DJ, Korsmeyer SJ, Martinou JC, Antonsson B (2005) Bax channel inhibitors prevent mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis and protect neurons in a model of global brain ischemia. J Biol Chem 280:42960–42970
Hokainiemi J, Massa SM, Breckinridge M, Sharp FR (1996) Global ischemia induces apoptosis-associated genes in hippocampus. Mol Brain Res 42:79–88
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Ellerby LM, Welsh K, Xie Y, Deveraux OL, Salvesen GS, Bredesen DE, Rosenthal RE, Fiskum G, Reed JC (1999) Release of caspase-9 from mitochondria during neuronal apoptosis and cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5752–5757
Perez-Pinzon MA, Xu GP, Born J, Lorenyo J, Busto R, Rosenthal M, Sick TJ (1999) Cytochrome C is released from mitochondria into the cytosol after cerebral anoxia or ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:39–43
Sugawara T, Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Kawase M, Chan PH (1999) Mitochondrial release of cytochrome c corresponds to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal CA1 neurons in rats after transient global cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 19:1–6
Taanman J-W (1999) The mitochondrial genome: structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1410:103–123
Wallace DC (1999) Mitochondrial disease in man and mouse. Science 283:1482–1488
Chomyn A, Enriquez JA, Micol V, Fernandez-Silva P, Attardi G (2000) The mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episode syndrome-associated human mitochondrial tRNALeu (UUR) mutation causes aminoacylation deficiency and concomitant reduced association of mRNA with ribosomes. J Biol Chem 275:19198–19209
Smeitink J, van den Heuvel L, DiMauro S (2001) The genetics and pathology of oxidative phosphorylation. Nat Rev Genet 2:342–352
Tryoen-Toth P, Richert S, Sohm B, Mine M, Marsac C, Van Dorsselaer A, Leize E, Florentz C (2003) Proteomic consequences of a human mitochondrial tRNA mutation beyond the frame of mitochondrial translation. J Biol Chem 278:24314–24323
Ramachandran A, Moellering DR, Ceaser E, Shiva S, Xu J, Darley-Usmar V, (2002) Inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis results in increased endothelial cell susceptibility to nitric oxide-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6643–6648
Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2004) Pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia and brain trauma: similarities and differences. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:133–150
Kirino T, Tsujita Y, Tamura A (1991) Induced tolerance to ischemia in gerbil hippocampal neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:299–307
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Kuwabara K, Tagaya M, Ohtsuki T, Hata R, Ueda H, Handa N, Kimura K, Kamada T (1991) “Ischemic tolerance” phenomenon detected in various brain regions. Brain Res 561:203–211
Liu Y, Kato H, Nakata N, Kogure K (1992) Protection of rat hippocampus against ischemic neuronal damage by pretreatment with sublethal ischemia. Brain Res 586:121–124
Nishi S, Taki W, Uemura Y, Higashi T, Kikuchi H, Kudoh H, Satoh M, Nagata K (1993) Ischemic tolerance due to the induction of HSP70 in a rat ischemic recirculation model. Brain Res 615:281–288
Simon RP, Niiro M, Gwinn R (1993) Prior ischemic stress protects against experimental stroke. Neurosci Lett 163:135–137
Perez-Pinzon MA, Born JG (1999) Rapid preconditioning neuroprotection following anoxia in hippocampal slices: role of the K+ATP channel and protein kinase C. Neuroscience 89:453–459
Dirnagl U, Simon RP, Hallenbeck JM (2003) Ischemic tolerance and endogenous neuroprotection. Trends Neurosci 26:248–254
Gidday JM (2006) Cerebral preconditioning and ischaemic tolerance. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:437–448
Kirino T (2002) Ischemic tolerance. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1283–1296
Perez-Pinzon MA, Basit A, Dave KR, Busto R, Veauvy C, Saul I, Ginsberg MD, Sick TJ (2002) Effect of the first window of ischemic preconditioning on mitochondrial dysfunction following global cerebral ischemia. Mitochondrion 2:181–189
Dave KR, Saul I, Busto R, Ginsberg MD, Sick TJ, Perez-Pinzon MA (2001) Ischemic preconditioning preserves mitochondrial function after global cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:1401–1410
Perez-Pinzon MA (2004) Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning in brain mitochondria following cerebral ischemia. J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:323–327
