Abstract
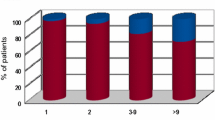
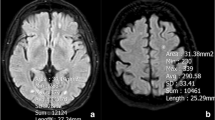
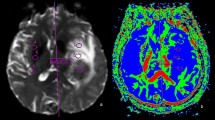
Brain metastases are major complications of common cancers. Tumor type and proneness to the CNS are thought to define the number and size of brain metastases. It is not known if intrinsic vascular factors can also have an effect. Restricted perfusion due to cerebral small vessel disease is frequent in elderly patients and causes white matter lesions (WML). The aim of this analysis was to evaluate a possible negative effect of WML and patient age on the number and size of brain metastases (BM) of different tumor entities. Pre-therapeutic 3 T brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of 200 patients with BM were analyzed. Location, size and number of BM (NoM) were determined. T2 hyperintensive WML were scored according to Fazekas-Score (grade I–III). Patients with WML grade 1 (NoM: 5.59; p = 0.009) and grade 2 (NoM: 3.68; p = 0.002) had significantly less BM than patients without WML (NoM: 6.99). This effect was present in subgroups of different tumors: NSCLC (p = 0.05), other tumors than NSCLC (p = 0.048). Age (≤65 or >65 years) was positively correlated with the degree of WML but not with number (pNoM = 0.832) or mean diameter (pmDM = 0.662) of brain metastases. While patient age did not appear to be relevant, increasing WML were associated with lower number of brain metastases in different tumor types.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Mutani R (2002) Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 249(10):1357–1369
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2011) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30(4):419–425
Nussbaum ES, Djalilian HR, Cho KH, Hall WA (1996) Brain metastases. Histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer 78(8):1781–1788
Patil CG, Pricola K, Garg SK, Bryant A, Black KL (2010) Whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) alone versus WBRT and radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (6):CD006121
Ellis TL, Neal MT, Chan MD (2012) The role of surgery, radiosurgery and whole brain radiation therapy in the management of patients with metastatic brain tumors. Int J Surg Oncol 2012:952345
Carbonell WS, Ansorge O, Sibson N, Muschel R (2009) The vascular basement membrane as “soil” in brain metastasis. PLoS One 4(6):e5857
Donnem T, Hu J, Ferguson M, Adighibe O, Snell C, Harris AL, Gatter KC, Pezzella F (2013) Vessel co-option in primary human tumors and metastases: an obstacle to effective anti-angiogenic treatment? Cancer Med 2(4):427–436
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Babb JS, Rabin ML, Mannon LJ, Kolson DL (2002) Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: volumetric MR imaging analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 8:1327–1333
Klein B, Kuschinsky W, Schrock H, Vetterlein F (1986) Interdependency of local capillary density, blood flow, and metabolism in rat brains. Am J Physiol 6:1333–1340
Ellenbogen RG, Abdulrauf SI, Sekhar N (2012) Principles of neurological surgery. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149(2):351–356
Seidel C, Hambsch P, Hering K, Bresch A, Rohde S, Kortmann RD, Gaudino C (2015) Analysis of frequency of deep white matter metastasis on cerebral MRI. J Neurooncol 123(1):135–139
Ebermann E (2016) Kolmogorov-Smirnov-Test mit SPSS. https://www.univie.ac.at/ksa/elearning/cp/quantitative/quantitative-62.html. Accessed 15 May 2016
Bühl A (2014) SPSS 22: einführung in die moderne datenanalyse (pearson studium—scientific tools), 14th edn. Pearson Deutschland GmbH, Hallbergmoos, Germany
Johnson, RA, Wichern, Dean W (2007) Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 6th edn. Pearson Education Limited, Essex
Pantoni L (2010) Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 9:689–701
Gouw AA, Seewann A, van der Flier WM, Barkhof F, Rozemuller AM, Scheltens P, Geurts JJ (2011) Heterogeneity of small vessel disease: a systematic review of MRI and histopathology correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 82:126–135
Brown WR, Thore CR (2011) Review: cerebral microvascular pathology in ageing and neurodegeneration. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(1):56–74
Okroglic S, Widmann CN, Urbach H, Scheltens P, Heneka MT (2013) Clinical symptoms and risk factors in cerebral microangiopathy patients. PLoS One 8(2):e53455
