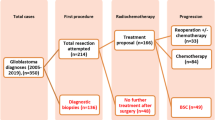
Abstract
The addition of concomitant and adjuvant chemotherapy to radiation therapy after surgical resection has increased significantly the survival of patients with glioblastoma (GB). In conjunction, there has been an increasing fraction of patients who present with new enlarged areas of contrast enhancement and edema on post-treatment imaging that improve without further treatment. It remains to be established how this phenomenon, commonly termed pseudoprogression, can be distinguished from true tumor recurrence defined as the histological presence of active high-grade tumor, as well as its prognostic significance. Data for over 500 patients undergoing surgery for recurrent GB were reviewed. Pathological specimens were categorized as those that contained active high-grade glioma in any amount, and those that did not. Patient survival was compared between these two groups, and independent associations were assessed using Cox proportionate hazards regression analysis. 59 patients met the study criteria including complete pathological and follow-up data. Mean age was 53 ± 11 years. Median survival from suspected recurrence and initial diagnosis were 8 [5–14] and 20 [12–30] months. Seventeen patients (29 %) had no evidence of active high-grade tumor and 42 (71 %) had at least focal active high-grade glioma. Pathologic pseudoprogression at re-operation (p = 0.03) and gross total resection (p = 0.01) were independently associated with survival. The histopathological features defined here and used to assess the tumor at reoperation were independently associated with survival. These findings may be important in designing treatment strategies and clinical trial endpoints for patients with GB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
de Wit MC, de Bruin HG, Eijkenboom W, Sillevis Smitt PA, van den Bent MJ (2004) Immediate post-radiotherapy changes in malignant glioma can mimic tumor progression. Neurology 63(3):535–537
Chamberlain MC, Glantz MJ, Chalmers L, Van Horn A, Sloan AE (2007) Early necrosis following concurrent Temodar and radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 82(1):81–83
Brandsma D, Stalpers L, Taal W, Sminia P, van den Bent MJ (2008) Clinical features, mechanisms, and management of pseudoprogression in malignant gliomas. Lancet Oncol 9(5):453–461
Chaskis C, Neyns B, Michotte A, De Ridder M, Everaert H (2009) Pseudoprogression after radiotherapy with concurrent temozolomide for high-grade glioma: clinical observations and working recommendations. Surg Neurol 72(4):423–428
Pouleau HB, Sadeghi N, Baleriaux D, Melot C, De Witte O, Lefranc F (2012) High levels of cellular proliferation predict pseudoprogression in glioblastoma patients. Int J Oncol 40(4):923–928
Young RJ, Gupta A, Shah AD, Graber JJ, Zhang Z, Shi W et al (2011) Potential utility of conventional MRI signs in diagnosing pseudoprogression in glioblastoma. Neurology 76(22):1918–1924
Hu X, Wong KK, Young GS, Guo L, Wong ST (2011) Support vector machine multiparametric MRI identification of pseudoprogression from tumor recurrence in patients with resected glioblastoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(2):296–305
Gunjur A, Lau E, Taouk Y, Ryan G (2011) Early post-treatment pseudo-progression amongst glioblastoma multiforme patients treated with radiotherapy and temozolomide: a retrospective analysis. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 55(6):603–610
Gahramanov S, Raslan AM, Muldoon LL, Hamilton BE, Rooney WD, Varallyay CG et al (2011) Potential for differentiation of pseudoprogression from true tumor progression with dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using ferumoxytol vs. gadoteridol: a pilot study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(2):514–523
Forsyth PA, Kelly PJ, Cascino TL, Scheithauer BW, Shaw EG, Dinapoli RP et al (1995) Radiation necrosis or glioma recurrence: is computer-assisted stereotactic biopsy useful? J Neurosurg 82(3):436–444
Topkan E, Topuk S, Oymak E, Parlak C, Pehlivan B (2012) Pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma multiforme after concurrent radiotherapy and temozolomide. Am J Clin Oncol 35(3):284–289
Bland JM, Altman DG (1998) Survival probabilities (the Kaplan–Meier method). BMJ 317(7172):1572
Stel VS, Dekker FW, Tripepi G, Zoccali C, Jager KJ (2011) Survival analysis I: the Kaplan–Meier method. Nephron Clin Pract 119(1):c83–c88
Hart MG, Grant R, Garside R, Rogers G, Somerville M, Stein K (2008) Chemotherapeutic wafers for high grade glioma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 16(3):CD007294
Perry J, Chambers A, Spithoff K, Laperriere N (2007) Gliadel wafers in the treatment of malignant glioma: a systematic review. Curr Oncol 14(5):189–194
Taal W, Brandsma D, de Bruin HG, Bromberg JE, Swaak-Kragten AT, Smitt PA et al (2008) Incidence of early pseudo-progression in a cohort of malignant glioma patients treated with chemoirradiation with temozolomide. Cancer 113(2):405–410
