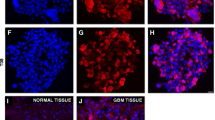
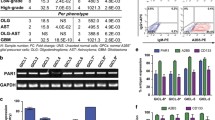
Abstract
SHP2 is a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) involved in multiple signaling pathways and was the first identified proto-oncogene PTPase. Previous work in glioblastoma (GBM) has demonstrated the role of SHP2 PTPase activity in modulating the oncogenic phenotype of adherent GBM cell lines. Mutations in PTPN11, the gene encoding SHP2, have been identified with increasing frequency in GBM. Given the importance of SHP2 in developing neural stem cells, and the importance of glioma stem cells (GSCs) in GBM oncogenesis, we explored the functional role of SHP2 in GSCs. Using paired differentiated and stem cell primary cultures, we investigated the association of SHP2 expression with the tumor stem cell compartment. Proliferation and soft agar assays were used to demonstrate the functional contribution of SHP2 to cell growth and transformation. SHP2 expression correlated with SOX2 expression in GSC lines and was decreased in differentiated cells. Forced differentiation of GSCs by removal of growth factors, as confirmed by loss of SOX2 expression, also resulted in decreased SHP2 expression. Lentiviral-mediated knockdown of SHP2 inhibited proliferation. Finally, growth in soft-agar was similarly inhibited by loss of SHP2 expression. Our results show that SHP2 function is required for cell growth and transformation of the GSC compartment in GBM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng GS (1999) Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase: signaling one cell or many. Exp Cell Res 253:47–54. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4668
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Tao B, Teng L, Li Y, Cao R, Gui Q, Ye M, Mou X, Cheng H, Hu H, Zhou R, Wu X, Xie Q, Ning W, Lai M, Shen H, Feng GS, Ke Y (2012) Loss of Shp2 in alveoli epithelia induces deregulated surfactant homeostasis, resulting in spontaneous pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J 26:2338–2350. doi:10.1096/fj.11-200139
Ostman A, Hellberg C, Bohmer FD (2006) Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:307–320. doi:10.1038/nrc1837
Chan G, Kalaitzidis D, Neel BG (2008) The tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 (PTPN11) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27:179–192. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9126-y
Grossmann KS, Rosario M, Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W (2010) The tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 in development and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 106:53–89. doi:10.1016/S0065-230X(10)06002-1
Shi ZQ, Yu DH, Park M, Marshall M, Feng GS (2000) Molecular mechanism for the Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase function in promoting growth factor stimulation of Erk activity. Mol Cell Biol 20:1526–1536
Kapoor GS, Zhan Y, Johnson GR, O’Rourke DM (2004) Distinct domains in the SHP-2 phosphatase differentially regulate epidermal growth factor receptor/NF-kappaB activation through Gab1 in glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 24:823–836
Wu CJ, Chen Z, Ullrich A, Greene MI, O’Rourke DM (2000) Inhibition of EGFR-mediated phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase (PI3-K) signaling and glioblastoma phenotype by signal-regulatory proteins (SIRPs). Oncogene 19:3999–4010. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203748
Tartaglia M, Mehler EL, Goldberg R, Zampino G, Brunner HG, Kremer H, van der Burgt I, Crosby AH, Ion A, Jeffery S, Kalidas K, Patton MA, Kucherlapati RS, Gelb BD (2001) Mutations in PTPN11, encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet 29:465–468. doi:10.1038/ng772
Ke Y, Zhang EE, Hagihara K, Wu D, Pang Y, Klein R, Curran T, Ranscht B, Feng GS (2007) Deletion of Shp2 in the brain leads to defective proliferation and differentiation in neural stem cells and early postnatal lethality. Mol Cell Biol 27:6706–6717. doi:10.1128/MCB.01225-07
