Abstract
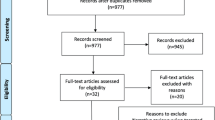
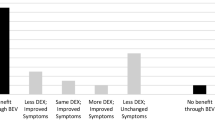
To retrospectively evaluate the clinical benefit and imaging response of bevacizumab when used to treat refractory adverse radiation effects (ARE) after stereotactic radiosurgery. Twenty-nine patients with brain tumors or vascular malformations developed clinical and/or imaging evidence of ARE after SRS and were treated using bevacizumab. Patients received an average dose of 7.4 mg/kg over a mean of 5.7 weeks at a median of 16 months following SRS. Initial diagnosis, SRS dose, bevacizumab treatment protocols, magnetic resonance imaging T2/FLAIR and T1 paramagnetic contrast enhanced edema volumes were compared before and after bevacizumab administration. Ninety percent (18/20) with clinically symptomatic ARE had neurological improvement after bevacizumab therapy. Twenty-six patients had a decrease of 62 % of T2/FLAIR volumes and a 50 % decrease in magnetic resonance imaging intravenous contrast enhancement volumes. Two patients showed progression of the T2/FLAIR and contrast enhancement volumes. One patient had progression of post-Gd-enhancement but regression of T2/FLAIR volume. Symptoms recurred in 11 of the 20 patients after discontinuing therapy. Patients who experienced a return of enhancement received a lower marginal dose during SRS. Our experience provides additional evidence that bevacizumab reduces both symptoms and reactive imaging changes in patients with ARE. After SRS, refractory ARE unresponsive to initial corticosteroids or other agents may benefit from a bevacizumab trial. The necessary duration and optimum dose of therapy is unknown and provides a further impetus to conduct a prospective trial.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giglio P, Gilbert MR (2003) Cerebral radiation necrosis. Neurology 9:180–188
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Friedman AH et al (1994) Treatment of radiation-induced nervous system injury with heparin and warfarin. Neurology 44:2020–2027
Rahmathulla G, Recinos PF, Valerio JE, Chao S, Barnett GH (2012) Laser interstitial thermal therapy for focal cerebral radiation necrosis: a case report and literature review. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 90:192–200
Kano K, Kondziolka D, Lobato-Polo J, Zorro O, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2010) T1/T2 matching to differentiate tumor growth from radiation effects after stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 66:486–492
Williamson R, Kondziolka D, Kanaan H, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC (2008) Adverse radiation effects after radiosurgery may benefit from oral vitamin e and pentoxifylline therapy: a pilot study. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86(6):359–366
Gonzalez J, Kumar A, Conrad C, Levin V (2008) Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(2):323–326
Levin V, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar A, Wefel J, Bekele N, Prabhu S, Loghin M, Gilbert M, Jackson E (2011) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 79(5):1487–1495
Trocuator R, Zuniga R, Mohan Y, Rock J, Doyle T, Anderson J, Gutierrez J, Ryu S, Jain R, Rosenblum M, Mikkelsen T (2009) Initial experience with bevacizumab treatment for biopsy confirmed cerebral radiation necrosis. J Neuroonol 94:63–68
Wong E, Huberman M, Lu X, Mahadevan A (2008) Bevacizumab reverses cerebral radiation necrosis. J Clin Oncol 26(34):5649–5650
Matuschek C, Bolke E, Nawatny J, Hoffmann T, Peiper M, Orth K, Gerber P, Rusnak E, Lammering G, Budach W (2011) Bevacizumab as a treatment option for radiation-induced cerebral necrosis. Strahlenther Onkol 187:135–139
Williams B, Park D, Sheehan J (2012) Bevacizumab used for the treatment of severe, refractory perilesional edema due to an arteriovenous malformation treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 116:972–977
Furuse M, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S (2011) Repeated treatments with bevacizumab for recurrent radiation necrosis in patients with malignant brain tumors: a report of 2 cases. J Neurooncol 102:471–475
Benoit A, Ducray F, Cartalat-Carel S, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Honnorat J (2011) Favorable outcome with bevacizumab after poor outcome with steroids in a patient with temporal lobe brainstem radiation necrosis. J Neurol 258:328–329
Sanborn RS, Danizh SF, Rosenfeld MR, O’Rougke D, Lee JY (2011) Treatment of steroid refractory, gamma knife related necrosis with bevacizumab: case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:798–802
Jeyaretna D, Curry W, Batchelor T, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Plotkin S (2011) Exacerbation of cerebral radiation necrosis by bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 29(7):e159–e162
Nonoguchi N, Miyatake S, Fukumoto M, Furuse M, Hiramatsu R, Kawabata S, Kuroiwa T, Tsuji M, Fukumoto M, Ono K (2011) The distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor-producing cells in clinical radiation necrosis of the brain: pathological consideration of their potential roles. J Neurooncol 105:423–431
Conflict of interest
Dr. Ahluwalia is a member of the board of Elekta AB and Genentech. Dr. Kondziolka is a consultant for Elekta AB. Dr. Lunsford is a consultant, stock holder and a member of the board for Elekta AB. The remaining authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deibert, C.P., Ahluwalia, M.S., Sheehan, J.P. et al. Bevacizumab for refractory adverse radiation effects after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 115, 217–223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1214-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1214-3