Abstract
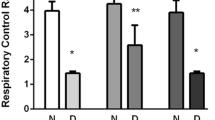
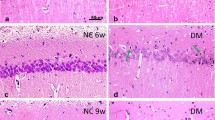
We examined, using a Western blot technique, the contents and compositions of a specific neuronal protein, NCAM, and of an astrocyte marker, GFAP, in the hippocampus and cortex of rats with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes and compared these indices with those in control (intact) animals and STZ-diabetic rats treated with melatonin. Behavioral cognitive indices manifested in the passive avoidance test (PAT) and Morris water maze (MWM) learning performance were also estimated in the above groups of animals. As was found, STZ-diabetic rats demonstrated clear cognitive deficits according to the values of the retention latency in the PAT and time of reaching the escape platform in the MWM performance. In these animals, the GFAP content was elevated, and the amount of degraded products of this protein increased, as compared with the control. Simultaneously, considerable down-regulation of the NCAM expression and modifications of NCAM isoform composition were found in diabetic animals. In addition, significantly increased levels of lipid peroxidation (according to the amounts of malondialdehyde + 4-hydroxyalkenals) were measured in the cortex and hippocampus of rats with stable diabetic hyperglycemia. All the above-mentioned shifts were significantly smoothed or even nearly completely compensated in the case of treatment of STZ-diabetic rats with melatonin (10 mg/kg per day). The role of diabetes-related changes in the amount and composition of specific neural and glial proteins in the development of cognitive deficits, the involvement of oxidative stress in the mechanisms of the respective shifts, and possible mechanisms of the neuroprotective effect of melatonin with respect to diabetes-related pathological biochemical and behavioral shifts are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Popovic, G. J. Biessels, R. L. Isaacson. and W. H. Gispen, “Learning and memory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats in a novel spatial-object discrimination task,” Behav. Brain Res., 122, No. 2, 201–207 (2001).
V. S. Nedzvetsky, P. A. Nerush, and S. V. Kirichenko, “Effect of melatonin on cognitive ability of rats and expression of NCAM in brain structures in streptozotocin-induced diabetes,” Neurophysiology, 35, No. 6, 422–427 (2003).
C. L. Hawkins and M. J. Davies, “Generation and propagation of radical reactions on proteins,” Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1504, No. 2, 196–219 (2001).
L. C. Ronn, V. Berezin, and E. Bock, “The neural cell adhesion molecule in synaptic plasticity and ageing,” Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 18, No. 1, 193–199 (2000).
A. G. Foley, K. Hedigan, P. Roullet, et al., “Consolidation of memory for odour-reward association requires transient polysialylation of the neural cell adhesion molecule in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci. Res., 74, No. 4, 570–576 (2003).
O. Bukalo, N. Fentrop, A. Y. Lee, et al., “Conditional ablation of the neural cell adhesion molecule reduces precision of spatial learning, long-term potentiation, and depression in the CA1 subfield of mouse hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 7, 1565–1577 (2004).
M. P. Vawter, M. A. Frye, J. J. Hemperly, et al., “Elevated concentration of N-CAM VASE isoforms in schizophrenia,” J. Psychiat. Res., 34, No. 1, 25–34 (2000).
H. Welzl and O. Stork, “Cell adhesion molecules: key players in memory nonsolidation?” News Physiol. Sci., 18, No. 2, 147–150 (2003).
J. L. Ridet, S. K. Malhotra, A. Privat, and F. H. Gage, “Reactive astrocytes: cellular and molecular cues to biological function,” Trends Neurosci., 20, No. 12, 570–577 (1997).
L. F. Eng, R. S. Ghirnikar, and Y. L. Lee, “Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000),” Neurochem. Res., 25, Nos. 9/10, 1439–1451 (2000).
M. Pekny and M. Pekna, “Astrocyte intermediate filaments in CNS pathologies and regeneration,” J. Pathol., 204, No. 4, 428–437 (2004).
D. L. Montgomery, “Astrocytes: form, function, and roles in disease,” Vet. Pathol., 31, 145–167, (1994).
M. D. Norenberg, “Astrocyte responses to CNS injury,” J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 53, No. 3, 213–220 (1994).
G. Baydas, V. S. Nedzvetskii, M. Tuzcu, et al., “Increase of glial fibrillary acidic protein and S-100B in hippocampus and cortex of diabetic rats: effects of vitamin E,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 462, 67–71 (2003).
G. Baydas, V. S. Nedzvetsky, P. A. Nerush, et al., “A novel role for melatonin: regulation of the expression of cell adhesion molecules in the rat hippocampus and cortex,” Neurosci. Lett., 326, No. 2, 109–112 (2002).
M. Sharma and Y. K. Gupta, “Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats produces both oxidative stress in the brain and cognitive impairment,” Life Sci., 68, No. 1, 1021–1029 (2001).
R. G. Morris, P. Garrud, J. N. Rawlins, and J. O’Keefe, “Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions,” Nature, 297, 681–683 (1982).
G. J. Biessels, A. Kamal, G. M. Ramakers, et al., “Place learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats,” Diabetes, 45, No. 9, 1259–1266 (1996).
U. K. Laemmli, “Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4,” Nature, 227, 680–685 (1970).
G. Baydas, R. J. Reiter, V. S. Nedzvetskii, et al., “Melatonin protects the central nervous system of rats against toluene-containing thinner intoxication by reducing reactive gliosis,” Toxicol. Lett., 137, No. 2, 169–174 (2003).
G. L. Miller, “Protein determination for large numbers of samples,” Anal. Chem., 31, No. 5, 964–966 (1959).
J. D. Rothstein and R. W. Kuncl, “Neuroprotective strategies in a model of chronic glutamate-mediated motor neuron toxicity,” J. Neurochem., 65, 643–651 (1995).
E. Ercel, G. Baydas, A. Akyol, et al., “The effect of vitamin E on the sciatic nerve lipid peroxidation in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus,” Biomed. Res., 10, No. 1, 95–101 (1999).
L. L. Guyot, F. G. Diaz, M. H. O’Regan, et al., “The effect of topical insulin on the release of excitotoxic and other amino acids from the rat cerebral cortex during streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic ischemia,” Brain Res., 872, 29–36 (2000).
G. Baydas, R. J. Reiter, A. Yasar, et al., “Melatonin reduces glial reactivity in the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats,” Free Radical. Biol. Med., 35, No. 3, 797–804 (2003).
V. S. Nedzvetskii, M. Tuzcu, A. Yasar, et al., “Effects of vitamin E against aluminum neurotoxicity in rats,” Biochemistry, 71, No. 3, 239–244 (2006).
K. Kaneko, A. Nakamura, K. Yoshida, et al., “Glial fibrillary acidic protein is greatly modified by oxidative stress in aceruloplasminemia brain,” Free Radical. Res., 36, No. 2, 303–306 (2002).
G. Baydas, S. T. Koz, M. Tuzcu, et al., “Effects of maternal hyperhomocysteinemia induced by high methionine diet on the learning and memory performance in offspring,” Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 25, No. 3, 133–139 (2007).
K. Fink, D. J. Dooley, W. P. Meder, et al., “Inhibition of neuronal Ca2+ influx by gabapentin and pregabalin in the human neocortex,” Neuropharmacology, 42, No. 2, 229–236 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 105–111, March–April, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baydas, G., Nedzvetskii, V.S., Kirichenko, S.V. et al. Astrogliosis in the hippocampus and cortex and cognitive deficits in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Effects of melatonin. Neurophysiology 40, 91–97 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9026-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9026-3