Abstract
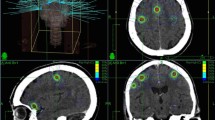
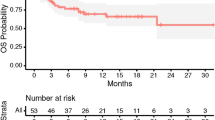
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is an accepted method of treatment for intracranial brain metastases with sub-millimeter accuracy. Frameless radiosurgery (FRS) is becoming an alternative to framed SRS due to its less invasive requirements. The purpose of this study is to describe the clinical outcomes and local patterns of failure for a novel 6 degrees of freedom CT guided method of localization for FRS of intracranial brain metastases. 42 patients underwent linear accelerator-based FRS to 94 intracranial brain metastases between 01/2009 and 07/2011. 78 and 22 % of treated sites were intact metastases and resection cavities, respectively. 55 % of patients had undergone prior brain radiotherapy (45 % SRS, 26 % whole brain radiation therapy). The 1 year actuarial local recurrence rate was 18 %, with a median imaging follow-up period of 13.2 months. Single fraction equivalent dose was the most important predictor of local recurrence. The 1 year actuarial first distant brain recurrence and total intracranial recurrence rate was 58 and 69 %, respectively. The crude radiographic radiation necrosis rate was 3 %. Of the 10 local recurrence events, 8 (80 %) were in-field only, 1 (10 %) was marginal only, and 1 (10 %) was both. The preponderance of in-field only patterns of failure suggests that geographic miss is not a major contributor to local recurrence using this novel localization method for FRS. The 1 year local control rate is comparable to other similar published series of framed and frameless radiosurgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (2005) Cancer, principles & practice of oncology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Lutz W, Winston KR, Maleki N (1988) A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14:373–381
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Breneman JC, Steinmetz R, Smith A, Lamba M, Warnick RE (2009) Frameless image-guided intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery: clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:702–706
Ramakrishna N, Rosca F, Friesen S, Tezcanli E, Zygmanszki P, Hacker F (2010) A clinical comparison of patient setup and intra-fraction motion using frame-based radiosurgery versus a frameless image-guided radiosurgery system for intracranial lesions. Radiotherapy and oncology. J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol 95:109–115
Lawson JD, Wang JZ, Nath SK, Rice R, Pawlicki T, Mundt AJ, Murphy K (2010) Intracranial application of IMRT based radiosurgery to treat multiple or large irregular lesions and verification of infra-red frameless localization system. J Neurooncol 97:59–66
Nath SK, Lawson JD, Wang JZ, Simpson DR, Newman CB, Alksne JF, Mundt AJ, Murphy KT (2010) Optically-guided frameless linac-based radiosurgery for brain metastases: clinical experience. J Neurooncol 97:67–72
Dhabaan A, Schreibmann E, Siddiqi A, Elder E, Fox T, Ogunleye T, Esiashvili N, Curran W, Crocker I, Shu HK (2012) Six degrees of freedom CBCT-based positioning for intracranial targets treated with frameless stereotactic radiosurgery. J Appl Clin Med Phys, Am Coll Med Phys 13:3916
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Feuvret L, Noel G, Mazeron JJ, Bey P (2006) Conformity index: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:333–342
Stinauer MA, Kavanagh BD, Schefter TE, Gonzalez R, Flaig T, Lewis K, Robinson W, Chidel M, Glode M, Raben D (2011) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: impact of single fraction equivalent dose on local control. Radiat Oncol 6:34
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 39:789–796
Welzel G, Fleckenstein K, Schaefer J, Hermann B, Kraus-Tiefenbacher U, Mai SK, Wenz F (2008) Memory function before and after whole brain radiotherapy in patients with and without brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1311–1318
Elaimy AL, Mackay AR, Lamoreaux WT, Fairbanks RK, Demakas JJ, Cooke BS, Lee CM (2011) Clinical outcomes of stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of patients with metastatic brain tumors. World neurosurg 75:673–683
Prabhu R, Shu HK, Hadjipanayis C, Dhabaan A, Hall W, Raore B, Olson J, Curran W, Oyesiku N, Crocker I (2012) Current dosing paradigm for stereotactic radiosurgery alone after surgical resection of brain metastases needs to be optimized for improved local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e61–66
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest exist for any of the authors except: Ian Crocker—Velocity Medical Systems shareholder and subject to receiving royalties through an agreement between Emory University Office of Technology Transfer (OTT) and Velocity Medical Systems
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhu, R.S., Dhabaan, A., Hall, W.A. et al. Clinical outcomes for a novel 6 degrees of freedom image guided localization method for frameless radiosurgery for intracranial brain metastases. J Neurooncol 113, 93–99 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1093-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1093-7