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Zhan Y, O’Rourke DM (2004) SHP-2-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation regulates EGFRvIII but not wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation and glioblastoma cell survival. Cancer Res 64:8292–8298. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3143
Furcht CM, Buonato JM, Skuli N, Mathew LK, Munoz Rojas AR, Simon MC, Lazzara MJ (2014) Multivariate signaling regulation by SHP2 differentially controls proliferation and therapeutic response in glioma cells. J Cell Sci 127:3555–3567. doi:10.1242/jcs.150862
Zhang L, Zhang W, Li Y, Alvarez A, Li Z, Wang Y, Song L, Lv D, Nakano I, Hu B, Cheng SY, Feng H (2016) SHP-2-upregulated ZEB1 is important for PDGFRalpha-driven glioma epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in mice and humans. Oncogene 35:5641–5652. doi:10.1038/onc.2016.100
Liu KW, Feng H, Bachoo R, Kazlauskas A, Smith EM, Symes K, Hamilton RL, Nagane M, Nishikawa R, Hu B, Cheng SY (2011) SHP-2/PTPN11 mediates gliomagenesis driven by PDGFRA and INK4A/ARF aberrations in mice and humans. J Clin Invest 121:905–917. doi:10.1172/JCI43690
Wang J, Cazzato E, Ladewig E, Frattini V, Rosenbloom DI, Zairis S, Abate F, Liu Z, Elliott O, Shin YJ, Lee JK, Lee IH, Park WY, Eoli M, Blumberg AJ, Lasorella A, Nam DH, Finocchiaro G, Iavarone A, Rabadan R (2016) Clonal evolution of glioblastoma under therapy. Nat Genet 48:768–776. doi:10.1038/ng.3590
Chen YN, LaMarche MJ, Chan HM, Fekkes P, Garcia-Fortanet J, Acker MG, Antonakos B, Chen CH, Chen Z, Cooke VG, Dobson JR, Deng Z, Fei F, Firestone B, Fodor M, Fridrich C, Gao H, Grunenfelder D, Hao HX, Jacob J, Ho S, Hsiao K, Kang ZB, Karki R, Kato M, Larrow J, La Bonte LR, Lenoir F, Liu G, Liu S, Majumdar D, Meyer MJ, Palermo M, Perez L, Pu M, Price E, Quinn C, Shakya S, Shultz MD, Slisz J, Venkatesan K, Wang P, Warmuth M, Williams S, Yang G, Yuan J, Zhang JH, Zhu P, Ramsey T, Keen NJ, Sellers WR, Stams T, Fortin PD (2016) Allosteric inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase inhibits cancers driven by receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature 535:148–152. doi:10.1038/nature18621
Kreso A, Dick JE (2014) Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell 14:275–291. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2014.02.006
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD, Dirks PB (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432:396–401. doi:10.1038/nature03128
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F, Vescovi A (2004) Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 64:7011–7021. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1364
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2003) Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:3983–3988. doi:10.1073/pnas.0530291100
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA, Masterman-Smith M, Geschwind DH, Bronner-Fraser M, Kornblum HI (2003) Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15178–15183. doi:10.1073/pnas.2036535100
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760. doi:10.1038/nature05236
Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A, Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E, Larocca LM, Peschle C, De Maria R (2006) Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death Differ 13:1238–1241. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401872
Aceto N, Sausgruber N, Brinkhaus H, Gaidatzis D, Martiny-Baron G, Mazzarol G, Confalonieri S, Quarto M, Hu G, Balwierz PJ, Pachkov M, Elledge SJ, van Nimwegen E, Stadler MB, Bentires-Alj M (2012) Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 promotes breast cancer progression and maintains tumor-initiating cells via activation of key transcription factors and a positive feedback signaling loop. Nat Med 18:529–537. doi:10.1038/nm.2645
Emlet DR, Gupta P, Holgado-Madruga M, Del Vecchio CA, Mitra SS, Han SY, Li G, Jensen KC, Vogel H, Xu LW, Skirboll SS, Wong AJ (2014) Targeting a glioblastoma cancer stem-cell population defined by EGF receptor variant III. Cancer Res 74:1238–1249. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1407
