Abstract
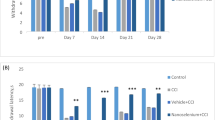
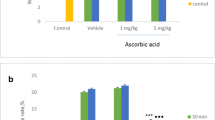
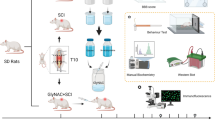
Oxidative stress is an important pathophysiological mechanism of many neurological diseases. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species have been cited as molecules involved in the nociceptive process. In this study, rats were submitted to sciatic nerve transection (SNT) for induction of neuropathic pain, and enzyme activities of SOD and catalase as well as lipid peroxidation (LPO) were measured in the lumbosacral spinal cord. The results show that LPO was not changed after SNT. SOD activity was reduced 7 days after SNT, while the change in catalase activity occurred on the third and seventh days in both sham and SNT animals. Hyperalgesia in SNT group was detected at the same points in time. These results suggest that SNT was not a strong enough stimulus to deplete all antioxidant content in the spinal cord, since increase in LPO was not detected. However, the role of oxidative stress in nociception can not be excluded.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sommer C, Myers RR (1995) Neurotransmitters in the spinal cord dorsal horn in a model of painful neuropathy and in nerve crush. Acta Neuropathol 90:478–485
Zimmermann M (2001) Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:23–37
Millan JM (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 57:1–164
Byers MR, Bonica JJ (2001) Peripheral pain mechanisms and nociceptor plasticity. In: Loeser JD, Butler SH, Chapman R, Turk DC (eds), Bonica’s management of pain, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp. 26–72
Rydh-Rinder M, Holmberg K, Elfvin LG, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Hökfelt T (1996) Effects of peripheral axotomy on neuropeptides and nitric oxide synthase in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of the guinea pig: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 707:180–188
Ma W, Bisby MA (1998) Partial and complete sciatic nerve injuries induce similar increases of neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal peptide immunoreactivities in primary sensory neurons and their central projections. Neuroscience 86:1217–1234
Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G, Chung K, Coggeshall RE, Chung JM (2004) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 111:116–124
Wang Z-Q, Porreca F, Cuzzocrea S, Galen K, Lightfoot R, Masini E, Muscoli C, Mollace V, Ndengele M, Ischiropoulos H, Salvemini DA (2004) Newly identified role for superoxide in inflammatory pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:869–878
Yu BP (1994) Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev 74:139–162
Fridovich I (1998) Oxygen toxicity: a radical explanation. J Exp Biol 201:1203–1209
Liochev SI, Fridovich I (2003) Mutant Cu,Zn superoxide dismutases and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: evaluation of oxidative hypotheses. Free Radic Biol Med 34:1383–1389
Lee YS, Sindhu RK, Lin CY, Ehdaie A, Lin VW, Vaziri ND (2004) Effects of nerve graft on nitric oxide synthase, NAD(P)H oxidase, and antioxidant enzymes in chronic spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med 36:330–339
Rosenfeld J, Cook S, James R (1997) Expression of superoxide dismutase following axotomy. Exp Neurol 147:37–47
Yu WH (2002) Spatial and temporal correlation of nitric oxide synthase expression with CuZn-superoxide dismutase reduction in motor neurons following axotomy. Ann. N Y Acad Sci 962:111–121
Rogerio F, Teixeira SA, de Rezende AC, de Sa RC, Queiroz L, De Nucci G, Muscara MN, Langone F (2005) Superoxide dismutase isoforms 1 and 2 in lumbar spinal cord of neonatal rats after sciatic nerve transection and melatonin treatment. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 154:217–225
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Marklund SL (1985). Pyrogallol autooxidation. In: Greenwald RA (eds) Handbook of methods for oxygen radical research, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 243–247
