Abstract
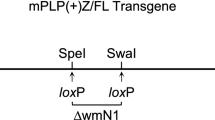
Jimpy (Plp jp) is an X-linked recessive mutation in mice that causes CNS dysmyelination and early death in affected males. It results from a point mutation in the acceptor splice site of myelin proteolipid protein (Plp) exon 5, producing transcripts that are missing exon 5, with a concomitant shift in the downstream reading frame. Expression of the mutant PLP product in Plp jp males leads to hypomyelination and oligodendrocyte death. Expression of our Plp-lacZ fusion gene, PLP(+)Z, in transgenic mice is an excellent readout for endogenous Plp transcriptional activity. The current studies assess expression of the PLP(+)Z transgene in the Plp jp background. These studies demonstrate that expression of the transgene is decreased in both the central and peripheral nervous systems of affected Plp jp males. Thus, expression of mutated PLP protein downregulates Plp gene activity both in oligodendrocytes, which eventually die, and in Schwann cells, which are apparently unaffected in Plp jp mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woodward K, Malcolm S (1999) Proteolipid protein gene: Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease in humans and neurodegeneration in mice. Trends Genet 15:125–128
Yool DA, Edgar JM, Montague P, Malcolm S (2000) The proteolipid protein gene and myelin disorders in man and animal models. Hum Mol Genet 9:987–992
Macklin WB, Gardinier MV, King KD, Kampf K (1987) An AG→GG transition at a splice site in the myelin proteolipid protein gene in jimpy mice results in the removal of an exon. FEBS Lett 223:417–421
Nave KA, Bloom FE, Milner RJ (1987) A single nucleotide difference in the gene for myelin proteolipid protein defines the jimpy mutation in mouse. J Neurochem 49:1873–1877
Macklin WB, Gardinier MV, Obeso ZO, King KD, Wight PA (1991) Mutations in the myelin proteolipid protein gene alter oligodendrocyte gene expression in jimpy and jimpy msd mice. J Neurochem 56:163–171
Boison D, Stoffel W (1989) Myelin-deficient rat: a point mutation in exon III (A → C, Thr75 → Pro) of the myelin proteolipid protein causes dysmyelination and oligodendrocyte death. EMBO J 8:3295–3302
Gencic S, Hudson LD (1990) Conservative amino acid substitution in the myelin proteolipid protein of jimpy msd mice. J Neurosci 10:117–124
Nadon NL, Duncan ID, Hudson LD (1990) A point mutation in the proteolipid protein gene of the ‘shaking pup’ interrupts oligodendrocyte development. Development 110:529–537
Gow A, Southwood CM, Lazzarini RA (1998) Disrupted proteolipid protein trafficking results in oligodendrocyte apoptosis in an animal model of Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease. J Cell Biol 140:925–934
Southwood CM, Garbern J, Jiang W, Gow A (2002) The unfolded protein response modulates disease severity in Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease. Neuron 36:585–596
Miller MJ, Haxhiu MA, Georgiadis P, Gudz TI, Kangas CD, Macklin WB (2003) Proteolipid protein gene mutation induces altered ventilatory response to hypoxia in the myelin-deficient rat. J Neurosci 23:2265–2273
Wight PA, Duchala CS, Readhead C, Macklin WB (1993) A myelin proteolipid protein-lacZ fusion protein is developmentally regulated and targeted to the myelin membrane in transgenic mice. J Cell Biol 123:443–454
Fuss B, Mallon B, Phan T, Ohlemeyer C, Kirchhoff F, Nishiyama A, Macklin WB (2000) Purification and analysis of in vivo-differentiated oligodendrocytes expressing the green fluorescent protein. Dev Biol 218:259–274
Fuss B, Afshari FS, Colello RJ, Macklin WB (2001) Normal CNS myelination in transgenic mice overexpressing MHC class I H-2Ld in oligodendrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci 18:221–234
Mallon BS, Shick HE, Kidd GJ, Macklin WB (2002) Proteolipid promoter activity distinguishes two populations of NG2-positive cells throughout neonatal cortical development. J Neurosci 22:876–885
Fewou SN, Büssow H, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Vanier MT, Macklin WB, Gieselmann V,Eckhardt M (2005) Reversal of non-hydroxy: α-hydroxy galactosylceramide ratio and unstable myelin in transgenic mice overexpressing UDP-galactose:ceramide galactosyltransferase. J Neurochem 94:469–481
Gonzalez JM, Bergmann CC, Fuss B, Hinton DR, Kangas C, Macklin WB, Stohlman SA (2005) Expression of a dominant negative IFN-γ receptor on mouse oligodendrocytes. Glia 51:22–34
Lee KK, de Repentigny Y, Saulnier R, Rippstein P, Macklin WB, Kothary R (2006) Dominant-negative β1 integrin mice have region-specific myelin defects accompanied by alterations in MAPK activity. Glia 53:836–844
Li S, Moore CL, Dobretsova A, Wight PA (2002) Myelin proteolipid protein (Plp) intron 1 DNA is required to temporally regulate Plp gene expression in the brain. J Neurochem 83:193–201
Bö L, Mork S, Kong PA, Nyland H., Pardo CA, Trapp BD (1994) Detection of MHC class II-antigens on macrophages and microglia, but not on astrocytes and endothelia in active multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroimmunol 51:135–146
