Abstract
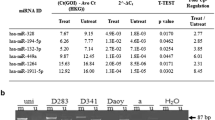
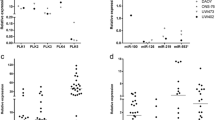
Medulloblastoma (MB) is a childhood tumor comprising four molecular subgroups: WNT, SHH, group 3 and group 4, with diagnostic and prognostic connotations. Very few studies are available on molecular subgrouping of adult MBs due to their rarity. Recently, loss of chromosome14q has been reported in SHH MBs, with downregulation of miR-379/miR-656 cluster (C14MC) in pediatric SHH MBs. Hence, the present study on adult MBs was undertaken to enumerate clinicopathological characteristics and molecular subgroups, and to analyze expression of C14MC and its transcriptional regulators, MEF2, JUN and ESRRG. Immunohistochemistry for β-catenin, GAB1 and YAP1 was performed to identify molecular subgroups. MYC amplification was evaluated by FISH. Expression profiling of 47 miRNAs from C14MC was performed using customized Taqman low-density array. Expression of transcriptional regulators was examined using RT-PCR. Seventy-one adult MBs were analyzed. They had male predominance and majority were located laterally (52 %). A significant proportion of cases were of Desmoplastic/nodular histology (32 %); MBEN was not seen. WNT tumors constituted 4.2 %, SHH 62 %, and non-WNT/non-SHH 33.8 %. MYC amplification was identified in 11.1 % cases. Patient outcome was worse in adults. Significant downregulation of C14MC was observed in all MB subgroups, and MEF-2 expression was downregulated. Adult MBs are distinct from childhood MBs in terms of location, histopathological subtypes, molecular subgroups, as well as prognosis. Silencing of C14MC in all MB subgroups suggests its role as a tumor suppressor locus in tumorigenesis. Deregulation of C14MC can possibly be attributed to repression of MEF2.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giangaspero F, Eberhart CG, Haapasalo H, Pietsch T, Wiestler OD, Ellison DW (2007) Medulloblastoma. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system. IARC: Lyon, 132–140
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A et al (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 123:465–472
Kaur K, Kakkar A, Kumar A et al (2016) Integrating molecular subclassification of medulloblastomas into routine clinical practice: a simplified approach. Brain Pathol 26:334–343
Ellison DW, Dalton J, Kocak M et al (2011) Medulloblastoma: clinicopathological correlates of SHH, WNT, and non-SHH/WNT molecular subgroups. Acta Neuropathol 121:381–396
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M et al (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, group 3, and group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol 123:473–484
Sarkar C, Pramanik P, Karak AK et al (2002) Are childhood and adult medulloblastomas different? A comparative study of clinicopathological features, proliferation index and apoptotic index. J Neurooncol 59:49–61
Remke M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA et al (2011) Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29:2717–2723
Al-Halabi H, Nantel A, Klekner A et al (2011) Preponderance of sonic hedgehog pathway activation characterizes adult medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:229–239
Northcott AP, Korshunov A, Witt H et al (2011) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29:1408–1414
Shih DJH, Northcott PA, Remke M et al (2014) Cytogenetic prognostication within medulloblastoma subgroups. Clin Oncol 32:886–896
da Rocha ST, Edwards CA, Ito M, Ogata T, Ferguson- Smith AC (2008) Genomic imprinting at the mammalian Dlk1-Dio3 domain. Trends Genet 24:306–316
Fiore R, Khudayberdiev S, Christensen M (2009) Mef2-mediated transcription of the miR379–410 cluster regulates activity-dependent dendritogenesis by fine-tuning Pumilio2 protein levels. EMBO J 28:697–710
Lucon DR, Rocha CS, Craveiro RB et al (2013) Downregulation of 14q32 microRNAs in primary human desmoplastic medulloblastoma. Front Oncol 3:254
Laddha SV, Nayak S, Paul D et al (2013) Genome-wide analysis reveals downregulation of miR-379/miR-656 cluster in human cancers. Biol Direct 8:10
Genovesi LA, Carter KW, Gottardo NG et al (2011) Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression in childhood medulloblastoma compared with neural stem cells. PLoS One 6:e23935
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2∆∆Ct method. Methods 25:402–408
Smoll NR, Drummond KJ (2012) The incidence of medulloblastomas and primitive neurectodermal tumours in adults and children. J Clin Neurosci 19:1541–1544
Gibson P, Tong Y, Robinson G et al (2010) Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature 468:1095–1099
Smoll NR (2012) Relative survival of childhood and adult medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs). Cancer 118:1313–1322
Winter J (2015) MicroRNAs of the miR379–410 cluster: new players in embryonic neurogenesis and regulators of neuronal function. Neurogenesis 2:e1004970.
Altuvia Y, Landgraf P, Lithwick G et al (2005) Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33:2697–2706
Kim VN, Nam JW (2006) Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 22:165–173
Gokhale A, Kunder R, Goel A et al (2010) Distinctive microRNA signature of medulloblastomas associated with the WNT signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Ther 6(521–52):9
Zehavi L, Avraham R, Barzilai A et al (2012) Silencing of a large microRNA cluster on human chromosome 14q32 in melanoma: biological effects of mir-376a and mir-376c on insulin growth factor 1 receptor. Mol Cancer 11:44
Gattolliat CH, Thomas L, Ciafrè SA et al (2011) Expression of miR-487b and miR-410 encoded by 14q32.31 locus is a prognostic marker in neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer 105:1352–1361
Nadal E, Zhong J, Lin J, et al (2014) A MicroRNA cluster at 14q32 drives aggressive lung adenocarcinoma. ClinCancer Res 20:3107–3117.
Costa FF, Bischof JM, Vanin EF et al (2011) Identification of microRNAs as potential prognostic markers in ependymoma. PLoS One 6:e25114
Northcott PA, Fernandez LA, Hagan JP et al (2009) The miR- 17/92 polycistron is upregulated in Sonic Hedgehog driven medulloblastomas and induced by Nmyc in Sonic Hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res 69:3249–3255
Luo X, Liu J, Cheng SY (2011) The role of microRNAs during genesis of medulloblastoma induced by hedgehog pathway. Biomed Res 25:42–48
Vogt PK (2002) Fortuitous convergences: the beginnings of JUN. Nat Rev Cancer 2:465–469
Nateri AS, Spencer-Dene B, Behrens A (2005) Interaction of phosphorylated c-Jun with TCF4 regulates intestinal cancer development. Nature 437:281–285
Gurzov EN, Bakiri L, Alfaro JM, Wagner EF, Izquierdo M (2008) Targeting Jun and JunB proteins as potential anticancer cell therapy. Oncogene 27:641–652
Robinson GW, Orr BA, Wu G et al (2015) Vismodegib exerts targeted efficacy against recurrent Sonic Hedgehog-subgroup medulloblastoma: results from phase II pediatric brain tumor consortium studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J Clin Oncol 3:2646–2654
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J et al (2009) Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449. N Engl J Med 361:1173–1178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kavneet Kaur and Aanchal Kakkar are co-first authors and have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, K., Kakkar, A., Kumar, A. et al. Clinicopathological characteristics, molecular subgrouping, and expression of miR-379/miR-656 cluster (C14MC) in adult medulloblastomas. J Neurooncol 130, 423–430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2250-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2250-6