Abstract
Purpose
New therapies for melanoma have been associated with increasing survival expectations, as opposed to the dismal outcomes of only a decade ago. Using a prospective registry, we aimed to define current survival goals for melanoma patients with brain metastases (BM), based on state-of-the-art multimodality care.
Methods
We reviewed 171 melanoma patients with BM receiving stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) who were followed with point-of-care data collection between 2012 and 2020. Clinical, molecular and imaging data were collected, including systemic treatment and radiosurgical parameters.
Results
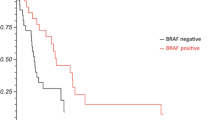
Mean age was 63 ± 15 years, 39% were female and 29% had BRAF-mutated tumors. Median overall survival after radiosurgery was 15.7 months (95% Confidence Interval 11.4–27.7) and 25 months in patients managed since 2015. Thirty-two patients survived \(\ge\) 5 years from their initial SRS. BRAF mutation-targeted therapies showed a survival advantage in comparison to chemotherapy (p = 0.009), but not to immunotherapy (p = 0.09). In a multivariable analysis, both immunotherapy and the number of metastases at 1st SRS were predictors of long-term survival (\(\ge\) 5 years) from initial SRS (p = 0.023 and p = 0.018, respectively). Five patients (16%) of the long-term survivors required no active treatment for \(\ge\) 5 years.
Conclusion
Long-term survival in patients with melanoma BM is achievable in the current era of SRS combined with immunotherapies. For those alive \(\ge\) 5 years after first SRS, 16% had been also off systemic or local brain therapy for over 5 years. Given late recurrences of melanoma, caution is warranted, however prolonged survival off active treatment in a subset of our patients raises the potential for cure.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sampson JH, Carter JH, Friedman AH, Seigler HF (1998) Demographics, prognosis, and therapy in 702 patients with brain metastases from malignant melanoma. J Neurosurg 88:11–20. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.88.1.0011
Skibber JM, Soong S, Austin L et al (1996) Cranial irradiation after surgical excision of brain metastases in melanoma patients. Ann Surg Oncol 3:118–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02305789
Patel H, Yacoub N, Mishra R et al (2020) Current advances in the treatment of BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancers (Basel) 12:E482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020482
Moravan MJ, Fecci PE, Anders CK et al (2020) Current multidisciplinary management of brain metastases. Cancer 126:1390–1406. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32714
Fecci PE, Champion CD, Hoj J et al (2019) The evolving modern management of brain metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 25:6570–6580. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1624
Saha S, Meyer M, Krementz ET et al (1994) Prognostic evaluation of intracranial metastasis in malignant melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol 1:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02303539
Geara FB, Ang KK (1996) Radiation therapy for malignant melanoma. Surg Clin North Am 76:1383–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70521-1
Doss LL, Memula N (1982) The radioresponsiveness of melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 8:1131–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(82)90060-8
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ et al (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.037
DiLuna ML, King JT, Knisely JPS, Chiang VL (2007) Prognostic factors for survival after stereotactic radiosurgery vary with the number of cerebral metastases. Cancer 109:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22367
Samlowski WE, Watson GA, Wang M et al (2007) Multimodality treatment of melanoma brain metastases incorporating stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Cancer 109:1855–1862. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22605
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock BE et al (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with “radioresistant” brain metastases. Neurosurgery 51:656–665 (discussion 665-667)
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock BE et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with “radioresistant” brain metastases. Neurosurgery 62(Suppl 2):790–801. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000316283.45242.e1
Tsao MN, Xu W, Wong RK et al (2018) Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD003869. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub4
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH et al (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2
Koc M, McGregor J, Grecula J et al (2005) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for intracranial metastatic melanoma: an analysis of survival and prognostic factors. J Neurooncol 71:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-2027-1
Mori Y, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC et al (1998) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma: factors affecting local disease control and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(98)00272-7
Powell JW, Chung CT, Shah HR et al (2008) Gamma Knife surgery in the management of radioresistant brain metastases in high-risk patients with melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and sarcoma. J Neurosurg 109(Suppl):122–128. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/12/S19
Somaza S, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD et al (1993) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral metastatic melanoma. J Neurosurg 79:661–666. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1993.79.5.0661
Korn EL, Liu P-Y, Lee SJ et al (2008) Meta-analysis of phase II cooperative group trials in metastatic stage IV melanoma to determine progression-free and overall survival benchmarks for future phase II trials. J Clin Oncol 26:527–534. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.12.7837
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:898–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.035
Fife KM, Colman MH, Stevens GN et al (2004) Determinants of outcome in melanoma patients with cerebral metastases. J Clin Oncol 22:1293–1300. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.08.140
Liszkay G, Kiss Z, Gyulai R et al (2021) Changing trends in melanoma incidence and decreasing melanoma mortality in Hungary between 2011 and 2019: a nationwide epidemiological study. Front Oncol 10:3236. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.612459
Puri P, Cortese D, Baliga S (2021) A time series analysis of immune checkpoint inhibitor use in the United States Medicare population: 2014–2019. J Dermatol Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2021.1962002
