Abstract
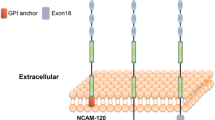
The neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM, is involved in multiple cis- and trans-homophilic interactions (NCAM binding to NCAM) thereby facilitating cell–cell adhesion through the formation of zipper-like NCAM-complexes. NCAM is also involved in heterophilic interactions with a number of proteins and extracellular matrix molecules. Some of these heterophilic interactions are mutually exclusive, and some interfere with or are dependent on homophilic NCAM interactions. Furthermore, both homo- and heterophilic interactions are modulated by posttranslational modifications of NCAM. Heterophilic NCAM-interactions initiate several intracellular signal transduction pathways ultimately leading to biological responses involving cellular differentiation, proliferation, migration and survival. Both homo- and heterophilic NCAM-interactions can be mimicked by synthetic peptides, which can induce NCAM-like signalling, and in vitroand in vivo studies suggest that such NCAM mimetics may be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Lawrence F. Eng.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walmod, P.S., Kolkova, K., Berezin, V. et al. Zippers Make Signals: NCAM-mediated Molecular Interactions and Signal Transduction. Neurochem Res 29, 2015–2035 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-004-6875-z
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-004-6875-z
Keywords
- ATP
- binding
- CD56
- cell adhesion molecule
- chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans
- fibroblast growth factor
- focal adhesion kinase
- Fyn
- glial cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor
- heparan sulfate proteoglycans
- HNK-1
- immunoglobulin
- interaction
- ligand
- mimetic
- NCAM
- neurite outgrowth
- palmitoylation
- peptide
- phosphorylation
- polysialic acid
- protein kinase
- protein structure
- signal transduction
- VASE