Spolveri S, Baruffi MC, Cappelletti C, Semerano F, Rossi S, Pracucci G, Inzitari D (1998) Vascular risk factors linked to multiple lacunar infarcts. Cerebrovasc Dis 8(3):152–157
Brown WR, Moody DM, Thore CR, Anstrom JA, Challa VR (2009) Microvascular changes in the white mater in dementia. J Neurol Sci 283(1–2):28–31
Breteler MM, van Swieten JC, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Claus JJ, van den Hout JH, van Harskamp F, Tanghe HL, de Jong PT, van Gijn J et al (1994) Cerebral white matter lesions, vascular risk factors, and cognitive function in a population-based study: The Rotterdam Study. Neurology 44:1246–1252
Yoo DH, Song SW, Yun TJ, Kim, Lee SH, Kim JH, Sohn CH, Park SH, Park CK, Kim IH, Choi SH (2015) MR imaging evaluation of intracerebral hemorrhages and T2 hyperintense white matter lesions appearing after radiation therapy in adult patients with primary brain tumors. PLoS One 10(8):e0136795
Sato S, Delcourt C, Heeley E, Arima H, Zhang S, Al-Shahi Salman R, Stapf C, Woo D, Flaherty ML, Vagal A, Levi C, Davies L, Wang J, Robinson T, Lavados PM, Lindley RI, Chalmers J, Anderson CS, INTERACT2 Investigators (2016) Significance of cerebral small-vessel disease in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 47(3):7017
Pantoni L, Garcia JH (1997) Cognitive impairment and cellular/vascular changes in the cerebral white matter. Ann NY Acad Sci 826:92–102
Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75(1):5–14
Mazzone PJ, Marchi N, Fazio V, Taylor JM, Masaryk T, Bury L, Mekhail T, Janigro D (2009) Small vessel ischemic disease of the brain and brain metastases in lung cancer patients. PLoS One 4(9):e7242
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Carmeliet P, Rakesh KJ (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical application of angiogenesis. Nature 473(7347):298–307
Berghoff AS, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Dinhof C, Magerle M, Hackl M, Widhalm G, Hainfellner JA, Dieckmann K, Pichler J, Hutterer M, Melchardt T, Bartsch R, Zielinski CC, Birner P, Preusser M (2015) Differential role of angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation in brain metastases according to primary tumor type: analysis of 639 cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41(2):e41–e55
Donnem T, Hu J, Ferguson M, Adighibe O, Snell C, Harris AL et al (2013) Vessel co-option in primary human tumors and metastases: an obstacle to effective anti-angiogenic treatment? Cancer Med 2(4):427–436
Hanbali A, Al-Khasawneh K, Cole-Johnson C, Divine G, Ali H (2007) Protective effect of diabetes against metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Arch Intern Med 167(5):513
Quattrocchi CC, Errante Y, Mallio CA, Carideo L, Scarciolla L, Santini D, Tonini G, Zobel BB (2014) Inverse spatial distribution of brain metastases and white matter hyperintensities in advanced lung and non-lung cancer patients. J Neurooncol 120(2):321–330
Bakker SL, de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM (1999) Cerebral vasomotor reactivity and cerebral white matter lesions in the elderly. Neurology 52:578–583
Kozera GM, Dubaniewicz M, Zdrojewski T, Madej-Dmochowska A, Mielczarek M, Wojczal J, Chwojnicki K, Swierblewska E, Schminke U, Wyrzykowski B, Nyka WM, SOPKARD Study Group (2010) Cerebral vaso- motor reactivity and extent of white matter lesions in middle-aged men with arterial hypertension: a pilot study. Am J Hypertens 23:1198–1203
Burns TC, Awad AJ, Li MD, Grant GA (2016) Radiation-induced brain injury: low-hanging fruit for neuroregeneration. Neurosurg Focus 40(5):E3
Nasel C, Boubela R, Kalcher K, Moser E (2016) Normalised time-to-peak-distribution curves correlate with cerebral white matter hyperintensities—Could this improve early diagnosis? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. [Epub ahead of print]
Acknowledgments
B.A.B was recipient of a merit-based doctoral scholarship from the Hans-Böckler Foundation funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research—Germany (BMBF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Benjamin-Andreas Berk and Sandra Nagel are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berk, BA., Nagel, S., Hering, K. et al. White matter lesions reduce number of brain metastases in different cancers: a high-resolution MRI study. J Neurooncol 130, 203–209 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2235-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2235-5