Abstract
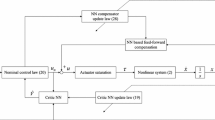
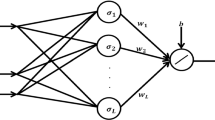
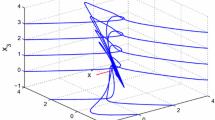
Intrinsically, Lagrange multipliers in nonlinear programming algorithms play a regulating role in the process of searching optimal solution of constrained optimization problems. Hence, they can be regarded as the counterpart of control input variables in control systems. From this perspective, it is demonstrated that constructing nonlinear programming neural networks may be formulated into solving servomechanism problems with unknown equilibrium point which coincides with optimal solution. In this paper, under second-order sufficient assumption of nonlinear programming problems, a dynamic output feedback control law analogous to that of nonlinear servomechanism problems is proposed to stabilize the corresponding nonlinear programming neural networks. Moreover, the asymptotical stability is shown by Lyapunov First Approximation Principle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazaraa MS, Sherali HD, Shetty CM (1993) Nonlinear programming: theory and algorithms 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Kinderlehrer D, Stampcchia G (1980) An introduction to variational inequalities and their applications. Academic, New York
Facchinei F, Fischer A, Kanzow C (1999) A simply constrained optimization reformulation of KKT systems arising from variational inequalities. Appl Math Optim 40: 19–37
Solodov MV, Tseng P (1996) Modified projection-type methods for monotone variational inequalities. SIAM J Control Optim 2: 1814–1830
Wachter A, Biegler LT (2005) Line search filter methods for nonlinear programming: motivation and global convergence. SIAM J Optim 16: 1–31
Tank DW, Hopfield JJ (1986) Simple neural optimization networks: an A/D converter, signal decision circuit, and a linear programming circuit. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst CAS 33(5): 533–541
Chua LO, Lin G-N (1984) Nonlinear programming without computation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst CAS 31(2): 182–188
Kennedy MP, Chua LO (1986) Unifying the tank and Hopeld linear programming circuit and the canonical nonlinear programming circuit of Chua and Lin. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst CAS 34(2): 210–214
Lillo WE, Loh MH, Hui S, Zak SH (1993) On solving constrained optimization problems with neural networks: a penalty method approach. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 4(6): 931–940
Rodriguez-Vazquez A, Dominguez-Castro R, Rueda A, Huertas JL, Sanchez-Sinencio E (1990) Nonlinear switched-capacitor neural networks for optimization problems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst 37(3): 384–398
Lillo WE, Hui S, Zak SH (1993) Neural networks for constrained optimization problems. Int J Circuit Theory Appl 21: 385–399
Cichocki A, Unbehauen R (1993) Neural networks for optimization and signal processing. Wiley, New York
Zak SH, Upatising V, Hui S (1995) Solving linear programming problems with neural networks: a comparative study. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 6(1): 94–103
Chong E, Hui S, Zak SH (1999) An analysis of a class of neural networks for solving linear programming problems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 44(11): 1995–2006
Forti M, Nistri P, Quincampoix M (2004) Generalized neural network for nonsmooth nonlinear programming problems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Reg Pap 51(9): 1741–1754
Forti M, Nistri P, Quincampoix M (2006) Convergence of neural networks for programming problems via a nonsmooth Lojasiewicz inequality. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(6): 1471–1486
Zhang S, Constandinides AG (1992) Lagrange programming neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, Analog Digit Signal Process 39(7): 441–452
Zhang S, Zhu X, Zou L-H (1992) Second-order neural nets for constrained optimization. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3(6): 1021–1024
Xia Y (2003) Global convergence analysis of Lagrangian networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Fund Theory Appl 50(6): 818–822
Huang YC (2002) A novel method to handle inequality constraints for convex programming neural network. Neural Process Lett 16(1): 17–27
Huang YC (2005) Lagrange-type neural networks for nonlinear programming problems with inequality constraints. In: Proceeding of the 44th conference on decision and control
Xia Y (1996) A new neural network for solving linear and quadratic programming problems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 7(6): 1544–1547
Xia Y, Wang J (2000) A recurrent neural network for solving linear projection equations. Neural Netw 13: 337–350
Zhang Y, Wang J (2002) A dual neural network for convex quadratic programming subject to linear equality and inequality constraints. Phys Lett A 298: 271–278
Xia Y, Feng G, Wang J (2004) A recurrent neural network with exponential convergence for solving convex quadratic program and related linear piecewise equations. Neural Netw 17: 1003–1015
Gao X-B, Liao L-Z, Xue W (2004) A neural network for a class of convex quadratic minimax problems with constraints. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(3): 622–628
Xia Y, Wang J (1998) A general methodology for designing globally convergent optimization neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 9(6): 1331–1343
Liang X-B, Wang J (2000) A recurrent neural network for nonlinear optimization with a continuously differentiable objective function and bound constraints. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11(6): 1251–1262
Xia Y, Leung H, Wang J (2002) Aprojection neural network and its application to constrained optimization problems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Fund Theory Appl 49(4): 447–458
Tao Q, Cao J, Xue M, Qiao H (2001) A high performance neural network for solving nonlinear programming problems with hybrid constraints. Phys Lett A 288(2): 88–94
Gao X-B (2004) A novel neural network for nonlinear convex programming. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(3): 613–621
Xia Y, Wang J (2005) A recurrent neural network for solving nonlinear convex programs subject to linear constraints. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(2): 379–386
Gao X-B (2003) Exponential stability of globally projected dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(2): 426–431
Xia Y, Wang J (2004) A general projection neural network for solving monotone variational inequality and related optimization problems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(2): 318–328
Gao X-B, Liao L-Z, Qi L (2005) A novel neural network for variational inequalities with linear and nonlinear constraints. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(6): 1305–1317
Hu X, Wang J (2006) Solving pseudomonotone variational inequalities and pseudoconvex optimization problems using the projection neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(6): 1487–1499
Hu X, Wang J (2007) Solving generally constrained generalized linear variational inequalities using the general projection neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 18(6): 1697–1708
Bertsekas DP (1999) Nonlinear programming 2nd edn. Massachusetts Athena Scientific, Belmont
Bertsekas DP (1982) Constrainted optimization and lagrange methods. Academic Press, New York
Avriel M (1976) Nonlinear programming analysis and methods. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Nocedal J, Wright SJ (1999) Numerical optimization. Springer, New York
Rockafellar RT (1993) Lagrange multiplier and optimality. SIAM Rev 35: 183–238
Isidori A (1995) Nonlinear control systems. Springer, New York
Isidori A, Byrnes CI (1990) Output regulation of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 35(2): 880–885
Huang J, Chen ZY (2004) A general framework for tackling the output regulation problem. IEEE Trans Autom Control 49(12): 2203–2218
Byrnes CI, Isidori A (2003) Limit sets, zero dynamics, and internal models in the problem of nonlinear output regulation. IEEE Trans Autom Control 48(10): 1712–1723
Byrnes CI, Isidori A (2000) Output regulation for nonlinear systems: an overview. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 10: 323–337
Davison EJ (1976) The Robust control of a servomechanism problem for linear time-invariant multivariable systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 21(1): 25–34
Francis BA (1977) The linear multivariable regulator problem. SIAM J Control Optim 14: 486–505
Francis BA, Wonham WM (1976) The internal model principle of control theory. Automatica 12(5): 457–465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y. On a Stabilization Problem of Nonlinear Programming Neural Networks. Neural Process Lett 31, 93–103 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-010-9129-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-010-9129-x