Abstract
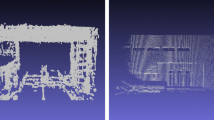
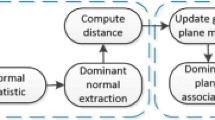
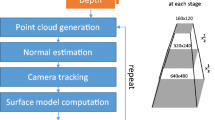
With the development of computer vision technologies, 3D reconstruction has become a hotspot. At present, 3D reconstruction relies heavily on expensive equipment and has poor real-time performance. In this paper, we aim at solving the problem of 3D reconstruction of an indoor scene with large vertical span. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for 3D reconstruction of indoor scenes with only a Kinect. Firstly, this method uses a Kinect sensor to get color images and depth images of an indoor scene. Secondly, the combination of scale-invariant feature transform and random sample consensus algorithm is used to determine the transformation matrix of adjacent frames, which can be seen as the initial value of iterative closest point (ICP). Thirdly, we establish the relative coordinate relation between pair-wise frames which are the initial point cloud data by using ICP. Finally, we achieve the 3D visual reconstruction model of indoor scene by the top-down image registration of point cloud data. This approach not only mitigates the sensor perspective restriction and achieves the indoor scene reconstruction of large vertical span, but also develops the fast algorithm of indoor scene reconstruction with large amount of cloud data. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has better accuracy, better reconstruction effect, and less running time for point cloud registration. In addition, the proposed method has great potential applied to 3D simultaneous location and mapping.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnard ST, Fischler MA (1982) Computational stereo. ACM Comput Surv 14(4):553–572
Thrun S, Burgard W, Fox D (2000) A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp 321–328
Huang MQ, Wang ZY, Hao LQ, Zhou LZ (2006) Laser aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis of individual aerosol particles from photooxidation of toluene. Opt Appl 36(1):1–5
Filipik A, Jan J, Peterlik I (2012) Time-of-Flight based calibration of an ultrasonic computed tomography system. Radio Eng 23(8):346–355
Zhang Z (2012) Microsoft kinect sensor and its effect. IEEE Multimed 19(2):4–10
Microsoft Kinect. http://www.xbox.com/de-de/kinect
Mair E, Strobl KH, Bodenmüller T, Suppa M, Burschka D (2010) Real-time image-based localization for hand-held 3D-modeling. KI-Künstl Intell 24(3):207–214
Besl PJ, McKay ND (2002) A method for registration of 3-D shapes. In: IEEE transactions on pattern analysis & machine intelligence, vol 14, no 2, pp 239–256
Rusinkiewicz S, Levoy M (2001) Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In: IEEE conference on 3D digital imaging and modeling, pp 145–152
Henry P, Krainin M, Herbst E, Ren X, Fox D (2012) RGB-D mapping: using Kinect-style depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments. Int J Robot Res 31(5):647–663
Newcombe RA, Izadi S, Hilliges O, Molyneaux D, Kim D, Davison AJ, Kohi P, Shotton J, Hodges S, Fitzgibbon A (2011)KinectFusion: real-time dense surface mapping and tracking. In: IEEE international symposium on mixed and augmented reality, pp 127–136
Izadi S, Kim D, Hilliges O, Molyneaux D, Newcombe R,Kohli P, Shotton J, Hodges S, FreemanD, Davison A (2011) KinectFusion: real-time 3D reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth camera. In: Proceedings of the 24th annual ACM symposium on user interface software and technology, pp 559–568
Liu X, Xu HR, Hu ZY (2012) GPU based fast 3D-object modeling with kinect. Acta Autom Sin 38(8):1288–1297
Zou Y, Chen W, Wu X, Liu Z (2012) Indoor localization and 3D scene reconstruction for mobile robots using the Microsoft Kinect sensor. In: IEEE international conference on industrial informatics, pp 1182–1187
Yue H, Chen W, Wu X, Liu J (2014) Fast 3D modeling in complex environments using a single Kinect sensor. Opt Lasers Eng 53(1):104–111
Wang K, Zhang G, Bao H (2014) Robust 3D reconstruction with an RGB-D camera. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(11):4893–4906
Choi S, Zhou QY, Koltun V (2015) Robust reconstruction of indoor scenes. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5556–5565