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microssomal lipid peroxidation. Meth Enzymol 52:302–309
Klein D, Kern RM, Sokol RZ (1995) A method for quantification and correction of proteins after transfer to immobilization membranes. Biochem Mol Biol Int 36:59–66
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Heales S, Lam A, Duncan A, Land J, (2004) Neurodegeneration or neuroprotection: the pivotal role of astrocytes. Neurochem Res 29:513–519
Gegg M, Beltran B, Salas-Pino S, Bolanos JP, Clark JB, Moncada S, Heales SJR (2003) Differential effect of nitric oxide on glutathione metabolism and mitochondrial function in astrocytes and neurones: implications for neuroprotection/neurodegeneration? J Neurochem 86:228–237
Zhang X, Verge V, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Ju G, Bredt D, Synder SH, Hokfelt T (1993) Nitric oxide synthase-like immunoreactivity in lumbar dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of rat and monkey and effect of peripheral axotomy. J Comp Neurol 335:563–575
Vizzard MA, Erdman SL, de Groat WC (1995) Increased expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in visceral neurons after nerve injury. J Neurosci 15:4033–4045
Cizkova D, Lukacova N, Marsala M, Marsala J (2002) Neuropathic pain is associated with alterations of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity and catalytic activity in dorsal root ganglia and spinal dorsal horn. Brain Res Bull 58:161–171
Yoneda T, Inagaki S, Hayashi Y, Nombra T, Takagi H (1992) Differential regulation of manganese and copper/zinc superoxide dismutases by the facial nerve transection. Brain Res 582:342–345
Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Ensz L, Mukhina G, Lebovitz R, Zwacka R, Engelhardt J, Oberley L, Dawson V, Dawson T (1998) Manganese superoxide dismutase protects nNOS neurons from NMDA and nitric oxide-mediated neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 18:2040–2055
Khalil Z, Liu T, Helme RD (1999) Free radicals contribute to the reduction in peripheral vascular responses and the maintenance of thermal hyperalgesia in rats with chronic constriction injury. Pain 79:31–37
Viggiano A, Monda M, Viggiano A, Viggiano D, Viggiano E, Chiefari M, Aurilio C, De Luca B (2005) Trigeminal pain transmission requires reactive oxygen species production. Brain Res 1050:72–78
Rhee SG, Bae YS, Lee SR, Kwon J (2000) Hydrogen peroxide: a key messenger that modulates protein phosphorylation through cysteine oxidation. Sci STKE 53: PE1
Sah R, Galeffi F, Ahrens R, Jordan G, Schwartz-Bloom RD (2002) Modulation of the GABA(A)-gated chloride channel by reactive oxygen species. J Neurochem 80:383–391
Frantseva MV, Perez Velazquez JL, Carlen PL (1998) Changes in membrane and synaptic properties of thalamocortical circuitry caused by hydrogen peroxide. J Neurophysiol 80:1317–1326
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guedes, R.P., Bosco, L.D., Teixeira, C.M. et al. Neuropathic Pain Modifies Antioxidant Activity in Rat Spinal Cord. Neurochem Res 31, 603–609 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9058-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9058-2
Keywords
- Neuropathic pain
- Reactive oxygen species
- Sciatic nerve transection
- Superoxide dismutase
- Catalase
- Spinal cord
- Rat
- Lipid peroxidation
- Oxidative stress
- Antioxidant
- Axotomy
- Hyperalgesia
- Nociceptive processing
- Western blot
- Hot plate test
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Superoxide
- Nervous system
- Pain
- Sciatic nerve
- Nitric oxide
- Nitric oxide synthase
- Peroxynitrite
- Inflammation
- Peripheral nerve lesion
- Neurons
- Astrocytes
- Malondialdeyde
- TBARS
- Bradford method
- Thermal hyperalgesia
- Sensitization
- Free radicals
- Nerve injury
- Nociception
- Gluthatione
- SOD
- CuZnSOD
- MnSOD
- Neurological disorders
- Withdrawal latency
- Electrophoresis
- LPO
- Polyclonal antibody
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- Chemiluminescence