Abstract
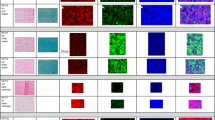
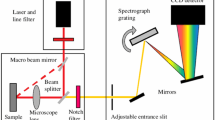
Raman spectroscopy provides a molecular signature of the region being studied. It is ideal for neurosurgical applications because it is non-destructive, label-free, not impacted by water concentration, and can map an entire region of tissue. The objective of this paper is to demonstrate the meaningful spatial molecular information provided by Raman spectroscopy for identification of regions of normal brain, necrosis, diffusely infiltrating glioma and solid glioblastoma (GBM). Five frozen section tissues (1 normal, 1 necrotic, 1 GBM, and 2 infiltrating glioma) were mapped in their entirety using a 300-µm-square step size. Smaller regions of interest were also mapped using a 25-µm step size. The relative concentrations of relevant biomolecules were mapped across all tissues and compared with adjacent hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections, allowing identification of normal, GBM, and necrotic regions. Raman peaks and peak ratios mapped included 1003, 1313, 1431, 1585, and 1659 cm−1. Tissue maps identified boundaries of grey and white matter, necrosis, GBM, and infiltrating tumor. Complementary information, including relative concentration of lipids, protein, nucleic acid, and hemoglobin, was presented in a manner which can be easily adapted for in vivo tissue mapping. Raman spectroscopy can successfully provide label-free imaging of tissue characteristics with high accuracy. It can be translated to a surgical or laboratory tool for rapid, non-destructive imaging of tumor margins.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (2007) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, Fourth Edition
Albert FK, Forsting M, Sartor K, Adams H-P, Kunze S (1994) Early postoperative magnetic resonance imaging after resection of malignant glioma: objective evaluation of residual tumor and its influence on regrowth and prognosis. Neurosurgery 34:45–61
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen H-J (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401
Smith JS, Chang EF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD, Cha S, Tihan T, VandenBerg S, McDermott MW, Berger MS (2008) Role of extent of resection in the long-term outcome of low-grade hemispheric gliomas. J Clin Oncol 26:1338–1345
Shaw EG, Berkey B, Coons SW, Bullard D, Brachman D, Buckner JC, Stelzer KJ, Barger GR, Brown PD, Gilbert MR, Mehta M (2008) Recurrence following neurosurgeon-determined gross-total resection of adult supratentorial low-grade glioma: results of a prospective clinical trial. J Neurosurg 109:835–841
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology 34:463–469
Burger PC, Heinz ER, Shibata T, Kleihues P (1988) Topographic anatomy and CT correlations in the untreated glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg 68:698–704
De Witt Hamer PC, Robles SG, Zwinderman AH, Duffau H, Berger MS (2012) Impact of intraoperative stimulation brain mapping on glioma surgery outcome: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 30:2559–2565
Price SJ, Jena R, Burnet NG, Hutchinson PJ, Dean AF, Peña A, Pickard JD, Carpenter TA, Gillard JH (2006) Improved delineation of glioma margins and regions of infiltration with the use of diffusion tensor imaging: an image-guided biopsy study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1969–1974
Kalkanis S, Kast R, Rosenblum M, Mikkelsen T, Yurgelevic S, Nelson K, Raghunathan A, Poisson L, Auner G (2014) Raman spectroscopy to distinguish grey matter, necrosis, and glioblastoma multiforme in frozen tissue sections. J Neurooncol 116:477–485
Amharref N, Beljebbar A, Dukic S, Venteo L, Schneider L, Pluot M, Manfait M (2007) Discriminating healthy from tumor and necrosis tissue in rat brain tissue samples by Raman spectral imaging. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1768:2605–2615
Koljenovic S, Choo-Smith L, Bakker Schut T, Kros J, van den Berge H, Puppels G (2002) Discriminating vital tumor from necrotic tissue in human glioblastoma tissue samples by Raman spectroscopy. Lab Invest 82:1265–1277
Koljenovic S, Schut T, Vincent A, Kros J, Puppels G (2005) Detection of meningioma in dura mater by Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 77:7958–7965
