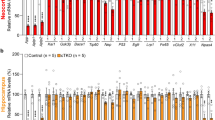
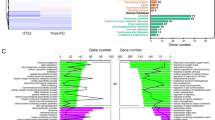
Mutations in genes for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) result in a modulating of gene expressions in the brains of patients with AD. The aim of this study was to identify genes whose expression is modulated due to the over-expression of human mutant presenilin-2 (N141I) (hPS2m) in transgenic mice, which has previously been produced by us. To test this, GeneFishingTM DEG101 technique was performed on large-scale screen of mRNA from transgenic and non-transgenic brains. A total of 40 transcriptional products corresponding to cDNA were compared between two brains, and 17 showed a differential expression between the samples in all sets of experiments. However, all showed significant homology to known genes. Initially, a cloning corresponding to human selenoprotein M (hSelM) was chosen for investigation further because SelM induced by sodium selenite, a pro-oxidant, may have a functional role in catalyze the free radicals. We found that mouse SelM had significantly suppressed on its transcriptional products in transgenic brains. In parallel, suppression of endogenous was not observed in transgenic brains. Moreover, the levels of green fluorescence on hSelM fusion protein with EGFP were suppressed in the cells transfected with hPS2m, and its levels had actually increased by treatments of sodium selenite. Thus, the results indicate that SelM might play a suppressive or protective role in the pathology of patients with AD and it will be necessary to investigate further on functional roles of other up- and down-regulated gene in future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Xia B. L. Ostaszewski W. T. Kimberly T. Rahmati C. L. Moore M. S. Wolfe D. J. Selkoe (2000) ArticleTitleFAD mutations in presenilin-1 or amyloid precursor protein decrease the efficacy of a γ-secretase inhibitor: evidence for direct involvement of PS1 in the γ-secretase cleavage complex Neurobiol. Dis. 7 673–681 Occurrence Handle10.1006/nbdi.2000.0322 Occurrence Handle11114265
E. Levy-Lahad W. Wasco P. Poorkaj D. M. Romano J. Oshima W. H. Pettingell C-E. Yu P. D. Jondro S. D. Schmidt K. Wang A. C. Crowley Y.-H. Wu S. Y. Guenette D. Galas E. Nemens E. M. Wijsman T. D. Bird G. D. Schellenberg R. E. Tanzi (1995) ArticleTitleCandidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus Science 269 973–977 Occurrence Handle7638622
S. Janicki M. J. Monteiro (1997) ArticleTitleIncreased apoptosis arising from increased expression of the Alzhemer’s disease-associated presenilin-2 mutation (N1411) J. Cell Biol. 139 485–495 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.139.2.485 Occurrence Handle9334350
T. W. Kim W. H. Pettingell O. G. Hallmark R. D. Moir W. Wasco R. E. Tanzi (1997) ArticleTitleEndproteolytic cleavage and proteosomal degradation of presenilin-2 in transfected cell J. Biol. Chem. 272 11006–11010 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.272.17.11006 Occurrence Handle9110991
T. W. Kim W. H. Pettingell Y. K. Jung D. M. Kovacs R. E. Tamzi (1997) ArticleTitleAlternative cleavage of Alzheimer-associated presenilins during apoptosis Science 277 373–376 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.277.5324.373 Occurrence Handle9219695
H. Letscher U. Deuschle M. Brockhaus D. Reinhardt P. Nelboeck J. Mous J. Grunberg C. Haass H. Jacobson (1997) ArticleTitlePresenilins are processed by caspase-type proteases J. Biol. Chem. 272 20655–20659 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.272.33.20655 Occurrence Handle9252383
A. M. Goate M. C. Chartier-Harlin M. Mullan J. Brown F. Crawford L. Fidani L. Giuffra A. Haynes N. Irving L. James R. Mant P. Newton K. Rooke P. Roques C. Taebot M. Pericak-Vance A. Roses R. Williamson M. Rossor M. Owen J. Hardy (1991) ArticleTitleSegregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precusor protein gene with familiar Alzheimer’s disease Nature 349 704–706 Occurrence Handle10.1038/349704a0 Occurrence Handle1671712