Mei F, Liu J, Li CP, Wang ZQ (2015) Improved RGB-D camera based indoor scene reconstruction. J Image Graph 20(10):1366–1373
Thomas D, Sugimoto A (2013) A flexible scene representation for 3D reconstruction using an RGB-D camera. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2800–2807
Yang Y, Gao M, Yin K, Wu Z (2015) High-quality depth map reconstruction combining stereo image pair. J Image Graph 20(1):1–10
Xiao JX, Owens A, Torralba A (2013) SUN3D: a database of big spaces reconstructed using sfm and object labels. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1625–1632
Zhang CH, Zhu RJ, Zhuang Y (2013) Indoor 3D scene reconstruction based on Kinect depth camera. Netw J Grad Sch Dalian Univ Technol 5:1–8
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Gool LV (2008) Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Chen XM, Jiang LT, Ying RD (2013) Research of 3D reconstruction and filtering algorithm based on depth information of Kinect. Appl Res Comput 30(4):1216–1218
Izadi S, Stamminger M (2013) Real-time 3D reconstruction at scale using voxel hashing. ACM Trans Graph 32(6):169–187
Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wu W, Liu K, Sun Z (2015) Model-driven indoor scenes modeling from a single image. In: Graphics interface conference canadian information processing society, pp 25–32
Li YF, Zhang GL, Xu J, Yao EL (2016) Improved ICP in frame-to-frame registration based on Kinect. Electron Opt Control 23(2):56–60
Du SY, Liu J, Zhang CJ, Zhu JH, Li K (2015) Probability iterative closest point algorithm for m-D point set registration with noise. Neurocomputing 157:187–198
Du SY, Liu J, Bi B, Zhu JH, Xue JR (2016) New iterative closest point algorithm for isotropic scaling registration of point sets with noise. J Vis Commun Image Represent 38:207–216
Ying S, Wu G, Wang Q, Shen D (2014) Hierarchical unbiased graph shrinkage (HUGS): a novel groupwise registration for large data set. Neuroimage 84(1):626–638
Ying S, Wang Y, Wen Z, Lin Y (2016) Nonlinear 2D shape registration via thin-plate spline and Lie group representation. Neurocomputing 195:129–136
Santos DRD, Basso MA, Khoshelham K, Oliveira ED, Pavan NL, Vosselman G (2016) Mapping indoor spaces by adaptive coarse-to-fine registration of RGB-D data. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 13(2):262–266
Xi L (2017) A real time implementation of 3D symmetric object reconstruction. Faculty of the Graduate School of the University of Maryland, College Park
Lv Q, Lin H, Wang G, Wei H, Wang Y (2017) ORB-SLAM-based tracing and 3D reconstruction for robot using Kinect 2.0. In: IEEE control and decision conference, pp 3319–3324
Nuchter A, Lingemann K, Hertzberg J (2007) Cached k-d tree search for ICP algorithms. In: IEEE international conference on 3D digital imaging and modeling, pp 419–426
Chen HM, Lin TH (2006) An algorithm to build convex hulls for 3D objects. J Chin Inst Eng 29(6):945–952
Lowe DG (1999) Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. Int Conf Comput Vis 2:1150–1157
Helmer S, Lowe DG (2004) Object class recognition with many local features. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshop, pp 182–187
Lindeberg T (2013) Image matching using generalized scale-space interest points. In: International conference on scale space and variational methods in computer vision, pp 355–367
Xu M, Lu J (2012) Distributed RANSAC for the robust estimation of three-dimensional reconstruction. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 324–333
Fischler MA, Bolles RC (1981) Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun ACM 24(6):381–395
Li C, Xue JR, Du SY, Zheng NN (2010) A fast multi-resolution iterative closest point algorithm. In: Chinese conference on pattern recognition, pp 1–5
Acknowledgements
The paper was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC) of China under Grant Nos. 61373077, 61365003 and Gansu Province Basic Research Innovation Group Project No. 1506RJIA031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Lu, B., Zhang, Y. et al. 3D Reconstruction of Indoor Scenes via Image Registration. Neural Process Lett 48, 1281–1304 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9781-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9781-0