Abstract
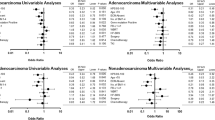
The aim of this study was to analyze prognostic factors and evaluate the value of four prognostic scores including RPA, DS-GPA BS-BM, GGS for the EGFR mutant BM patients from lung adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR-TKI. Data of NSCLC were retrospectively reviewed from August 2010 to June 2015 using the medical database of Shanxi Provincial Cancer Hospital. Patients with BM from lung adenocarcinoma with mutant EGFR treated by EGFR-TKI or a combination of EGFR-TKI and WBRT were included. Potential prognostic factors were statistically examined. The C-index of each prognostic score was calculated. A total of 1063 BM patients with lung adenocarcinoma that had been identified with EGFR mutations were reviewed. A total of 104 patients that had been diagnosed with BM were confirmed to have mutant EGFR in primary tumors. These patients received treatment with EGFR-TKI or EGFR-TKI with WBRT to BM. The potential predictive factors in multivariable analysis included KPS (70 vs.70–80 vs. 90–100) and number of brain metastatic lesions. In the log-rank test, the indexes of RPA, DS-GPA BS-BM, and GGS were all significant predictors of OS. The C-indexes of each prognostic score were 0.79, 0.76, 0.77, and 0.74 in DS-GPA, RPA, GGS, and BS-BM, respectively. The indexes of RPA, DS-GPA BS-BM, GGS were applicable for asessing survival stratification in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with presented EGFR mutations in our independent population. The DS-GPA appears to be the best predictive value. However, all four of the indexes could not evaluate the exact independent prognostic factors in multivariable analysis. A prognostic index specific for this group of patients was needed for targeted lung cancer therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol 22(14):2865–2872
Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY (2012) Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 14:48–54
Ding X, Dai HH, Hui ZG, Ji W, Liang J, Lv J et al (2012) Risk factors of brain metastases in completely resected pathological stageIIIA-N2non-smallcell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:119
Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HAM, Twijnstra A (2002) Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer 94:2698–2705
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors 316 in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37(4):745–751
Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Massager N et al (2004) Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases: estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:218–224
Sperduto PW, Berkey B, Gaspar LE, Mehta M, Curran W (2008) A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: an analysis of 1,960 patients in the RTOG database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(2):510–514
Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK et al (2010) Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:655–661
Cairncross JG, Kim JH, Posner JB (1980) Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Ann Neurol 7:529–541
Noel G, Medioni J, Valery CA, Boisserie G, Simon JM, Cornu P et al (2003) Three irradiation treatment options including radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary lung cancer. Lung Cancer 41:333–343
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Fokas E, Henzel M, Surber G, Kleinert G, Hamm K, Engenhart-Cabillic R (2012 Aug) Stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: comparison of efficacy and toxicity in 260 patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 109(1):91–98
Yuankai Shi, Joseph Siu-Kie Au, Sumitra Thongprasert, Sankar Srinivasan, Chun-Ming Tsai, Mai Trong Khoa, Karin Heeroma, Yohji Itoh, Gerardo Cornelio, Pan-Chyr Yang, Prospective A (2014 Feb) Molecular epidemiology study of egfr mutations in asian patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol 9(2):154–162
Li Z, Guo H (2011) The retrospective analysis of the frequency of EGFR mutations and efficacy of gefitinib in NSCLC patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 29:e18065
Wu C, Li YL, Wang ZM, Li Z, Zhang TX, Wei Z (2007) Gefitinib as palliative therapy for lung adenocarcinoma metastatic to the brain. Lung Cancer 57:359–364
Kim JE, Lee DH, Choi Y, Yoon DH, Kim SW, Suh C et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as a first-line therapy for never-smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung having asymptomatic synchronous brain metastasis. Lung Cancer 65:351–354
Wu YL, Zhou C, Cheng Y, Lu S, Chen GY, Huang C, Huang YS, Yan HH, Ren S, Liu Y, Yang JJ (2013) Erlotinib as second-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and asymptomatic brain metastases: a phase II study (CTONG-0803). Ann Oncol 24(4):993–999
R Core Team (2013). R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Golden DW, Lamborn KR, McDermott MW, Kunwar S, Wara WM, Nakamura JL, Sneed PK (2008) Prognostic factors and grading systems for overall survival in patients treated with radiosurgery for brain metastases: variation by primary site. J Neurosurg. 109:77–86
Porta R, Sánchez-Torres JM, Paz-Ares L, Massutí B, Reguart N, Mayo C, Lianes P, Queralt C, Guillem V, Salinas P, Catot S, Isla D, Pradas A, Gúrpide A, de Castro J, Polo E, Puig T, Tarón M, Colomer R (2011) Rosell RBrain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: the importance of EGFR mutation. Eur Respir J 37(3):624–631
Venur VA, Ahluwalia MS (2016) Targeted therapy in brain metastases: ready for primetime? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 35:e123–e130
Soffietti R, Trevisan E, Rudà R (2012) Targeted therapy in brain metastasis. Curr Opin Oncol 24(6):679–686
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JPS, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) The Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment (gpa) for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(5):2111–2117
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JPS, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 30(4): 419–425
Wilkins A, Furness A, Corbett RW Bloomfield A, Porta N, Morris S, Ali Z, Larkin J, Harrington K (2015) The melanoma-specific graded prognostic assessment does not adequately discriminate prognosis in a modern population with brain metastases from malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer 113(9):1275–1281
Byeon S, Ham JS, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Park K, Ahn MJ (2016) Analysis of the benefit of sequential cranial radiotherapy in patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastasis. Med Oncol 33(8):97
Jiang T, Su C, Li X, Zhao C, Zhou F, Ren S, Zhou C, Zhang J EGFR (2016) TKIs plus WBRT demonstrated no survival benefit other than that of TKIs alone in patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol 11(10):1718–1728
Kalikaki A, Koutsopoulos A, Trypaki M, Souglakos J, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, Mavroudis D, Voutsina A (2008) Comparison of EGFR and K-RAS gene status between primary tumours and corresponding metastases in NSCLC. Br J Cancer 99:923–929
Kun-Ming Rau, Han-Ku Chen, Li-Yen Shiu, Tsai-Ling Chao, Yi-Ping Lo, Chin-Chou Wang, Meng-Chih Lin (2016) Chao-cheng huang discordance of mutation statuses of epidermal growth factor receptor and K-ras between primary adenocarcinoma of lung and brain metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 17(4):524
Wang S, Wang Z (2015) Meta-analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS gene status between primary and corresponding metastatic tumours of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 27(1):30–39
Daniele L, Cassoni P, Bacillo E, Cappia S, Righi L, Volante M, Tondat F, Inghirami G, Sapino A, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, Novello S (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene in primary tumor and metastatic sites from non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 4(6):684–688
Acknowledgements
We thank LetPub (http://www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involved in human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Hongwei Li and Jianhong Lian have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Lian, J., Jin, H. et al. Assessment of prognostic scores of brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Neurooncol 133, 129–135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2411-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2411-2