W. Wasco W. P. Pettingell P. D. Jondro S. D. Schmidt S. Gurubhagavatula L. Rodes T. DiBlasi D. M. Romano S. Y. Guenette D. M. Kovacs J. H. Growdon R. E. Tanzi (1995) ArticleTitleFamilial Alzheimer’s chromosome 14 mutations Nat. Med. 1 848 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0995-848a
J. Peret-Tur S. Froelich G. Prihar R. Crook M. Baker K. Duff M. Wragg F. Busfield C. Lendon R. F. Clark P. Roques R. A. Fuldner J. Johnson R. Cowburn C. Forcell K. Axelman L. Lilius H. Houlden E. Karran G. W. Robert M. Rossor M. D. Adams J. Hardy A. Goate L. Lannfelt M. Hutton (1995) ArticleTitleA mutation in Alzheimer’s disease destroying a splice acceptor site in the presenilin-1 gene NeuroReport 7 297–301 Occurrence Handle8742474
R. Sherrington E. Rogaev Y. Liang E. A. Rogaeva G. Levesque M. Ikeda H. Chi C. Lin G. Li K. Holman T. Tsuda L. Mar J. F. Foncin A. C. Bruni M. P. Montesi S. Sorbi I. Rainero L. Pinessi L. Nee I. Chumacov D. Pollen A. Brookes P. Sanseau R. J. Polinski W. Wasco H. A. R. Da Silva J. L. Haines M. A. Pericak Vance R. E. Tanzi A. D. Roses P. E. Fraser J. M. Rommans P. H. St George-Hyslop (1995) ArticleTitleCloning of a gene bearing missense mutation in early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease Nature 375 754–760 Occurrence Handle10.1038/375754a0 Occurrence Handle7596406
D. Scheuner C. Eckman M. Jensen X. Song M. Citron N. Suzuki T. D. Bird J. Hardy M. Hutton W. Kukull E. Larson E. Levy-Lahad M. Viitanen E. Peskind P. Poorkaj G. Schellenberg R. Tanzi W. Wasco L. Lannfelt D. Selkoe S. Younkin (1996) ArticleTitleSecreted amyloid β-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease and APP mutation linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease Nat. Med. 2 864–870 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0896-864 Occurrence Handle8705854
S. C. Low M. J. Berry (1996) ArticleTitleKnowing when not to stop: selenocysteine incorporation in eukaryotes Trends Biochem. Sci. 21 203–208 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0968-0004(96)10025-6 Occurrence Handle8744353
M. J. Berry G. W. Martin Suffix3rd S. C. Low (1997) ArticleTitleRNA and protein requirements for eukaryotic selenoprotein syntesis Biomed. Environ. Sci. 10 182–189 Occurrence Handle9315309
R. Walczak E. Westhof P. Carbon A. Krol (1996) ArticleTitleA novel RNA structural motif in the selenosysteine insertion element of eukaryotic selenoprotein mRNA RNA 2 367–379 Occurrence Handle8634917
D. Fagegaltier N. Hubert K. Yamada T. Mizutani P. Carbon A. Krol (2000) ArticleTitleCharacterization of mSelB, a novel mammalian elongation factor for selenoprotein translation EMBO J. 19 4796–4805 Occurrence Handle10970870
R. M. Tujebaseva P. R. Copeland X. M. Xu B. A. Carlson J. W. Harney D. M. Driscoll D. A. Hatfield M. J. Berry (2000) ArticleTitleDecoding apparatus for eukaryotic selenocysteine insertion EMBO Rep. 1 158–163 Occurrence Handle10.1093/embo-reports/kvd033 Occurrence Handle11265756
M. J. Berry L. Banu W. Harney P. R. Larsen (1993) ArticleTitleFunctional characterization of the eukaryotic SECIS elements which direct selenocysteine insertion at UGA codon EMBO J. 12 3315–3322 Occurrence Handle8344267
K. V. Korotkov S. V. Novoselov D. L. Hatfield V. N. Gradyshev (2002) ArticleTitleMammalian selenoprotein in which selenocysteine (Sec) incorporation is supported by a new form of sec insertion sequence element Mol. Cell Biol. 22 1402–1411 Occurrence Handle10.1128/MCB.22.5.1402-1411.2002 Occurrence Handle11839807
D. Y. Hwang K. R. Chae T. S. Kang J. H. Hwang C. H. Lim H. K. Kang J. S. Goo M. R. Lee H. J. Lim S. H. Min J. Y. Cho J. T. Hong C. W. Song S. G. Paik J. S. Cho Y. K. Kim (2002) ArticleTitleAlterations in behavior, amyloid β-42, caspase-3, Cox-2 in mutant PS2 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease FASEB J. 16 805–813 Occurrence Handle10.1096/fj.01-0732com Occurrence Handle12039862
