Abstract
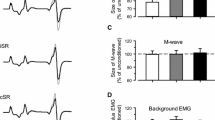
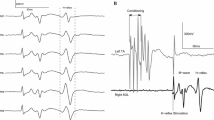
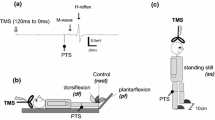
In healthy humans, we studied the influence of conditioning voluntary arm movements on the H reflex induced by transcutaneous stimulation of the tibial nerve and recorded from the soleus muscle. We examined the effects of flexion and extension of the forearm, as well as of finger clenching performed with the maximum rate. Conditioning arm movements were self-induced or realized upon presentation of a visual signal (light flash). We found that the pattern of changes in the H reflex is determined by the position of the subject’s body in the course of tests. The ipsilateral arm flexion in the elbow joint in the standing position resulted in depression of the H reflex lasting about 100 msec from the beginning of the movement, while the effect observed in the lying position (on the couch with the feet hanging free in the air) looked like a facilitation of the reflex lasting about 100 to 200 msec. The direction and dynamics of modifications of the H reflex under conditions of the use of different conditioning movements (forearm flexions/extensions and finger clenching of the ipsilateral arm, as well as contralateral forearm flexions in the elbow joint) were rather similar. We also showed that the observed facilitation of the H reflex began earlier than the voluntary arm movement (40 to 50 msec prior to the beginning). We hypothesize that these conditioning influences result from the action of central motor commands and represent the factor related to anticipatory postural rearrangements. Such rearrangements are directed toward the maintenance of equilibrium of the body in the course of a future movement. These commands depend significantly on the spatial position of the subject’s body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Hiraoka, “Phase-dependent modulation of the soleus H-reflex during rhythmical arm swing in humans,” Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 41, No. 1, 43–47 (2001).
K. Hiraoka and A. Iwata, “Cyclic modulation of H-reflex depression in ipsilateral and contralateral soleus muscles during rhythmic arm swing,” Somatosensor. Motor Res., 23, No. 3, 127–133 (2006).
A. Frigon, D. F. Collins, and E. P. Zehr, “Effect of rhythmic arm movement on reflexes in the legs: modulation of soleus H-reflexes and somatosensory conditioning,” J. Neurophysiol., 91, No. 4, 1516–1523 (2004).
T. Kasai and T. Komiyama, “Soleus reflex depression induced by ballistic voluntary arm movement in humans,” Brain Res., 714, Nos. 1/2, 125–134 (1996).
M. Kawanishi, S. Yahagi, and T. Kasai, “Neural mechanisms of soleus H-reflex depression accompanying voluntary arm movement in standing humans,” Brain Res., 832, No. 1/2, 13–22 (1999).
S. Bouisset and M. Zattara, “Biomechanical study of the programming of anticipatory postural adjustments associated with voluntary movement,” J. Biomech., 20, No. 8, 735–742 (1987).
M. Zattara and S. Bouisset, “Posturo-kinetic organization during the early phase of voluntary upper limb movement. 1. Normal subjects,” J. Neurol., Neurosurg., Psychiat., 51, No. 7, 956–965 (1988).
A. S. Aruin and M. L. Latash, “Directional specificity of postural muscles in feed-forward postural reactions during fast voluntary arm movements,” Exp. Brain Res., 103, No. 2, 323–332 (1995).
A. S. Aruin, W. R. Forrest, and M. L. Latash, “Anticipatory postural adjustments in conditions of postural instability,” Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 109, No. 4, 350–359 (1998).
A. S. Aruin, “The effect of changes in the body configuration on anticipatory postural adjustments,” Motor Control, 7, No. 3, 264–277 (2003).
H.-M. Meinck and B. Piesiur-Strehlow, “Reflexes evoked in leg muscles from arm afferents: a propriospinal pathway in man?” Exp. Brain Res., 43, No. 1, 78–86 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 147–154, March–April, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slivko, É.I., Bogutskaya, G.A. Modulation of the soleus muscle H reflex caused by ballistic voluntary arm movements in humans. Neurophysiology 40, 130–136 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9023-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9023-6