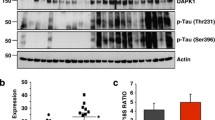
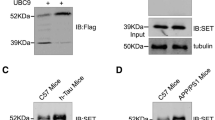
Pin1 binds mitotically phosphorylated Thr231–Pro232 and Thr212–Pro213 sites on tau, and a Pin1 deficiency in mice leads to tau hyperphosphorylation. The aim of this study was to determine if the dephosphorylation or inhibition of tau and GSK3β phosphorylation induces the Pin1 phosphorylation. To test this, human SK-N-MC cells were stably transfected with a fusion gene containing neuron-specific enolase (NSE)-controlled APPsw gene(NSE/APPsw), to induce Aβ-42. The stable transfectants were then transiently transfected with NSE/Splice, lacking human tau (NSE/Splice), or NSE/hTau, containing human tau, into the cells. The NSE/Splice- and NSE/hTau-cells were then treated with lithium. We concluded that (i) there was more C99-β APP accumulation than C83-βAPP in APPsw-tansfectant and thereby promoted Aβ-42 production in transfectants. (ii) the inhibition of tau and GSK3β phosphorylations correlated with increase in Pin1 activation in NSE/hTau- cells. Thus, these observations suggest that Pin1 might have an inhibitive role in phosphorylating tau and GSK3β for protecting against Alzheimer’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. P. Hanger K. Hughes J. R. Woodgett J. P. Brion B. H. Anderton (1992) ArticleTitleGlycogen synthase kinase-3 induces Alzheimer’s disease-like phosphorylation of tau; Generation of paired helical filament epitopes and neuronal localization of kinase Neurosci. lett. 147 58–62 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(92)90774-2 Occurrence Handle1336152
S. Lovestone C. H. Reynolds D. Latimer D. R. Davis B. H. Anderson M. GalloJ (1994) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease-like phosphorylation of the microtuble-associated protein tau by glycogen synthase kinase in transfected mammalian cells Curr. Biol. 4 1077–1086 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00246-3 Occurrence Handle7704571
K. Ishiguro A. Shiratsuchi S. Sato A. Omori M. Arioka S. Kobayashi T. Uchida K. Imahori (1993) ArticleTitleGlycogen synthase kinase 3β is identical to tau protein kinase 1 generating several epitopes of paired helical filaments FEBS Lett. 325 167–172 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-5793(93)81066-9 Occurrence Handle7686508
C. J. Phiel C. A. Wilson VM-Y. Lee P. S. Klein (2003) ArticleTitleGSK-3α regulates production of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-β peptides Nature 423 435–439 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01640 Occurrence Handle12761548
M. Hong D. C. Chen P. S. Klein V. M. Lee (1997) ArticleTitleLithium reduces tau phosphorylation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 J. Biol. Chem. 272 25326–25332 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.272.40.25326 Occurrence Handle9312151
X. Sun S. Sato H. Maruyama A. Takashima (2002) ArticleTitleLithium inhibits amyloid secretion in COS cells transfected with amyloid precursor protein C100 Neurosci. Lett. 321 61–64 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(01)02583-6 Occurrence Handle11872257
K. P. Lu S. D. Hanes T. Humter (1996) ArticleTitleA human peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis Nature. 380 544–547 Occurrence Handle10.1038/380544a0 Occurrence Handle8606777
K. E. Winkler K. I. Swenson S. Kornbluth A. R. Means (2000) ArticleTitleRequirement of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 for the replication checkpoint Science 287 1644–1647 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.287.5458.1644 Occurrence Handle10698738
P. Ramakrishnan D. W. Dickson P. Davies (2003) ArticleTitlepin 1 colocalization with phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies Neurobiol. Dis. 14 251–264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0969-9961(03)00109-8 Occurrence Handle14572447
P. J. Lu G. Wulf X. Z. Zhou P. Davies K. P. Lu (1999) ArticleTitleThe prolyl isomerase Pin1 restores the function of Alzheimer-associated phosphorylated tau protein Nature 399 784–788 Occurrence Handle10.1038/21650 Occurrence Handle10391244
J. R. Thorpe S. Mosahef L. Hashemzadeh-Bonehi N. J. Cairns J. E. Kay S. J. Morley S. L. Rulten (2004) ArticleTitleShortfalls in the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase protein Pin1 in neurons are associated with frontotemporal dementias Neurobiol. Dis. 17 237–249 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.nbd.2004.07.008 Occurrence Handle15474361
C. Smet A-V. Sambo J-M. Wieruszeski A. Leroy I. Landrien L. Buee G. Lippens (2004) ArticleTitleThe peptidyl prolyl cis/trans-isomerase Pin1 recognizes the phospho-Thr212-Pro213 site on tau Biochemistry 43 2032–2040 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi035479x Occurrence Handle14967043
Y. C. Lious A. Sun A. Ryo X. Z. Zhou Z. X. Yu H. K. Huang T. Uchida R. Bronson G. Bing X. Li T. Hunter K. P. Lu (2003) ArticleTitleRole of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 in protecting agaist age-dependent neurogeneration Nature 424 556–561 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01832 Occurrence Handle12891359
D. Y. Hwang J. S. Cho S. H. Lee K. R. Chae H. J. Lim S. H. Min S. J. Seo Y. S. Song C. W. Song S. K. Park Y. Y. Sheen Y. K. Kim (2004) ArticleTitleAberrant expressions of pathogenic phenotype in Alzheimer’s diseased transgenic mice carrying NSE-controlled APPsw Exp. Neurol. 186 20–32 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.expneurol.2003.09.021 Occurrence Handle14980807
S. Forss P. E. Denielson S. Catsicas E. Battenberg J. Price M. Nerenberg M. Sutcliffe (1990) ArticleTitleTransgenic mice expressing β-galactosidase in mature neuron under neyron-specific enolase promoter control Cell 5 187–197
MP. Mattson (2004) ArticleTitlePathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease Nature 430 631–639 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02621 Occurrence Handle15295589
M. Takahashi K. Yasutake K. Tomizawa (1999) ArticleTitleLithium inhibits neurite growth and tau protein kinase1/glycogen synthase kinase-3β-dependent phosphorylation of juvenile tau in cultured hippocampal neurons J. Neurochem. 73 2073–2083 Occurrence Handle10537067
J. R. Munoz-Montano F. J. Moreno J. Avila J. Diaz-Nido (1997) ArticleTitleLithium inhibits Alzheimer’s disease-like tau protein phosphorylation in neuron FEBS Lett. 411 183–188 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00688-1 Occurrence Handle9271202
T. Ishii H. Fruoka Y. Muroi M. Nishimura (2003) ArticleTitleInactivation of integrin-linked kinase induces aberrant tau phosphorylation via sustained activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells J. Biol. Chem. 278 26970–26975 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M304113200 Occurrence Handle12714590
S. Lovestone D. R. Davis M. T. Webster S. Kaech J. P. Brion A. Matus B. H. Anderton (1999) ArticleTitleLithium reduces tau phosphorylation: effects in living cells and neurons at therapeutic concentrations Biol. Psychiatry. 45 995–1003 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-3223(98)00183-8 Occurrence Handle10386182
P. S. Klein D. A. Melton (1996) ArticleTitleA molecular mechanism for the effect of lithium on development Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 8455–8459 Occurrence Handle8710892
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, S.H., Cho, J.S., Oh, J.H. et al. Tau and GSK3β Dephosphorylations are Required for Regulating Pin1 Phosphorylation. Neurochem Res 30, 955–961 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6177-0
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6177-0