H. J. Lim C. J. Lim D. Y. Hwang S. H. Lee S. H. Min Y. S. Song S. J. Seo H. K. Park Y. Y. Sheen J. S. Cho Y. K. Kim (2004) ArticleTitleCarboxyl-terminus of the amyloid protein precursor and ERβ are required for estrogenic effect in activating mitogen-activated protein kinase Int. J. Mol. Med. 13 691–696 Occurrence Handle15067372
R. F. Burk K. E. Hill (1999) ArticleTitleOrphan selenoproteins BioEssays 21 231–237 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199903)21:3<231::AID-BIES7>3.0.CO;2-D Occurrence Handle10333732
Y. C. Lee Y. C. Tang Y. H. Chen C. M. Wong A. P. Tsou (2003) ArticleTitleSelenite-induced survival of HuH7hepetoma cells involves activation of focal adhesion-kinase-phosphohatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway and Rac 1 J. Biol. Chem. 278 39615–39624 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M304095200 Occurrence Handle12896980
L. Zuo J. Li Y. Yang X. Wang T. Shen C. M. Xu Z. N. Zhang (2004) ArticleTitleSodium selenite induces apoptosis in acute promyelocyte leukemia-induced-derived NB4 cells by a caspase-3-dependent mechanism and a redox pathway different from that of arsenic trioxide Ann. Hematol. 83 751–758 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00277-004-0920-5 Occurrence Handle15480664
E. J. Rogaev R. Sherrington E. A. Rogaeva (1996) ArticleTitleFamilial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutation in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene Nature 376 775–778 Occurrence Handle10.1038/376775a0
E. H. Corder A. M. Saunders D. E. Strittmatter P. C. Gaskell G. W. Small A. D. Roses J. L. Haines M. A. Pericak-Vance (1993) ArticleTitleGene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families Science 261 828–829 Occurrence Handle8346434
P. Liang A. B. Pardee (1992) ArticleTitleDifferential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction Science 257 967–971 Occurrence Handle1354393
D. A. Butterfield J. Drake C. Pocernich A. Castegna (2001) ArticleTitleEvidence of oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease brain: central role for amyloid beta peptide Trends Mol. Med. 7 548–554 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1471-4914(01)02173-6 Occurrence Handle11733217
C. W. Cotman N. C. Berchtold (2002) ArticleTitleExercise: a behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity Trends Neurosci. 25 295–301 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0166-2236(02)02143-4 Occurrence Handle12086747
A. I. Bush C. L. Masters R. E. Tanzi (2003) ArticleTitleCopper, beta amyloid, and Alzheimer’s disease: tapping a sensitive connection Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 11193–11194 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.2135061100 Occurrence Handle14506299
D. Morgan D. M. Diamond P. E. Gottschall K. E. Ugen C. Dickey J. Hardy K. Duff P. Jantzen G. DiCarlo D. Wilcock K. Connor J. Hatcher C. Hope M. Gordon G. W. Arendash (2000) ArticleTitleA beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease Nature 408 982–985 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35050116 Occurrence Handle11140686
D. Butterfield A. Castegna C. Pocermic J. Drake G. Scapagnini V. Calabrese (2002) ArticleTitleNutritional approaches to combat oxidative stress in Alzheimr’s disease J. Nutr. Biochem. 13 444–461 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0955-2863(02)00205-X Occurrence Handle12165357
G. S. Watson S. Craft (2003) ArticleTitleThe role of insulin resistance in the Alzheimer’s disease: implication for treatment CNS Drugs 17 27–25 Occurrence Handle12467491
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, D.Y., Cho, J.S., Oh, J.H. et al. Differentially Expressed Genes in Transgenic Mice Carrying Human Mutant Presenilin-2 (N141I): Correlation of Selenoprotein M with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 30, 1009–1019 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6787-6
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6787-6