Atkins MB, Sosman JA, Agarwala S et al (2008) Temozolomide, thalidomide, and whole brain radiation therapy for patients with brain metastasis from metastatic melanoma: a phase II Cytokine Working Group study. Cancer 113:2139–2145. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23805
Ott PA, Chang JL, Oratz R et al (2009) Phase II trial of dacarbazine and thalidomide for the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Chemotherapy 55:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1159/000219435
Tarhini AA, Kirkwood JM, Gooding WE et al (2008) A phase 2 trial of sequential temozolomide chemotherapy followed by high-dose interleukin 2 immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma. Cancer 113:1632–1640. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23791
Kouvaris JR, Miliadou A, Kouloulias VE et al (2007) Phase II study of temozolomide and concomitant whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases from solid tumors. Onkologie 30:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1159/000102557
Bamias A, Aravantinos G, Deliveliotis C et al (2004) Docetaxel and cisplatin with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) versus MVAC with G-CSF in advanced urothelial carcinoma: a multicenter, randomized, phase III study from the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 22:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.02.152
Patel M, Eckburg A, Gantiwala S et al (2021) Resistance to molecularly targeted therapies in melanoma. Cancers (Basel) 13:1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051115
Rulli E, Legramandi L, Salvati L, Mandala M (2019) The impact of targeted therapies and immunotherapy in melanoma brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer 125:3776–3789. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32375
Tawbi HA, Forsyth PA, Hodi FS et al (2021) Long-term outcomes of patients with active melanoma brain metastases treated with combination nivolumab plus ipilimumab (CheckMate 204): final results of an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 22:1692–1704. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00545-3
Lutterbach J, Bartelt S, Ostertag C (2002) Long-term survival in patients with brain metastases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 128:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-002-0354-1
Kotecha R, Suh JH, Barnett G et al (2015) A cure is possible: a study of 10 year survivors of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93:E98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.796
Dasgupta A, Co J, Winter J et al (2021) Clinicopathologic and treatment features of long-term surviving brain metastasis patients. Curr Oncol 28:549–559. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28010054
Vosoughi E, Lee JM, Miller JR et al (2018) Survival and clinical outcomes of patients with melanoma brain metastasis in the era of checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies. BMC Cancer 18:490. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4374-x
Niemiec M, Głogowski M, Tyc-Szczepaniak D et al (2011) Characteristics of long-term survivors of brain metastases from lung cancer. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 16:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2011.01.002
Nguyen SM, Castrellon A, Vaidis O, Johnson AE (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery and ipilimumab versus stereotactic radiosurgery alone in melanoma brain metastases. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1511
Martins F, Schiappacasse L, Levivier M et al (2020) The combination of stereotactic radiosurgery with immune checkpoint inhibition or targeted therapy in melanoma patients with brain metastases: a retrospective study. J Neurooncol 146:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03363-0
Corti F, Randon G, Bini M et al (2020) Risk of disease progression (PD) following discontinuation of BRAF±MEK targeted therapies for reasons other than PD in patients (pts) with metastatic or unresectable melanoma. JCO 38:10053–10053. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.10053
Bédouelle E, Nguyen JM, Varey E et al (2021) Should targeted therapy be continued in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients after complete remission? DRM. https://doi.org/10.1159/000518718
Asher AL, Alvi MA, Bydon M et al (2021) Local failure after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for intracranial metastasis: analysis from a cooperative, prospective national registry. J Neurooncol 152:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03698-7
Kotecha R, Miller JA, Venur VA et al (2018) Melanoma brain metastasis: the impact of stereotactic radiosurgery, BRAF mutational status, and targeted and/or immune-based therapies on treatment outcome. J Neurosurg 129:50–59. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.1.JNS162797
Sawrie SM, Guthrie BL, Spencer SA et al (2008) Predictors of distant brain recurrence for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.05.084
Yu C, Chen JCT, Apuzzo MLJ et al (2002) Metastatic melanoma to the brain: prognostic factors after gamma knife radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:1277–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(01)02772-9
Davies MA, Saiag P, Robert C et al (2017) Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAF V600–mutant melanoma brain metastases (COMBI-MB): a multi-cohort, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:863–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30429-1
Savas B, Arslan G, Gelen T et al (1999) Multidrug resistant malignant melanoma with intracranial metastasis responding to immunotherapy. Anticancer Res 19:4413–4420
Guirguis LM, Yang JC, White DE et al (2002) Safety and efficacy of high-dose interleukin-2 therapy in patients with brain metastases. J Immunother 25:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002371-200201000-00009
Minniti G, Anzellini D, Reverberi C et al (2019) Stereotactic radiosurgery combined with nivolumab or Ipilimumab for patients with melanoma brain metastases: evaluation of brain control and toxicity. J Immunother Cancer 7:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0588-y
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the NYU Langone Health Tech Hub for providing us with efficient access to the clinical data lake.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: DK, AB. Material preparation: AB, JDA, RM, JG, MM, KM, AP. Data collection: AB, JDA, RM. Data analysis: AB, KB. Data interpretation: DK, AB, JS, ES, BD, JW, JG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the NYU Langone Health Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, A., Bernstein, K., Alzate, J.D. et al. Significant survival improvements for patients with melanoma brain metastases: can we reach cure in the current era?. J Neurooncol 158, 471–480 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04036-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04036-1