Abstract
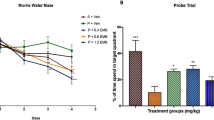
Status epilepticus (SE) is associated with a significant risk of cognitive impairment, and the increase of nitric oxide (NO) releasing has been reported during SE. We investigated the effects of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) inhibitor, 7-nitroindazole (7-NI) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibitor, aminoguanidine (AG), on spatial performance of rats in the Morris water maze. Treatment with 7-NI, but not with AG, improved the performance of rats after SE not only in acquisition of the task but also in probe test. Furthermore, the level of SE-induced malondialdehyde (MDA), end product of lipid peroxidation, was significantly decreased only in animals receiving 7-NI injection. Taken together, the results of the present study provided evidence that the NO pathway contributed to oxidative stress after SE, and nNOS/NO pathway may underlie one of the potential mechanisms contributing to SE-induced spatial memory deficits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmes GL, Thompson JL, Marchi TA, Gabriel PS, Hogan MA, Carl FG, Feldman DS (1990) Effects of seizures on learning, memory, and behavior in the genetically epilepsyprone rat. Ann Neurol 27:24–32
Rice AC, Floyd CL, Lyeth BG, Hamm RJ, De Lorenzo RJ (1998) Status epilepticus causes long-term NMDA receptor-dependent behavioral changes and cognitive deficits. Epilepsia 39:1148–1157
Milatovic D, Zivin M, Gupta RC, Dettbarn WD (2001) Alterations in cytochrome c oxidase activity and energy metabolites in response to kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res 912:67–78
Gupta RC, Dettbarn WD (2003) Prevention of kainic acid seizures-induced changes in levels of nitric oxide and high-energy phosphates by 7-nitroindazole in rat brain regions. Brain Res 981:184–192
Dawson VL, Dawson TM, London ED, Bredt DS (1991) Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6368–6371
Dawson VL, Kizushi VM, Huang PL, Snyder SH, Dawson TM (1996) Resistance to neurotoxicity in cortical cultures from neuronal nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice. J Neurosci 16:2479–2487
Mulsch A, Busse R, Mordvintcev PI, Vanin AF, Nielsen EO, Scheel-Kruger J, Olesen SP (1994) Nitric oxide promotes seizure activity in kainate-treated rats. NeuroReport 5:2325–2328
Castagne V, Gautschi M, Lefevre K, Posada A, Clarke PGH (1999) Relationships between neuronal death and the cellular redox status: focus on the developing nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 59:397–423
Iihan A, Aladag MA, Kocer A, Boluk A, Gurel A, Armutcu F (2005) Erdosteine ameliorates PTZ-induced oxidative stress in mice seizure model. Brain Res Bull 30:495–499
Rajasekaran K (2005) Seizure-induced oxidative stress in rat brain regions: blockade by nNOS inhibition. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:263–272
Frantseva MV, Velazquez JL, Hwang PA, Carlen PL (2000) Free radical production correlates with cell death in an in vitro model of epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci 12:1431–1439
Patel M, Liang LP, Roberts LJ II (2001) Enhanced hippocampal F2-isoprostane formation following kainate-induced seizures. J Neurochem 79:1065–1069
Rauca C, Wiswedel I, Zerbe R, Keilhoff G, Krug M (2004) The role of superoxide dismutase and alpha-tocopherol in the development of seizures and kindling induced by pentylenetetrazol-influence of the radical scavenger alpha-phenyl-N-tert-butyl nitrone. Brain Res 1009:203–212
Gupta RC, Milatovic D, Dettbarn WD (2001) Depletion of energy metabolites following cetylcholinesterase inhibitor-induced status epilepticus: protection by antioxidants. Neurotoxicology 22:271–282
Brown GC (1999) Nitric oxide and mitochondrial respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1411:351–369
Beckman JS, Koppenol WH (1996) Nitric oxide superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad and the ugly. Am J Physiol 271:C1424–C1437
Holmes GL, Khazipov R, Ben-Ari Y (2002) Seizure-induced damage in the developing human: relevance of experimental models. Prog Brain Res 135:321–334
Löscher W (2002) Animal models of epilepsy for the development of antiepileptogenic and disease-modifying drugs. A comparison of the pharmacology of kindling and post-status epilepticus models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 50:105–123
Stewart LS, Persinger MA (2001) Ketamine prevents learning impairment when administered immediately after status epilepticus onset. Epilepsy Behav 2:585–591
Faverjon S, Silveira DC, Fu DD, Cha BH, Akman C, Hu Y, Holmes GL (2002) Beneficial effects of enriched environment following status epilepticus in immature rats. Neurology 59:1356–1364
Kubova H, Mares P, Suchomelova L, Brozek G, Druga R, Pitkanen A (2004) Status epilepticus in immature rats leads to behavioural and cognitive impairment and epileptogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 19:3255–3265
Dube´ C, Boyet S, Marescaux C, Nehlig A (2001) Relationship between neuronal loss and interictal glucose metabolism during the chronic phase of the lithiumpilocarpine model of epilepsy in the immature and adult rat. Exp Neurol 167:227–241
Roch C, Leroy C, Nehlig A, Namer IJ (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging in the study of the lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy in adult rats. Epilepsia 43:325–335
Voutsinos-Porche B, Koning E, Clement Y, Kaplan H, Ferrandan A, Motte J, Nehlig A (2006) EAAC1 glutamate transporter expression in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1419–1430