Asotra K, Macklin WB (1993) Protein kinase C activity modulates myelin gene expression in enriched oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci Res 34:571–588
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Dobretsova A, Kokorina NA, Wight PA (2000) Functional characterization of a cis-acting DNA antisilencer region that modulates myelin proteolipid protein gene expression. J Neurochem 75:1368–1376
Meng F, Zolova O, Kokorina NA, Dobretsova A, Wight PA (2005) Characterization of an intronic enhancer that regulates myelin proteolipid protein (Plp) gene expression in oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci Res 82:346–356
Benjamins JA, Skoff RP, Beyer K (1984) Biochemical expression of mosaicism in female mice heterozygous for the jimpy gene. J Neurochem 2:487–492
Benjamins JA, Studzinski DM, Skoff RP (1986) Biochemical correlates of myelination in brain and spinal cord of mice heterozygous for the jimpy gene. J Neurochem 6:1857–1863
Benjamins JA, Studzinski DM, Skoff RP, Nedelkoska L, Carrey EA, Dyer CA (1989) Recovery of proteolipid protein in mice heterozygous for the jimpy gene. J Neurochem 53:279–286
Skoff RP (1982) Increased proliferation of oligodendrocytes in the hypomyelinated mouse mutant-jimpy. Brain Res 248:19–31
Knapp PE, Skoff RP, Redstone DW (1986) Oligodendroglial cell death in jimpy mice: an explanation for the myelin deficit. J Neurosci 10:2813–2822
Knapp PE, Skoff RP (1987) A defect in the cell cycle of neuroglia in the myelin deficient jimpy mouse. Brain Res 432:301–306
Vermeesch MK, Knapp PE, Skoff RP, Studzinski DM, Benjamins JA (1990) Death of individual oligodendrocytes in jimpy brain precedes expression of proteolipid protein. Dev Neurosci 12:303–315
Sorg BJ, Agrawal D, Agrawal HC, Campagnoni AT (1986) Expression of myelin proteolipid protein and basic protein in normal and dysmyelinating mutant mice. J Neurochem 46:379–387
Sorg BA, Smith MM, Campagnoni AT (1987) Developmental expression of the myelin proteolipid protein and basic protein mRNAs in normal and dysmyelinating mutant mice. J Neurochem 49:1146–1154
Verity AN, Levine MS, Campagnoni AT (1990) Gene expression in the jimpy mutant: evidence for fewer oligodendrocytes expressing myelin protein genes and impaired translocation of myelin basic protein mRNA. Dev Neurosci1 2:359–372
Shiota C, Ikenaka K, Mikoshiba K (1991) Developmental expression of myelin protein genes in dysmyelinating mutant mice: analysis by nuclear run-off transcription assay, in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry. J Neurochem 56:818–826
Ghandour MS, Skoff RP (1988) Expression of galactocerebroside in developing normal and jimpy oligodendrocytes in situ. J Neurocytol 17:485–498
Thomson CE, Anderson TJ, McCulloch MC, Dickinson P, Vouyiouklis DA, Griffiths IR (1999) The early phenotype associated with the jimpy mutation of the proteolipid protein gene. J Neurocytol 28:207–221
Sidman RL, Dickie MM, Appel SH (1964) Mutant mice (quaking and jimpy) with deficient myelination in the central nervous system. Science 144:309–310
Anderson TJ, Montague P, Nadon N, Nave K-A, Griffiths IR (1997) Modification of Schwann cell phenotype with Plp transgenes: evidence that the PLP and DM20 isoproteins are targeted to different cellular domains. J Neurosci Res 50:13–22
Cokol M, Nair R, Rost B (2000) Finding nuclear localization signals. EMBO Rep 1:411–415
Nair R, Carter P, Rost B (2003) NLSdb: database of nuclear localization signals. Nucleic Acids Res 31:397–399
Jiang H, Duchala CS, Awatramani R, Shumas S, Carlock L, Kamholz J, Garbern J, Scherer SS, Shy ME, Macklin WB (2000) Proteolipid protein mRNA stability is regulated by axonal contact in the rodent peripheral nervous system. J Neurobiol 44:7–19
Mallon BS, Macklin WB (2002) Overexpression of the 3′-untranslated region of myelin proteolipid protein mRNA leads to reduced expression of endogenous proteolipid mRNA. Neurochem Res 27:1349–1360
Roussel G, Neskovic NM, Trifilieff E, Artault JC, Nussbaum JL (1987) Arrest of proteolipid transport through the Golgi apparatus in Jimpy brain. J Neurocytol 16:195–204
Verrall S, Hall ZW (1992) The N-terminal domains of acetylcholine receptor subunits contain recognition signals for the initial steps of receptor assembly. Cell 68:23–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NS25304, WBM) and a postdoctoral fellowship from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (CSD). The authors thank Dannette DeWeese, Leigh Hayes and Tom Phan for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Anthony Campagnoni.
Patricia A. Wight and Cynthia S. Duchala contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wight, P.A., Duchala, C.S., Shick, H.E. et al. Expression of a Myelin Proteolipid Protein (Plp)-lacZ Transgene is Reduced in both the CNS and PNS of Plp jp Mice. Neurochem Res 32, 343–351 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9202-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9202-z