Abstract
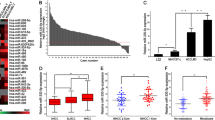
Heat shock protein 47 (HSP47), also known as SERPINH1, is a product of CBP2 gene located at chromosome 11q13.5, a region frequently amplified in human cancers. HSP47 has been demonstrated to effect on limiting tumor invasion and motility. The previous studies showed that HSP47 is overexpressed in many human cancers, including stomach cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and ulcerative colitis-associated carcinomas. However, the role of HSP47 in human glioma is still unknown. Here, we examined the expression of HSP47 in a group of glioma tumors and matched non-tumor brain tissues using qRT-PCR. We found that HSP47 is significantly overexpressed in glioma tissues and cell lines and associated with glioma tumor grade. Next, we knockdown the expression of HSP47 in the glioma cells using small interfering RNAs. The result showed that knockdown of HSP47 inhibits glioma cell growth, migration and invasion in vitro. We further investigated the posttranscriptional regulation of HSP47 by microRNAs using bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. The results suggested that the expression of HSP47 is regulated by miR-29a. Finally, stable knockdown of HSP47 using shRNA inhibits glioma tumor growth and induces apoptosis in mice models in vivo. Therefore, our data suggested that HSP47 regulated by miR-29a to enhance glioma tumor growth and invasion. Taken together, HSP47 plays important role in tumor growth and invasion and thus could be a therapeutic target for treating glioma in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP (2010) Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 17:98–110
McLendon R, Friedman A, Bigner D, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ, Mastrogianakis GM, Olson JJ, Mikkelsen T, Lehman N, Aldape K (2008) Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455:1061–1068
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC-H, Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Siu I-M, Gallia GL (2008) An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 321:1807–1812
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60:166–193
Chen J, McKay RM, Parada LF (2012) Malignant glioma: lessons from genomics, mouse models, and stem cells. Cell 149:36–47
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Matsumoto S, Noguchi T (2007) Antisense oligonucleotide inhibition of heat shock protein (HSP) 47 improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Respir Res 8:37
Hirai K, Kikuchi S, Kurita A, Ohashi S, Adachi E, Matsuoka Y, Nagata K, Watanabe M (2006) Immunohistochemical distribution of heat shock protein 47 (HSP47) in scirrhous carcinoma of the stomach. Anticancer Res 26:71–78
Lee SS, Tseng LH, Li YC, Tsai CH, Chang YC (2011) Heat shock protein 47 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas and upregulated by arecoline in human oral epithelial cells. J Oral Pathol Med 40:390–396
Poschmann G, Sitek B, Sipos B, Ulrich A, Wiese S, Stephan C, Warscheid B, Klöppel G, Vander Borght A, Ramaekers FC (2009) Identification of proteomic differences between squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and bronchial epithelium. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:1105–1116
Maitra A, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Rahman A, Sohn TA, Argani P, Meyer R, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Goggins M, Kern SE (2002) Immunohistochemical validation of a novel epithelial and a novel stromal marker of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identified by global expression microarrays sea urchin fascin homolog and heat shock protein 47. Am J Clin Pathol 118:52–59
Araki K, Mikami T, Yoshida T, Kikuchi M, Sato Y, Oh-ishi M, Kodera Y, Maeda T, Okayasu I (2009) High expression of HSP47 in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinomas: proteomic approach. Br J Cancer 101:492–497
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-[Delta][Delta] CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Xia H, Yan Y, Hu M, Wang Y, Wang Y, Dai Y, Chen J, Di G, Chen X, Jiang X (2013) MiR-218 sensitizes glioma cells to apoptosis and inhibits tumorigenicity by regulating ECOP-mediated suppression of NF-κB activity. Neuro-oncology 15:413–422
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Jakola AS, Myrmel KS, Kloster R, Torp SH, Lindal S, Unsgård G, Solheim O (2012) Comparison of a strategy favoring early surgical resection vs a strategy favoring watchful waiting in low-grade gliomassurgical resection vs waiting in low-grade gliomas. JAMA 308:1881–1888
Negrini M, Ferracin M, Sabbioni S, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNAs in human cancer: from research to therapy. J Cell Sci 120:1833–1840
Wang Y, Jing S, Yan LY, Zhu YS, Yun SC, Gang CD, Zuo W, Juan SC, Ling AT, Jun WY (2003) Effects of miR-29a on CDC42 expression and glioma cell migration and invasion. J Clin Oncol 11:629–633
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Grant Number: 81201994, 81301882.
Conflict of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Dan Zhao and Xiaochun Jiang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Jiang, X., Yao, C. et al. Heat shock protein 47 regulated by miR-29a to enhance glioma tumor growth and invasion. J Neurooncol 118, 39–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1412-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1412-7