Sturla LM, Zinn PO, Ng K, Nitta M, Kozono D, Chen CC, Kasper EM (2011) Src homology domain-containing phosphatase 2 suppresses cellular senescence in glioblastoma. Br J Cancer 105:1235–1243. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.345
Zhan Y, Counelis GJ, O’Rourke DM (2009) The protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is required for EGFRvIII oncogenic transformation in human glioblastoma cells. Exp Cell Res 315:2343–2357. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.05.001
Akers JC, Ramakrishnan V, Kim R, Phillips S, Kaimal V, Mao Y, Hua W, Yang I, Fu CC, Nolan J, Nakano I, Yang Y, Beaulieu M, Carter BS, Chen CC (2015) miRNA contents of cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol 123:205–216. doi:10.1007/s11060-015-1784-3
Cheng P, Phillips E, Kim SH, Taylor D, Hielscher T, Puccio L, Hjelmeland AB, Lichter P, Nakano I, Goidts V (2015) Kinome-wide shRNA screen identifies the receptor tyrosine kinase AXL as a key regulator for mesenchymal glioblastoma stem-like cells. Stem Cell Rep 4:899–913. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.03.005
Yin J, Park G, Kim TH, Hong JH, Kim YJ, Jin X, Kang S, Jung JE, Kim JY, Yun H, Lee JE, Kim M, Chung J, Kim H, Nakano I, Gwak HS, Yoo H, Yoo BC, Kim JH, Hur EM, Lee J, Lee SH, Park MJ, Park JB (2015) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) expression induced by EGFRvIII promotes self-renewal and tumor progression of glioma stem cells. PLoS Biol 13:e1002152. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002152
Kim SH, Kim EJ, Hitomi M, Oh SY, Jin X, Jeon HM, Beck S, Kim JK, Park CG, Chang SY, Yin J, Kim T, Jeon YJ, Song J, Lim YC, Lathia JD, Nakano I, Kim H (2015) The LIM-only transcription factor LMO2 determines tumorigenic and angiogenic traits in glioma stem cells. Cell Death Differ 22:1517–1525. doi:10.1038/cdd.2015.7
Prabhu A, Sarcar B, Miller CR, Kim SH, Nakano I, Forsyth P, Chinnaiyan P (2015) Ras-mediated modulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity regulates mitochondrial reserve capacity and contributes to glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Neuro-oncol 17:1220–1230. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou369
Feng H, Lopez GY, Kim CK, Alvarez A, Duncan CG, Nishikawa R, Nagane M, Su AJ, Auron PE, Hedberg ML, Wang L, Raizer JJ, Kessler JA, Parsa AT, Gao WQ, Kim SH, Minata M, Nakano I, Grandis JR, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Lin HK, Furnari FB, Cavenee WK, Hu B, Yan H, Cheng SY (2014) EGFR phosphorylation of DCBLD2 recruits TRAF6 and stimulates AKT-promoted tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 124:3741–3756. doi:10.1172/JCI73093
Jeon HM, Kim SH, Jin X, Park JB, Joshi K, Nakano I, Kim H (2014) Crosstalk between glioma-initiating cells and endothelial cells drives tumor progression. Cancer Res 74:4482–4492. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1597
Mao P, Joshi K, Li J, Kim SH, Li P, Santana-Santos L, Luthra S, Chandran UR, Benos PV, Smith L, Wang M, Hu B, Cheng SY, Sobol RW, Nakano I (2013) Mesenchymal glioma stem cells are maintained by activated glycolytic metabolism involving aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:8644–8649. doi:10.1073/pnas.1221478110
Suva ML, Rheinbay E, Gillespie SM, Patel AP, Wakimoto H, Rabkin SD, Riggi N, Chi AS, Cahill DP, Nahed BV, Curry WT, Martuza RL, Rivera MN, Rossetti N, Kasif S, Beik S, Kadri S, Tirosh I, Wortman I, Shalek AK, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Regev A, Louis DN, Bernstein BE (2014) Reconstructing and reprogramming the tumor-propagating potential of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell 157:580–594. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.030
Matalkah F, Martin E, Zhao H, Agazie YM (2016) SHP2 acts both upstream and downstream of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases to promote basal-like and triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 18:2. doi:10.1186/s13058-015-0659-z
Borisov N, Aksamitiene E, Kiyatkin A, Legewie S, Berkhout J, Maiwald T, Kaimachnikov NP, Timmer J, Hoek JB, Kholodenko BN (2009) Systems-level interactions between insulin-EGF networks amplify mitogenic signaling. Mol Syst Biol 5:256. doi:10.1038/msb.2009.19