Burda J, Hrehorovska M, Bonilla LG, Danielisova V, Cizkova D, Burda R, Nemethova M, Fando JL, Salinas M (2003) Role of protein synthesis in the ischemic tolerance acquisition induced by transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. Neurochem Res 28:1213–1219
Tanaka H, Yokota H, Jover T, Cappuccio I, Calderone A, Simionescu M, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2004) Ischemic preconditioning: neuronal survival in the face of caspase-3 activation. J Neurosci 24:2750–2759
Lee CP, Sciamanna M, Peterson PL (1993) Intact rat brain mitochondria from a single animal: preparation and properties. Methods Toxicol 2:41–49
Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi RA, Bennett JP (2006) Parkinson’s disease brain mitochondrial complex I has oxidatively damaged subunits and is functionally impaired and misassembled. J Neurosci 26:5256–5264
Slavik J (1982) Anilinonaphthalene sulfonate as a probe of membrane composition and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 694:1–25
DeGracia DJ, Kumar R, Owen CR, Krause GS, White BC (2002) Molecular pathways of protein synthesis inhibition during brain reperfusion: implications for neuronal survival or death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:127–141
Hossmann K-A (1993) Disturbances of cerebral protein synthesis and ischemic cell death. Prog Brain Res 96:161–177
Smialek M, Hamberger A (1970) The effect of moderate hypoxia and ischemia on cytochrome oxidase activity and protein synthesis in brain mitochondria. Brain Res 17:369–371
Liu Y, Kato H, Nakata N, Kogure K (1993) Temporal profile of heat shock protein 70 synthesis in ischemic tolerance induced by preconditioning ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 56:921–927
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM, Green DR (2000) Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol 2:469–475
Tsuchiya D, Hong S, Matsumori Y, Shiina H, Kayama T, Swanson RA, Dillman WH, Liu J, Panter SS, Weinstein PR (2003) Overexpression of rat heat shock protein 70 is associated with reduction of early mitochondrial cytochrome c release and subsequent DNA fragmentation after permanent focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:718–727
Erster S, Mihara M, Kim RH, Petrenko O, Moll UM (2004) In vivo mitochondrial p53 translocation triggers a rapid first wave of cell death in response to DNA damage that can precede p53 target gene activation. Mol Cell Biol 24:6728–6741
Marchenko ND, Zaika A, Moll UM (2000) Death signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria. A potential role in apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem 275:16202–16212
Culmsee C, Zhu X, Yu QS, Chan SL, Camandola S, Guo Z, Greig NH, Mattson MP, (2001) A synthetic inhibitor of p53 protects neurons against death induced by ischemic and excitotoxic insults, and amyloid beta-peptide. J Neurochem 77:220–228
Leker RR, Aharonowiz M, Greig NH, Ovadia H (2004) The role of p53-induced apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: effects of the p53 inhibitor pifithrin alpha. Exp Neurol 187:478–486
Crumrine RC, Thomas AL, Morgan PF (1994) Attenuation of p53 expression protects against focal ischemic damage in transgenic mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:887–891
Maeda K, Hata R, Gillardon F, Hossmann K-A (2001) Aggravation of brain injury after transient focal ischemia in p53-deficient mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 88:54–61
Yonekura I, Takai K, Asai A, Kawahara N, Kirino T (2006) p53 potentiates hippocampal neuronal death caused by global ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1332–1340
Tomasevic G, Shamloo M, Israeli D, Wieloch T (1999) Activation of p53 and its target genes p21 (WAF1/Cip1) and PAG608/Wig-1 in ischemic preconditioning. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 70:304–313
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79:1431–1568
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of Slovak Republic (grant VEGA 1/1192/04 to P.R.). We would like to thank Zdenka Cetlova and Jolana Bencatova for excellent technical assistance
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Racay, P., Tatarkova, Z., Drgova, A. et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitochondrial P53 Translocation after Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Neurochem Res 32, 1823–1832 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9437-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9437-3