Krafft C, Sobottka SB, Schackert G, Salzer R (2005) Near infrared Raman spectroscopic mapping of native brain tissue and intracranial tumors. Analyst 130:1070–1077
Krafft C, Sobottka SB, Schackert G, Salzer R (2006) Raman and infrared spectroscopic mapping of human primary intracranial tumors: a comparative study. J Raman Spectrosc 37:367–375
Krafft C, Kirsch M, Beleites C, Schackert G, Salzer R (2007) Methodology for fiber-optic Raman mapping and FTIR imaging of metastases in mouse brains. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:1122–1142
Kirsch M, Schackert G, Salzer R, Krafft C (2010) Raman spectroscopic imaging for in vivo detection of cerebral brain metastases. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:1707–1713
Bergner N, Bocklitz T, Romeike BFM, Reichart R, Kalff R, Krafft C, Popp J (2012) Identification of primary tumors of brain metastases by Raman imaging and support vector machines. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 117:224–232
Phillips GR, Harris JM (1990) Polynomial filters for data sets with outlying or missing observations: application to charge-coupled-device-detected Raman spectra contaminated by cosmic rays. Anal Chem 62:2351–2357
Mazet V, Carteret C, Brie D, Idier J, Humbert B (2005) Background removal from spectra by designing and minimising a non-quadratic cost function. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 76:121–133
Eilers PHC (2003) A perfect smoother. Anal Chem 75:3631–3636
Bergner N, Romeike BFM, Reichart R, Kalff R, Krafft C, Popp J (2011) Raman and FTIR microspectroscopy for detection of brain metastasis. In: Ramanujam N, Popp J (eds) SPIE, Munich, pp 80870X–80876
Beleites C, Geiger K, Kirsch M, Sobottka S, Schackert G, Salzer R (2011) Raman spectroscopic grading of astrocytoma tissues: using soft reference information. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:2801–2816
Krafft C, Miljanic S, Sobottka SB, Schackert G, Salzer R (2003) Near-infrared Raman spectroscopy to study the composition of human brain tissue and tumors. Proc SPIE-Int Soc Opt Eng 5141:230–236
Beljebbar A, Dukic S, Amharref N, Manfait M (2010) Ex vivo and in vivo diagnosis of C6 glioblastoma development by Raman spectroscopy coupled to a microprobe. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:477–487
Socrates G (2001) Infrared and Raman characteristic group frequencies. Wiley, West Sussex
Morell P, Quarles R (1999) Characteristic composition of myelin. In: Siegel GJAB, Albers RW et al (eds) Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular and medical aspects, 6th edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Mizuno A, Kitajima H, Kawauchi K, Muraishi S, Ozaki Y (1994) Near-infrared Fourier transform Raman spectroscopic study of human brain tissues and tumours. J Raman Spectrosc 25:25–29
Mizuno A, Hayashi T, Tashibu K, Maraishi S, Kawauchi K, Ozaki Y (1992) Near-infrared FT-Raman spectra of the rat brain tissues. Neurosci Lett 141:47–52
Ong CW, Shen ZX, He Y, Lee T, Tang SH (1999) Raman microspectroscopy of the brain tissues in the substantia nigra and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease. J Raman Spectrosc 30:91–96
Koehler M, Machill S, Salzer R, Krafft C (2009) Characterization of lipid extracts from brain tissue and tumors using Raman spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:1513–1520
Movasaghi Z, Rehman S, Rehman IU (2007) Raman spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl Spectrosc Rev 42:493–541
Sato H, Chiba H, Tashiro H, Ozaki Y (2001) Excitation wavelength-dependent changes in Raman spectra of whole blood and hemoglobin: comparison of the spectra with 514.5−, 720−, and 1,064-nm excitation. J Biomed Opt 6:366–370
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Funding
This work was partially funded by the Hermelin Brain Tumor Center at Henry Ford Hospital, the Smart Sensors and Integrated Microsystems Program at Wayne State University, and the Paul U. Strauss/TEAMS endowed chair position at Wayne State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kast, R.E., Auner, G.W., Rosenblum, M.L. et al. Raman molecular imaging of brain frozen tissue sections. J Neurooncol 120, 55–62 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1536-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1536-9