Chan RJ, Feng GS (2007) PTPN11 is the first identified proto-oncogene that encodes a tyrosine phosphatase. Blood 109:862–867. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-028829
Bentires-Alj M, Gil SG, Chan R, Wang ZC, Wang Y, Imanaka N, Harris LN, Richardson A, Neel BG, Gu H (2006) A role for the scaffolding adapter GAB2 in breast cancer. Nat Med 12:114–121. doi:10.1038/nm1341
Bentires-Alj M, Paez JG, David FS, Keilhack H, Halmos B, Naoki K, Maris JM, Richardson A, Bardelli A, Sugarbaker DJ, Richards WG, Du J, Girard L, Minna JD, Loh ML, Fisher DE, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Meyerson M, Sellers WR, Neel BG (2004) Activating mutations of the noonan syndrome-associated SHP2/PTPN11 gene in human solid tumors and adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 64:8816–8820. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1923
Brummer T, Schramek D, Hayes VM, Bennett HL, Caldon CE, Musgrove EA, Daly RJ (2006) Increased proliferation and altered growth factor dependence of human mammary epithelial cells overexpressing the Gab2 docking protein. J Biol Chem 281:626–637. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509567200
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Muto S, Sugiyama T, Azuma T, Asaka M, Hatakeyama M (2002) SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 295:683–686. doi:10.1126/science.1067147
Voena C, Conte C, Ambrogio C, Boeri Erba E, Boccalatte F, Mohammed S, Jensen ON, Palestro G, Inghirami G, Chiarle R (2007) The tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 interacts with NPM-ALK and regulates anaplastic lymphoma cell growth and migration. Cancer Res 67:4278–4286. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4350
Qu CK, Shi ZQ, Shen R, Tsai FY, Orkin SH, Feng GS (1997) A deletion mutation in the SH2-N domain of Shp-2 severely suppresses hematopoietic cell development. Mol Cell Biol 17:5499–5507
Venere M, Fine HA, Dirks PB, Rich JN (2011) Cancer stem cells in gliomas: identifying and understanding the apex cell in cancer’s hierarchy. Glia 59:1148–1154. doi:10.1002/glia.21185
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H, Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL, Yu JS (2006) Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer 5:67. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-67
Graham V, Khudyakov J, Ellis P, Pevny L (2003) SOX2 functions to maintain neural progenitor identity. Neuron 39:749–765
Gangemi RM, Griffero F, Marubbi D, Perera M, Capra MC, Malatesta P, Ravetti GL, Zona GL, Daga A, Corte G (2009) SOX2 silencing in glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells causes stop of proliferation and loss of tumorigenicity. Stem Cells 27:40–48. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2008-0493
Zhao L (2015) Hirudin inhibits cell growth via ERK/MAPK signaling in human glioma. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:20983–20987
Funding
M.B.-A. is supported by the Novartis Research Foundation, the European Research Council (ERC starting Grant 243211-PTPsBDC), the Swiss Cancer League, the Swiss National Foundation, and the Krebsliga Beider Basel. N.D. is supported by NIH Grant R01-NS-093120. D.M.O. is supported by NIH Grant 5R01NS042645-13. Z.A.B. is supported by the Templeton Family Initative In Neuro-Oncology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the University of Pennsylvania and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. The research was conducted in accordance with a Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania’s Institutional Review Board-approved protocol #816686. Written consent was obtained from all patients in accordance with the protocol.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roccograndi, L., Binder, Z.A., Zhang, L. et al. SHP2 regulates proliferation and tumorigenicity of glioma stem cells. J Neurooncol 135, 487–496 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2610-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2610-x