Abstract
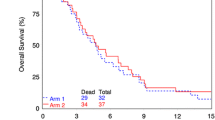
The average survival time for patients with recurrent glioblastoma is between 5 and 9 months. Phase I and II trials have shown a modest survival benefit with combination temozolomide and other chemotherapeutics. We conducted a phase I trial of dose-escalating temozolomide with bevacizumab and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib for patients with recurrent disease. Three groups of three patients were scheduled to receive daily doses of temozolomide at 25, 50, and 75 mg/m2. Fixed doses of bortezomib and bevacizumab were given at standard intervals. Patients were monitored for dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) to determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD) of temozolomide with this regimen. No DLT were seen in the first two groups (25 and 50 mg/m2 temozolomide). One patient in the 75 mg/m2 group experienced a grade 4 elevation of ALT and three more patients were accrued for a total of six patients at that dose level. No other DLT occurred, thus making 75 mg/m2 the MTD. Progression-free survival was 3.27 months for all patients and mean overall survival was 20.75 months. The MTD of temozolomide was 75 mg/m2 in combination with bevacizumab and bortezomib for recurrent glioblastoma. Only one patient experienced a severe (Grade 4) elevation of ALT. This study will provide the framework for further studies to elicit effectiveness and better determine a safety profile for this drug combination.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grossman SA, Ye X, Piantadosi S et al (2010) Survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma treated with radiation and temozolomide in research studies in the United States. Clin Cancer Res 16(8):2443–2449
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10(5):459–466
Brada M, Hoang-Xuan K, Rampling R et al (2001) Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Ann Oncol 12(2):259–266
Brandes AA, Ermani M, Basso U et al (2001) Temozolomide as a second-line systemic regimen in recurrent high-grade glioma: a phase II study. Ann Oncol 12(2):255–257
Kong DS, Lee JI, Kim WS et al (2006) A pilot study of metronomic temozolomide treatment in patients with recurrent temozolomide-refractory glioblastoma. Oncol Rep 16(5):1117–1121
Wick A, Felsberg J, Steinbach JP et al (2007) Efficacy and tolerability of temozolomide in an alternating weekly regimen in patients with recurrent glioma. J Clin Oncol 25(22):3357–3361
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J et al (2000) A phase II study of temozolomide vs. procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer 83(5):588–593
Olson JJ, Nayak L, Ormond DR, Wen PY, Kalkanis SN, Committee ACJG (2014) The role of cytotoxic chemotherapy in the management of progressive glioblastoma: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 118(3):501–555
Cohen MH, Shen YL, Keegan P, Pazdur R (2009) FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Oncologist 14(11):1131–1138
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY et al (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27(28):4733–4740
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K et al (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27(5):740–745
Olson JJ, Nayak L, Ormond DR et al (2014) The role of targeted therapies in the management of progressive glioblastoma: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 118(3):557–599
Styczynski J, Olszewska-Slonina D, Kolodziej B, Napieraj M, Wysocki M (2006) Activity of bortezomib in glioblastoma. Anticancer Res 26(6B):4499–4503
Koschny R, Holland H, Sykora J et al (2007) Bortezomib sensitizes primary human astrocytoma cells of WHO grades I to IV for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 13(11):3403–3412
Bota DA, Alexandru D, Keir ST, Bigner D, Vredenburgh J, Friedman HS (2013) Proteasome inhibition with bortezomib induces cell death in GBM stem-like cells and temozolomide-resistant glioma cell lines, but stimulates GBM stem-like cells’ VEGF production and angiogenesis. J Neurosurg 119(6):1415–1423
Unterkircher T, Cristofanon S, Vellanki SH et al (2011) Bortezomib primes glioblastoma, including glioblastoma stem cells, for TRAIL by increasing tBid stability and mitochondrial apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res 17(12):4019–4030
Gong X, Schwartz PH, Linskey ME, Bota DA (2011) Neural stem/progenitors and glioma stem-like cells have differential sensitivity to chemotherapy. Neurology 76(13):1126–1134
Vlachostergios PJ, Hatzidaki E, Befani CD, Liakos P, Papandreou CN (2013) Bortezomib overcomes MGMT-related resistance of glioblastoma cell lines to temozolomide in a schedule-dependent manner. Invest New Drugs 31(5):1169–1181