Moore PK, Babbedge RC, Wallace P, Gaffen ZA, Hart SL (1993) 7-Nitro indazole, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, exhibits anti-nociceptive activity in the mouse without increasing blood pressure. Br J Pharmacol 108(2):296–297 Feb
Southan GJ, Szabo C (1996) Selective pharmacological inhibition of distinct nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Biochem Pharmacol 51(4):383–394 Feb 23
Komatsu T, Sakurada C, Sasaki M, Sanai K, Tsuzuki M, Bagetta G, Sakurada S, Sakurada T (2007) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and nitric oxide synthase mediate intrathecal morphine-induced nociceptive behavior. Neuropharmacology. 52(5):1237–1243. Apr. Epub 2007 Jan 14
Di Matteo V, Benigno A, Pierucci M, Giuliano DA, Crescimanno G, Esposito E, Di Giovanni G (2006) 7-nitroindazole protects striatal dopaminergic neurons against MPP+-induced degeneration: an in vivo microdialysis study. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1089:462–471 Nov
Manzanedo C, Aguilar MA, Rodriguez-Arias M, Navarro M, Minarro J (2004) 7-Nitroindazole blocks conditioned place preference but not hyperactivity induced by morphine. Behav Brain Res 150(1–2):73–82 Apr 2
Montecot C, Rondi-Reig L, Springhetti V, Seylaz J, Pinard E (1998) Inhibition of neuronal (type 1) nitric oxide synthase prevents hyperaemia and hippocampal lesions resulting from kainate-induced seizures. Neuroscience 84:791–800
Danielisova V, Nemethova M, Burda J (2004) The protective effect of aminoguanidine on cerebral ischemic damage in the rat brain. Physiol Res 53:533–540
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
Lee SK, Kim DW, Kim KK, Chung CK, Song IC, Chang KH (2005) Effect of seizure on hippocampus in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and neocortical epilepsy: an MRS study. Neuroradiology 47:916–923
Reiter RJ (1998) Oxidative damage in the central nervous system: protection by melatonin. Prog Neurobiol 56:359–384
Fridovich I (1989) Superoxide dismutases: an adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J Biol Chem 264:19328–19333
Chavko M, Auker CR, McCarron RM (2003) Relationship between protein nitration and oxidation and development of hyperoxic seizures. Nitric Oxide 9:18–23
Erdogan F, Golgeli A, Arman F, Ersoya AO (2004) The effects of pentylenetetrazole-induced status epilepticus on behavior, emotional memory, and learning in rats. Epilepsy Behav 5:388–393
Boukhezra O, Riviello P, Fu DD, Lui X, Zhao Q, Akman C, Holmes GL (2003) Effect of the postictal state on visual–spatial memory in immature rats. Epilepsy Res 55:165–175
O’Neill MJ, Hicks C, Ward M (1996) Neuroprotective effects of 7-nitroindazole in the gerbil model of global cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 310:343–354
Schulz JB, Henshaw DR, Siwek D, Jenkins BG, Ferrante R.J., Cipolloni P.B., Kowall NW, Rosen BR, Beal MF (1995) Involvement of free radicals in excitotoxicity in vivo. J Neurochem 64:2239–2247
Murashima YL, Yoshii M, Suzuki J (2000) Role of nitric oxide in the epileptogenesis of EL mice. Epilepsia 41:S195–S199
MacKenzie GM, Rose S, Bland-Ward PA, Moore PK, Jenner P, Marsden CD, (1994) Time course of inhibition of brain nitric oxide synthase by 7-nitro indazole. Neuroreport 5:1851–1852
Ebadi M, Sharma S (2006) Metallothioneins 1 and 2 attenuate peroxynitrite-induced oxidative stress in Parkinson disease. Exp Biol Med 231:1576–1583
Reiter TA (2006) NO chemistry: a diversity of targets in the cell. Redox Rep 11:194–206
Chirino YI, Orozco-Lbarra M, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2006) Role of peroxynitrite anion in different diseases. Rev Invest Clin 58:350–358
Erakovic V, Zupan G, Varljen J, Laginja J, Simonic A (2000) Lithium plus pilocarpine induced status epilepticus—biochemical changes. Neurosci Res 36:157–166
Asahi M, Fujii J, Suzuki K, Seo HG, Kuzuya T, Hori M, Tada M, Fujii S, Taniguchi N (1995) Inactivation of glutathione peroxidase by NO: implication for cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 270:21035–21039
Mayer B, Klatt P, Werner ER, Schmidt K (1994) Molecular mechanisms of porcine brain nitric oxide synthase by the ntinociceptive drug 7-nitroindazole. Neuropharmacology 33:1253–1259
Vanaja P, Ekambaram P (2004) Demonstrating the dose- and time-related effects of 7-nitroindazole on picrotoxin-induced convulsions, memory formation, brain nitric oxide synthase activity, and nitric oxide concentration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:1–8
Zhuo M, Laitinen JT, Li XC, Hawkins RD (1999) On the respective roles of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Learn Mem 6:63–76
Licinio J, Prolo P, McCann SM, Wong ML (1999) Brain iNOS: current understanding and clinical implications. Mol Med Today 5:225–232
Yang R, Huang ZN, Cheng JS (2000) Anticonvulsion effect of acupuncture might be related to the decrease of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthases. Acupunct Electrother Res 25:137–143
Al-Shabanah OA, Alam K, Nagi MN, Al-Rikabi AC, Al-Bekairi AM (2000) Protective effect of aminoguanidine, a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Life Sci 66:265–270
De Alba J, Cardenas A, Moro MA, Leza JC, Lorenzo P, Bosca L, Lizasoain I (1999) Down-regulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by nitric oxide after oxygen-glucose deprivation in rat forebrain slices. J Neurochem 72:248–254
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30470453, 30640037), Municipal Science Foundation Research of TianJin (06YFJMJC09400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z.W., Zhang, T. & Yang, Z. Involvement of Nitric Oxide in Spatial Memory Deficits in Status Epilepticus Rats. Neurochem Res 32, 1875–1883 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9374-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9374-1