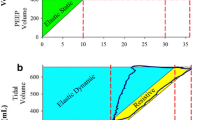
There are limited reports on using a mathematical approach to relate the respiration rate with the cerebrovascular flow rate during and after periods of deep breathing (DB) in humans. Here, modeling was applied to estimate the cerebral oxygen delivery (CDO2) impacted by three episodes of DB of different durations on a few parameters, including the respiration rate (RF) and oxygen saturation (SpO2). Results indicated that the DB groups of tested subjects achieved a qualitatively lower RF and greater CDO2 during the follow-up session. This suggests that the constant practice of deep breathing leads to a reduction in the RF and an increment in the CDO2, which can potentially improve cognitive abilitiy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. West, Pulmonary Pathophysiology: the Essentials, Wolters Kuwer/Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Health, Philadelphia (2013).
J. Jongbloed, C. L. C. van Nieuwenhuizen, and H. van Goor, “A heart function test with continuous registration of oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production,” Circulation, 15, 54-63 (1957).
P. J. Eames, J. F. Potter, and R. B. Panerai, “Influence of controlled breathing patterns on cerebrovascular autoregulation and cardiac baroreceptor sensitivity,” Clin. Sci., 106, 155-162 (2004).
S. J. E. Lucas, N. C. S. Lewis, E. L. G. Sikken, et al., “Slow breathing as a means to improve orthostatic tolerance : a randomized sham-controlled trial,” J. Appl. Physiol., 115, 202-211 (2013).
W. Karlen, H. Gan , M. Chiu, et al., “Improving the accuracy and efficiency of respiratory rate measurements in children using mobile devices,” PLoS One, 9, 1-9 (2014).
J. W. Severinghaus, “Simple, accurate equations for human blood O2 dissociation computations,” J. Appl. Physiol., 46, 599-602 (1979).
R. O. Crapo, R. L. Jensen, M. Hegewald, and D. P. Tashkin, “Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters,” Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 160, 1525-1531 (1999).
S. K. Piechnik, P. A. Chiarelli, and P. Jezzard, “Modelling vascular reactivity to investigate the basis of the relationship between cerebral blood volume and flow under CO2 manipulation,” NeuroImage, 39, 107-118 (2008).
R. Lampe, N. Botkin, V. Turova, et al., “Mathematical modelling of cerebral blood circulation and cerebral autoregulation: towards preventing intracranial hemorrhages in preterm newborns,” Comput. Math. Methods Med., 2014, 1-9 (2014).
R. MecPherson and M. Pincus, Henry’s Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods, Saunders (2011).
E. Tharion, P. Samuel, R. Rajalakshmi, et al., “Influence of deep breathing exercise on spontaneous respiratory rate and heart rate variability: a randomised controlled trial in healthy subjects,” Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 56, 80-87 (2012).
G. Bilo, M. Revera, M Bussotti, et al., “Effects of slow deep breathing at high altitude on oxygen saturation, pulmonary and systemic hemodynamics,” PLoS One, 7, 1-7 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, K.S., Lee, P.F. A Physiological/Model Study on the Effects of Deep Breathing on the Respiration Rate, Oxygen Saturation, and Cerebral Oxygen Delivery in Humans. Neurophysiology 50, 351–356 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-019-09761-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-019-09761-4