Chamberlain MC (2008) Pseudoprogression in glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 26(26):4359 (author reply 4359–4360)
Sanghera P, Perry J, Sahgal A, Symons S, Aviv R, Morrison M et al (2010) Pseudoprogression following chemoradiotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme. Can J Neurol Sci 37(1):36–42
Yaman E, Buyukberber S, Benekli M, Oner Y, Coskun U, Akmansu M et al (2010) Radiation induced early necrosis in patients with malignant gliomas receiving temozolomide. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112(8):662–667
Yang I, Huh NG, Smith ZA, Han SJ, Parsa AT (2010) Distinguishing glioma recurrence from treatment effect after radiochemotherapy and immunotherapy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 21(1):181–186
Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Spagnolli F, Frezza G, Leonardi M, Calbucci F et al (2008) Disease progression or pseudoprogression after concomitant radiochemotherapy treatment: pitfalls in neurooncology. Neuro Oncol 10(3):361–367
Zhou J, Blakeley JO, Hua J, Kim M, Laterra J, Pomper MG et al (2008) Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging. Magn Reson Med 60(4):842–849
Sanghera P, Perry J, Sahgal A, Symons S, Aviv R, Morrison M et al (2010) Pseudoprogression following chemoradiotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme. Can J Neurol Sci 37(1):36–42
Brandes AA, Franceschi E, Tosoni A, Blatt V, Pession A, Tallini G et al (2008) MGMT promoter methylation status can predict the incidence and outcome of pseudoprogression after concomitant radiochemotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. J Clin Oncol 26(13):2192–2197
Ozdemir N, Celkan T (2010) Pseudoprogression after radiotherapy with concurrent temozolomide in a child with anaplastic astrocytoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 27(4):317–319
Pytel P, Lukas RV (2009) Update on diagnostic practice: tumors of the nervous system. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133(7):1062–1077
Roldan GB, Scott JN, McIntyre JB, Dharmawardene M, de Robles PA, Magliocco AM et al (2009) Population-based study of pseudoprogression after chemoradiotherapy in GBM. Can J Neurol Sci 36(5):617–622
Yang I, Aghi MK (2009) New advances that enable identification of glioblastoma recurrence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(11):648–657
Gahramanov S, Raslan AM, Muldoon LL, Hamilton BE, Rooney WD, Varallyay CG et al (2011) Potential for differentiation of pseudoprogression from true tumor progression with dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using ferumoxytol vs. gadoteridol: a pilot study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(2):514–523
Brandsma D, van den Bent MJ (2009) Pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse in the treatment of gliomas. Curr Opin Neurol 22(6):633–638
Salhotra A, Lal B, Laterra J, Sun PZ, van Zijl PC, Zhou J (2008) Amide proton transfer imaging of 9L gliosarcoma and human glioblastoma xenografts. NMR Biomed 21(5):489–497
Zhao X, Wen Z, Huang F, Lu S, Wang X, Hu S et al (2011) Saturation power dependence of amide proton transfer image contrasts in human brain tumors and strokes at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 66(4):1033–1041
Zhou J, Lal B, Wilson DA, Laterra J, van Zijl PC (2003) Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn Reson Med 50(6):1120–1126
Barajas RF Jr, Chang JS, Segal MR, Parsa AT, McDermott MW, Berger MS et al (2009) Differentiation of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme from radiation necrosis after external beam radiation therapy with dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging. Radiology 253(2):486–496
Tsien C, Galban CJ, Chenevert TL, Johnson TD, Hamstra DA, Sundgren PC et al (2010) Parametric response map as an imaging biomarker to distinguish progression from pseudoprogression in high-grade glioma. J Clin Oncol 28(13):2293–2299
Tihan T, Barletta J, Parney I, Lamborn K, Sneed PK, Chang S (2006) Prognostic value of detecting recurrent glioblastoma multiforme in surgical specimens from patients after radiotherapy: should pathology evaluation alter treatment decisions? Hum Pathol 37(3):272–282
Kim JH, Bae Kim Y, Han JH, Cho KG, Kim SH, Sheen SS et al (2012) Pathologic diagnosis of recurrent glioblastoma: morphologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular analysis of 20 paired cases. Am J Surg Pathol 36(4):620–628
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Departments of Neurosurgery, Oncology, and Pathology for their support of this project. The authors did not have any funding related to this study or manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodworth, G.F., Garzon-Muvdi, T., Ye, X. et al. Histopathological correlates with survival in reoperated glioblastomas. J Neurooncol 113, 485–493 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1141-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1141-3