Vlachostergios PJ, Hatzidaki E, Stathakis NE, Koukoulis GK, Papandreou CN (2013) Bortezomib downregulates MGMT expression in T98G glioblastoma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33(3):313–318
Vlachostergios PJ, Papandreou CN (2015) Efficacy of low dose temozolomide in combination with bortezomib in U87 glioma cells: a flow cytometric analysis. Arch Med Sci 11(2):307–310
Lu S, Chen Z, Yang J et al (2010) The effects of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib on a P-gp positive leukemia cell line K562/A02. Int J Lab Hematol 32(1 Pt 1):e123–131
Rumpold H, Salvador C, Wolf AM, Tilg H, Gastl G, Wolf D (2007) Knockdown of PgP resensitizes leukemic cells to proteasome inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Research Communications 361(2):549–554
Nakamura T, Tanaka K, Matsunobu T et al (2007) The mechanism of cross-resistance to proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and overcoming resistance in Ewing’s family tumor cells. International journal of oncology 31(4):803–811
Raizer JJ, Chandler JP, Ferrarese R, Grimm SA (2016) A phase II trial evaluating the effects and intra-tumoral penetration of bortezomib in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 129(1):139–146
Olson JJ, Bowers G, Zhang Z (2004) Protease inhibitors in a brain tumor model. In: Adams J (ed) Totowa: Humana Press Inc. pp 161–170
Kubicek GJ, Werner-Wasik M, Machtay M et al (2009) Phase I trial using proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy for central nervous system malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(2):433–439
Phuphanich S, Supko JG, Carson KA et al (2010) Phase 1 clinical trial of bortezomib in adults with recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 100(1):95–103
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8(7):1277–1280
Sarganas G, Orzechowski HD, Klimpel A et al (2012) Severe sustained cholestatic hepatitis following temozolomide in a patient with glioblastoma multiforme: case study and review of data from the FDA adverse event reporting system. Neuro Oncol 14(5):541–546
Perry JR, Belanger K, Mason WP et al (2010) Phase II trial of continuous dose-intense temozolomide in recurrent malignant glioma: RESCUE study. J Clin Oncol 28(12):2051–2057
Jagannath S, Barlogie B, Berenson J et al (2004) A phase 2 study of two doses of bortezomib in relapsed or refractory myeloma. Br J Haematol 127(2):165–172
Chamberlain MC, Johnston SK (2010) Salvage therapy with single agent bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 96(2):259–269
Reynes G, Martinez-Sales V, Vila V et al (2016) Phase II trial of irinotecan and metronomic temozolomide in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Anticancer Drugs 27(2):133–137
Reynes G, Balana C, Gallego O, Iglesias L, Perez P, Garcia JL (2014) A phase I study of irinotecan in combination with metronomic temozolomide in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Anticancer Drugs 25(6):717–722
Clarke JL, Iwamoto FM, Sul J et al (2009) Randomized phase II trial of chemoradiotherapy followed by either dose-dense or metronomic temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27(23):3861–3867
Bota ZE DA, Reardon DA, Fu BD, Norfleet J, Desjardins A, Linskey ME, Peters K, Friedman HS, Vredenburgh JJ (2011) Phase II clinical trial of bortezomib and bevacizumab combination in recurrent glioblastoma. ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol 29:2011 (suppl; abstr 2056)
Wen P, Macdonald D, Reardon D et al (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28(11):1963–1972
Friday BB, Anderson SK, Buckner J et al (2012) Phase II trial of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib in recurrent glioblastoma: a north central cancer treatment group study. Neuro Oncol 14(2):215–221
Acknowledgments
D.J.M. wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data, E.C.C. performed all chart reviews, collected data, assisted in manuscript creation, A.D.V. and W.L.R. were co-investigators for the clinical trial, J.J.O. served as the Primary Investigator for the clinical trial and oversaw all aspects related to its implementation.
Funding
Funding for trial provided through Genetech, Takeda, and Merck.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts-of-interest to report with respect to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCracken, D.J., Celano, E.C., Voloschin, A.D. et al. Phase I trial of dose-escalating metronomic temozolomide plus bevacizumab and bortezomib for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 130, 193–201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2234-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2234-6